NBOMes-Highly Potent and Toxic Alternatives of LSD - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
NBOMes-Highly Potent and Toxic Alternatives of LSD
Jolanta B Zawilska et al. Front Neurosci. 2020.
Abstract
Recently, a new class of psychedelic compounds named NBOMe (or 25X-NBOMe) has appeared on the illegal drug market. NBOMes are analogs of the 2C family of phenethylamine drugs, originally synthesized by Alexander Shulgin, that contain a _N_-(2-methoxy)benzyl substituent. The most frequently reported drugs from this group are 25I-NBOMe, 25B-NBOMe, and 25C-NBOMe. NBOMe compounds are ultrapotent and highly efficacious agonists of serotonin 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors (Ki values in low nanomolar range) with more than 1000-fold selectivity for 5-HT2A compared with 5-HT1A. They display higher affinity for 5-HT2A receptors than their 2C counterparts and have markedly lower affinity, potency, and efficacy at the 5-HT2B receptor compared to 5-HT2A or 5-HT2C. The drugs are sold as blotter papers, or in powder, liquid, or tablet form, and they are administered sublingually/buccally, intravenously, via nasal insufflations, or by smoking. Since their introduction in the early 2010s, numerous reports have been published on clinical intoxications and fatalities resulting from the consumption of NBOMe compounds. Commonly observed adverse effects include visual and auditory hallucinations, confusion, anxiety, panic and fear, agitation, uncontrollable violent behavior, seizures, excited delirium, and sympathomimetic signs such mydriasis, tachycardia, hypertension, hyperthermia, and diaphoresis. Rhabdomyolysis, disseminated intravascular coagulation, hypoglycemia, metabolic acidosis, and multiorgan failure were also reported. This survey provides an updated overview of the pharmacological properties, pattern of use, metabolism, and desired effects associated with NBOMe use. Special emphasis is given to cases of non-fatal and lethal intoxication involving these compounds. As the analysis of NBOMes in biological materials can be challenging even for laboratories applying modern sensitive techniques, this paper also presents the analytical methods most commonly used for detection and identification of NBOMes and their metabolites.
Keywords: NBOMe; analytical methods; metabolism; new psychoactive substances; phenethylamines; psychedelics; toxicity.
Copyright © 2020 Zawilska, Kacela and Adamowicz.
Figures
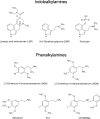
FIGURE 1
Chemical structures of main classes of psychedelics.
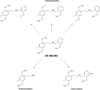
FIGURE 2
Main phase I metabolic pathways of 25I-NBOMe.
Similar articles
- 2-(4-Iodo-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-N-[(2-methoxyphenyl)methyl]ethanamine (25I-NBOME): A Harmful Hallucinogen Review.
Kamińska K, Świt P, Malek K. Kamińska K, et al. J Anal Toxicol. 2021 Jan 21;44(9):947-956. doi: 10.1093/jat/bkaa022. J Anal Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 32128596 - Case series: toxicity from 25B-NBOMe--a cluster of N-bomb cases.
Gee P, Schep LJ, Jensen BP, Moore G, Barrington S. Gee P, et al. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2016;54(2):141-6. doi: 10.3109/15563650.2015.1115056. Epub 2015 Dec 1. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2016. PMID: 26621342 - Comparative neuropharmacology of N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine (NBOMe) hallucinogens and their 2C counterparts in male rats.
Elmore JS, Decker AM, Sulima A, Rice KC, Partilla JS, Blough BE, Baumann MH. Elmore JS, et al. Neuropharmacology. 2018 Nov;142:240-250. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.02.033. Epub 2018 Mar 1. Neuropharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29501528 Free PMC article. - Pharmacology and Toxicology of N-Benzylphenethylamine ("NBOMe") Hallucinogens.
Halberstadt AL. Halberstadt AL. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2017;32:283-311. doi: 10.1007/7854_2016_64. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28097528 Review. - DARK Classics in Chemical Neuroscience: NBOMes.
Poulie CBM, Jensen AA, Halberstadt AL, Kristensen JL. Poulie CBM, et al. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2020 Dec 2;11(23):3860-3869. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.9b00528. Epub 2019 Nov 12. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31657895 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Neurotoxicological profile of the hallucinogenic compound 25I-NBOMe.
Herian M, Wojtas A, Maćkowiak M, Wawrzczak-Bargiela A, Solarz A, Bysiek A, Madej K, Gołembiowska K. Herian M, et al. Sci Rep. 2022 Feb 21;12(1):2939. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-07069-8. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35190675 Free PMC article. - 2C-B-Fly-NBOMe Metabolites in Rat Urine, Human Liver Microsomes and C. elegans: Confirmation with Synthesized Analytical Standards.
Nykodemová J, Šuláková A, Palivec P, Češková H, Rimpelová S, Šíchová K, Leonhardt T, Jurásek B, Hájková K, Páleníček T, Kuchař M. Nykodemová J, et al. Metabolites. 2021 Nov 12;11(11):775. doi: 10.3390/metabo11110775. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 34822433 Free PMC article. - Novel Psychoactive Phenethylamines: Impact on Genetic Material.
Cocchi V, Gasperini S, Hrelia P, Tirri M, Marti M, Lenzi M. Cocchi V, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 17;21(24):9616. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249616. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33348640 Free PMC article. - Effect of -NBOMe Compounds on Sensorimotor, Motor, and Prepulse Inhibition Responses in Mice in Comparison With the 2C Analogs and Lysergic Acid Diethylamide: From Preclinical Evidence to Forensic Implication in Driving Under the Influence of Drugs.
Tirri M, Bilel S, Arfè R, Corli G, Marchetti B, Bernardi T, Boccuto F, Serpelloni G, Botrè F, De-Giorgio F, Golembiowska K, Marti M. Tirri M, et al. Front Psychiatry. 2022 Apr 21;13:875722. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.875722. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35530025 Free PMC article. - Prevalence of self-reported adverse effects associated with drug use among nightclub and festival attendees, 2019-2022.
Palamar JJ, Le A. Palamar JJ, et al. Drug Alcohol Depend Rep. 2023 Mar 22;7:100149. doi: 10.1016/j.dadr.2023.100149. eCollection 2023 Jun. Drug Alcohol Depend Rep. 2023. PMID: 37025564 Free PMC article.
References
- Abiero A., Botanas C. J., Sayson L. V., Custodio R. J., de la Peña J. B., Kim M., et al. (2019). 5-Methoxy-α-methyltryptamine (5-MeO-AMT), a tryptamine derivative, induces head-twitch responses in mice through the activation of serotonin receptor 2a in the prefrontal cortex. Behav. Brain Res. 359 828–835. 10.1016/j.bbr.2018.07.020 - DOI - PubMed
- Al-Iman A., AbdulMajeed B. A. (2017). NBOMe compounds: systematic review and data crunching of the surface web. Glob. J. Health Sci. 9 126–139.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials