Safety and efficacy of different anesthetic regimens for parturients with COVID-19 undergoing Cesarean delivery: a case series of 17 patients - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
Safety and efficacy of different anesthetic regimens for parturients with COVID-19 undergoing Cesarean delivery: a case series of 17 patients
Rong Chen et al. Can J Anaesth. 2020 Jun.
Abstract
Purpose: To assess the management and safety of epidural or general anesthesia for Cesarean delivery in parturients with coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and their newborns, and to evaluate the standardized procedures for protecting medical staff.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed the cases of parturients diagnosed with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) infection disease (COVID-19). Their epidemiologic history, chest computed tomography scans, laboratory measurements, and SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid positivity were evaluated. We also recorded the patients' demographic and clinical characteristics, anesthesia and surgery-related data, maternal and neonatal complications, as well as the health status of the involved medical staff.
Results: The clinical characteristics of 17 pregnant women infected with SARS-CoV-2 were similar to those previously reported in non-pregnant adult patients. All of the 17 patients underwent Cesarean delivery with anesthesia performed according to standardized anesthesia/surgery procedures. Fourteen of the patients underwent continuous epidural anesthesia with 12 experiencing significant intraoperative hypotension. Three patients received general anesthesia with tracheal intubation because emergency surgery was needed. Three of the parturients are still recovering from their Cesarean delivery and are receiving in-hospital treatment for COVID-19. Three neonates were born prematurely. There were no deaths or serious neonatal asphyxia events. All neonatal SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid tests were negative. No medical staff were infected throughout the patient care period.
Conclusions: Both epidural and general anesthesia were safely used for Cesarean delivery in the parturients with COVID-19. Nevertheless, the incidence of hypotension during epidural anesthesia appeared excessive. Proper patient transfer, medical staff access procedures, and effective biosafety precautions are important to protect medical staff from COVID-19.
RéSUMé: OBJECTIF: Évaluer la gestion et la sécurité de l’anesthésie péridurale ou de l’anesthésie générale pour un accouchement par césarienne chez des parturientes infectées par la maladie à coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) et pour leurs nouveau-nés, et évaluer les procédures standardisées visant la protection du personnel médical. MéTHODES: Nous avons revu de manière rétrospective les cas de parturientes ayant un diagnostic de syndrome respiratoire aigu sévère lié à l’infection (SARS-CoV-2) par le coronavirus (COVID-19). L’enquête épidémiologique, leurs examens de tomodensitométrie thoracique, les analyses de laboratoire et leur positivité pour l’acide nucléique du SARS-CoV-2 ont été évalués. Nous avons également consigné les caractéristiques démographiques et cliniques des patientes, les données liées à l’anesthésie et à la chirurgie, les complications maternelles et néonatales, ainsi que l’état de santé du personnel médical concerné. RéSULTATS: Les caractéristiques cliniques des 17 femmes enceintes infectées par le SARS-CoV-2 étaient semblables à celles précédemment rapportées chez des patientes adultes non enceintes. Les 17 patientes ont subi un accouchement par césarienne sous anesthésie effectué selon les procédures standardisées d’anesthésie et de chirurgie. Parmi les quatorze patientes ayant eu une anesthésie péridurale continue, 12 patientes ont présenté une hypotension peropératoire significative. Trois patientes ont accouché sous anesthésie générale avec intubation trachéale, car nécessitant une chirurgie d’urgence. Trois parturientes sont encore en convalescence après leur accouchement par césarienne et reçoivent un traitement à l’hôpital pour la COVID-19. Trois nouveau-nés sont nés prématurément. Il n’y a pas eu de décès ou d’événement asphyxique néonatal grave. Toutes les recherches d’acide nucléique du SARS-CoV-2 chez les nouveau-nés ont été négatives. Aucun membre du personnel médical n’a été infecté pendant la durée des soins aux patientes. CONCLUSIONS: L’anesthésie par péridurale et l’anesthésie générale ont été utilisées sans danger pour l’accouchement par césarienne de parturientes atteintes de COVID-19. Cependant, l’incidence de l’hypotension au cours de l’anesthésie péridurale a paru excessive. Un transfert approprié des patientes, les procédures d’accès du personnel médical et des précautions efficaces de biosécurité sont importants pour protéger le personnel médical contre la COVID-19.
Figures
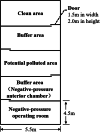
Fig. 1
Overall layout design of surgical workspaces
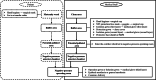
Fig. 2
Standard operating procedures for dressing biosafety level 3 protective medical equipment
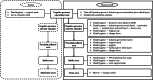
Fig. 3
Standard operating procedures for undressing biosafety level 3 grade protective wear
Comment in
- Uncertainty in using chest computed tomography in early coronavirus disease (COVID-19).
Mungmunpuntipantip R, Wiwanitkit V. Mungmunpuntipantip R, et al. Can J Anaesth. 2020 Jul;67(7):897. doi: 10.1007/s12630-020-01639-y. Epub 2020 Apr 2. Can J Anaesth. 2020. PMID: 32240519 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Regional anesthesia in patients with suspected COVID-19 infection.
Altiparmak B, Korkmaz Toker M, Uysal AI, Gümüş Demi Rbi Lek S. Altiparmak B, et al. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2021 Jan;46(1):91-92. doi: 10.1136/rapm-2020-101477. Epub 2020 Apr 3. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2021. PMID: 32245840 No abstract available. - Spinal anesthesia for Cesarean delivery in women with COVID-19 infection: questions regarding the cause of hypotension.
Benhamou D, Meyer HK, Morau E, Chassard D, Mercier FJ; French Obstetric Anesthesia Working Group (Club Anesthésie-Réanimation en Obstétrique [CARO]). Benhamou D, et al. Can J Anaesth. 2020 Aug;67(8):1097-1098. doi: 10.1007/s12630-020-01663-y. Epub 2020 Apr 27. Can J Anaesth. 2020. PMID: 32342348 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Care of the pregnant woman with coronavirus disease 2019 in labor and delivery: anesthesia, emergency cesarean delivery, differential diagnosis in the acutely ill parturient, care of the newborn, and protection of the healthcare personnel.
Ashokka B, Loh MH, Tan CH, Su LL, Young BE, Lye DC, Biswas A, Illanes SE, Choolani M. Ashokka B, et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Jul;223(1):66-74.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.04.005. Epub 2020 Apr 10. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020. PMID: 32283073 Free PMC article. - Comparison of perioperative outcomes and anesthetic-related complications of morbidly obese and super-obese parturients delivering by cesarean section.
Nivatpumin P, Lertbunnaphong T, Maneewan S, Vittayaprechapon N. Nivatpumin P, et al. Ann Med. 2023 Dec;55(1):1037-1046. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2023.2187877. Ann Med. 2023. PMID: 36947155 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Our anesthesia experiences in COVID-19 positive patients delivering by cesarean section: A retrospective single-center cohort study.
Karasu D, Kilicarslan N, Ozgunay SE, Gurbuz H. Karasu D, et al. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2021 Aug;47(8):2659-2665. doi: 10.1111/jog.14852. Epub 2021 May 13. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2021. PMID: 33987925 Free PMC article. - Anesthesia and protection in an emergency cesarean section for pregnant woman infected with a novel coronavirus: case report and literature review.
Du Y, Wang L, Wu G, Lei X, Li W, Lv J. Du Y, et al. J Anesth. 2020 Aug;34(4):613-618. doi: 10.1007/s00540-020-02796-6. Epub 2020 May 19. J Anesth. 2020. PMID: 32430561 Free PMC article. Review. - Infection Prevention Precautions for Routine Anesthesia Care During the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic.
Bowdle A, Jelacic S, Shishido S, Munoz-Price LS. Bowdle A, et al. Anesth Analg. 2020 Nov;131(5):1342-1354. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000005169. Anesth Analg. 2020. PMID: 33079853 Review.
Cited by
- Effect of COVID-19 on Mortality of Pregnant and Postpartum Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
Karimi L, Makvandi S, Vahedian-Azimi A, Sathyapalan T, Sahebkar A. Karimi L, et al. J Pregnancy. 2021 Mar 5;2021:8870129. doi: 10.1155/2021/8870129. eCollection 2021. J Pregnancy. 2021. PMID: 33728066 Free PMC article. - Vertical transmission of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2: A scoping review.
Tolu LB, Ezeh A, Feyissa GT. Tolu LB, et al. PLoS One. 2021 Apr 22;16(4):e0250196. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0250196. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33886645 Free PMC article. - Experimental study on the exposure level of surgical staff to SARS-CoV-2 in operating rooms with mixing ventilation under negative pressure.
Bi Y, Aganovic A, Mathisen HM, Cao G. Bi Y, et al. Build Environ. 2022 Jun 1;217:109091. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2022.109091. Epub 2022 Apr 21. Build Environ. 2022. PMID: 35469260 Free PMC article. - COVID-19 and pregnancy: A comparison of case reports, case series and registry studies.
Young EM, Green O, Stewart J, King Y, O'Donoghue K, Walker KF, Thornton JG. Young EM, et al. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2022 Jan;268:135-142. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2021.12.002. Epub 2021 Dec 6. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2022. PMID: 34920270 Free PMC article. Review. - Anesthesia in the times of COVID-19.
Yamakage M. Yamakage M. J Anesth. 2021 Jun;35(3):325-327. doi: 10.1007/s00540-020-02798-4. J Anesth. 2021. PMID: 32451627 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous