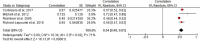Emotion dysregulation in adults with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a meta-analysis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Meta-Analysis
Emotion dysregulation in adults with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a meta-analysis
Ashkan Beheshti et al. BMC Psychiatry. 2020.
Abstract
Background: Emotional symptoms are increasingly considered a core feature of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). We aimed to quantify the evidence of emotional dysregulation and its respective facets in individuals with adult ADHD compared to healthy controls using meta-analysis.
Methods: Two electronic databases (PubMed, PsycINFO) were reviewed to identify studies. Studies were eligible for inclusion that had reports on any measure of emotion (dys) regulation in adults (> 18 years of age) in clinically diagnosed patients with ADHD as well as healthy control participants. We included a total of 13 studies (N = 2535) to assess (1) the standardized mean difference in emotion dysregulation (ED) as a general factor and its specific facets (i.e., emotional lability, negative emotional responses, and emotion recognition) between adults with ADHD and healthy controls; and (2) the association between ADHD symptom severity and ED.
Results: Compared to healthy controls, adults with ADHD revealed significantly higher levels of general ED (Hedges' g = 1.17, p < 0.001; Hedges' g is the adjusted effect size). With regard to intermediate dimensions of ED, emotional lability exhibited the strongest weighted effect (Hedges' g = 1.20, CI [0.57, 1.83], p < 0.001). Furthermore, symptom severity and general ED correlated significantly (r = 0.54, p < 0.001). Regarding intermediate dimensions of ED, negative emotional responses correlated closely with ADHD symptom severity (r = 0.63, p < 0.001) and emotional lability (r = 0.52, p < 0.001).
Conclusions: Our findings support ED symptoms as a core feature of ADHD's psychopathology. With respect to dimensions of ED, emotional lability, and negative emotional responses play a more definitive role in the psychopathology of adults with ADHD. Due to insufficient statistical reports in the included studies, we could not perform meta-regressions to control the role of moderator variables.
Keywords: ADHD; Emotion dysregulation; Meta-analysis; adults.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
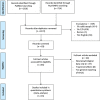
Fig. 1
Systematic Search of the Literature: PRISMA Flow-Chart
Fig. 2
Meta-Analysis Forrest Plot (random-model analysis) comparing ED in ADHD and healthy controls
Fig. 3
Meta-Analysis Forrest Plot on Correlation Coefficients between measures of ADHD symptom severity and ED
Fig. 4
Funnel Plot a) refers to the meta-analysis comparing ED in ADHD and healthy controls b) refers to the meta-analysis of the correlation coefficients between measures of ADHD symptom severity and ED
Similar articles
- Emotional dysregulation is a primary symptom in adult Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD).
Hirsch O, Chavanon M, Riechmann E, Christiansen H. Hirsch O, et al. J Affect Disord. 2018 May;232:41-47. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2018.02.007. Epub 2018 Feb 13. J Affect Disord. 2018. PMID: 29477097 - Clinical features and subjective/physiological responses to emotional stimuli in the presence of emotion dysregulation in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder.
Taskiran C, Karaismailoglu S, Cak Esen HT, Tuzun Z, Erdem A, Balkanci ZD, Dolgun AB, Cengel Kultur SE. Taskiran C, et al. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2018 May;40(4):389-404. doi: 10.1080/13803395.2017.1353952. Epub 2017 Jul 19. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2018. PMID: 28721740 - [Is emotional dysregulation a component of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)?].
Villemonteix T, Purper-Ouakil D, Romo L. Villemonteix T, et al. Encephale. 2015 Apr;41(2):108-14. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2013.12.004. Epub 2014 Apr 1. Encephale. 2015. PMID: 24703785 French. - Effects of stimulants and atomoxetine on emotional lability in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Moukhtarian TR, Cooper RE, Vassos E, Moran P, Asherson P. Moukhtarian TR, et al. Eur Psychiatry. 2017 Jul;44:198-207. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2017.05.021. Epub 2017 May 25. Eur Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28646732 Review. - Similarities between emotional dysregulation in adults suffering from ADHD and bipolar patients.
Richard-Lepouriel H, Etain B, Hasler R, Bellivier F, Gard S, Kahn JP, Prada P, Nicastro R, Ardu S, Dayer A, Leboyer M, Aubry JM, Perroud N, Henry C. Richard-Lepouriel H, et al. J Affect Disord. 2016 Jul 1;198:230-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2016.03.047. Epub 2016 Mar 15. J Affect Disord. 2016. PMID: 27031290 Review.
Cited by
- Inflammation and emotion regulation: a narrative review of evidence and mechanisms in emotion dysregulation disorders.
Petruso F, Giff AE, Milano BA, De Rossi MM, Saccaro LF. Petruso F, et al. Neuronal Signal. 2023 Nov 15;7(4):NS20220077. doi: 10.1042/NS20220077. eCollection 2023 Dec. Neuronal Signal. 2023. PMID: 38026703 Free PMC article. Review. - Differential Predictive Effect of Self-Regulation Behavior and the Combination of Self- vs. External Regulation Behavior on Executive Dysfunctions and Emotion Regulation Difficulties, in University Students.
de la Fuente J, Martínez-Vicente JM, Pachón-Basallo M, Peralta-Sánchez FJ, Vera-Martínez MM, Andrés-Romero MP. de la Fuente J, et al. Front Psychol. 2022 Jun 22;13:876292. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.876292. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35814083 Free PMC article. - Echinacea Supplementation Does Not Impact Aerobic Capacity and Erythropoiesis in Athletes: A Meta-Analysis.
Deccy S, Bartkowiak C, Rodricks N, Paultre K. Deccy S, et al. Nutrients. 2024 Jun 22;16(13):1991. doi: 10.3390/nu16131991. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38999738 Free PMC article. Review. - Antidotal Effects of the Antihistamine Diphenhydramine Against Cholinesterase Inhibitor Poisoning: A Meta-Analysis of Median Lethal Doses in Experimental Animals.
Mohammad FK, Mohammed AA, Faris GA, Al-Baggou B, Mousa YJ. Mohammad FK, et al. Cureus. 2024 Feb 18;16(2):e54403. doi: 10.7759/cureus.54403. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38505441 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Association AP. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-5®) American psychiatric pub. 2013. - PubMed
- Barkley RA, Murphy KR, Fischer M. Adult ADHD: What the science says. New York: Guilford; 2008.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical