Diabetes is a risk factor for the progression and prognosis of COVID-19 - PubMed (original) (raw)
doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3319. Epub 2020 Apr 7.
Mingyue Li 1, Yalan Dong 1, Haifeng Zhou 1, Zili Zhang 1, Chunxia Tian 1, Renjie Qin 1, Haijun Wang 2, Yin Shen 2, Keye Du 2, Lei Zhao 3, Heng Fan 1, Shanshan Luo 4, Desheng Hu 1 4
Affiliations
- PMID: 32233013
- PMCID: PMC7228407
- DOI: 10.1002/dmrr.3319
Diabetes is a risk factor for the progression and prognosis of COVID-19
Weina Guo et al. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2020 Oct.
Abstract
Backgound: To figure out whether diabetes is a risk factor influencing the progression and prognosis of 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19).
Methods: A total of 174 consecutive patients confirmed with COVID-19 were studied. Demographic data, medical history, symptoms and signs, laboratory findings, chest computed tomography (CT) as well the treatment measures were collected and analysed.
Results: We found that COVID-19 patients without other comorbidities but with diabetes (n = 24) were at higher risk of severe pneumonia, release of tissue injury-related enzymes, excessive uncontrolled inflammation responses and hypercoagulable state associated with dysregulation of glucose metabolism. Furthermore, serum levels of inflammation-related biomarkers such as IL-6, C-reactive protein, serum ferritin and coagulation index, D-dimer, were significantly higher (P < .01) in diabetic patients compared with those without, suggesting that patients with diabetes are more susceptible to an inflammatory storm eventually leading to rapid deterioration of COVID-19.
Conclusions: Our data support the notion that diabetes should be considered as a risk factor for a rapid progression and bad prognosis of COVID-19. More intensive attention should be paid to patients with diabetes, in case of rapid deterioration.
Keywords: COVID-19; diabetes; prognosis.
© 2020 The Authors. Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest regarding this publication.
Figures
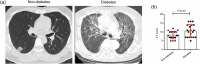
FIGURE 1
CT results of the patients with diabetes and patients without diabetes. A. The representative CT images of the patients with diabetes and patients without diabetes. B, The CT score of the patients with diabetes and patients without diabetes. P < .05 was considered statistically significant. CT, computed tomography
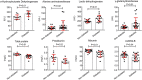
FIGURE 2
Biochemical examination results of the patients with diabetes and patients without diabetes. P < .05 was considered statistically significant
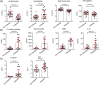
FIGURE 3
Other laboratory tests of the patients with diabetes and patients without diabetes. A, Blood test results of the patients with diabetes and patients without diabetes. B, Inflammation‐related laboratory results of the patients with diabetes and patients without diabetes. C, Coagulation‐related laboratory results of the patients with diabetes and patient without diabetes. P < .05 was considered statistically significant
Comment in
- Technology Gap Deepened by Coronavirus Pandemic.
Rigla M. Rigla M. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2020 Jul;14(4):774-775. doi: 10.1177/1932296820929390. Epub 2020 May 27. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2020. PMID: 32460626 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Serum amyloid A protein has been undervalued as a biomarker of COVID-19.
Gonçalves CA, Sesterheim P. Gonçalves CA, et al. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2021 Jan;37(1):e3376. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3376. Epub 2020 Jul 18. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2021. PMID: 32588938 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Diabetes and Covid-19: An interplay difficult to dissect.
Napoli R. Napoli R. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2021 Jan;37(1):e3387. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3387. Epub 2020 Aug 20. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2021. PMID: 32818297 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
- Tipnis SR, Hooper NM, Hyde R, Karran E, Christie G, Turner AJ. A human homolog of angiotensin‐converting enzyme. Cloning and functional expression as a captopril‐insensitive carboxypeptidase. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(43):33238‐33243. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 31770983/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81601747/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81974249/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- The project of thousand youth talents
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials