Rosmarinus officinalis L. (Rosemary) Extracts Containing Carnosic Acid and Carnosol are Potent Quorum Sensing Inhibitors of Staphylococcus aureus Virulence - PubMed (original) (raw)
Rosmarinus officinalis L. (Rosemary) Extracts Containing Carnosic Acid and Carnosol are Potent Quorum Sensing Inhibitors of Staphylococcus aureus Virulence
Seitaro Nakagawa et al. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020.
Abstract
Staphylococcus aureus is an opportunistic pathogen and a common cause of skin infection. S. aureus also plays a role in the pathogenesis of the chronic inflammatory skin disease, atopic dermatitis. S. aureus virulence involves activation of the quorum sensing agr operon. In this paper, we show that the diterpene carnosic acid, present in R. officinalis L. (rosemary) leaves, is a specific inhibitor of S. aureus agr expression as low as 5 μM. Carnosol and rosmarinic acid are two other phytochemicals present in rosemary leaves. Carnosol, but not rosmarinic acid, is also a potent agr expression inhibitor. Natural rosemary extracts containing carnosic acid and carnosol inhibit S. aureus agr expression, both in luciferase reporter strains and in wild type strains isolated from patients with atopic dermatitis. Specific inhibition of S. aureus virulence using topical formulations of rosemary extract may offer a practical approach to preventing and treating flares of atopic dermatitis.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; agr; anti-virulence therapy; atopic dermatitis; quorum sensing inhibition; skin microbiome.
Conflict of interest statement
GGH is a full-time employee of Amway Corporation, Ada, MI.
Figures
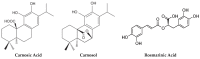
Figure 1
Major phytochemicals in rosemary.
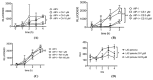
Figure 2
Effect of (A) carnosic acid (CA), (B) carnosol (CS) (C) rosmarinic acid (RA) on AIP-induced S. aureus agr RNAIII gene expression relative to total bacterial density (OD600). (D) Effect of carnosic acid (CA) on _psm_α gene expression. Data are presented as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
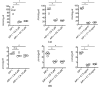
Figure 3
Dose response of AIP-induced RNAIII inhibition by rosemary extracts C1–C9 ((A–I), respectively). See Table 1 for carnosic acid, carnosol and rosmarinic acid concentrations in each extract. Data are presented as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
Figure 4
qPCR determination of (A) RNAIII and (B) psmα gene expression inhibition by (left to right) carnosic acid (CA), carnosol (CS) and rosemary extract (C1) in an AD clinical strain of S. aureus. Bars represents mean of each group. *p < 0.05, by Mann–Whitney two-tailed _t_-test. n.s., not significant.
Similar articles
- Relevance of carnosic acid, carnosol, and rosmarinic acid concentrations in the in vitro antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Rosmarinus officinalis (L.) methanolic extracts.
Jordán MJ, Lax V, Rota MC, Lorán S, Sotomayor JA. Jordán MJ, et al. J Agric Food Chem. 2012 Sep 26;60(38):9603-8. doi: 10.1021/jf302881t. Epub 2012 Sep 18. J Agric Food Chem. 2012. PMID: 22957812 - COX-2 Docking Structural Analysis with Phytochemical Extracts of Rosemary: A Possible Cytotoxicity on Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Line (HEp-2).
Abd El-Hamid IS, Mouselhy YY, El-Shafei MM, Sayed MM, Mohamed AF, Farag DB. Abd El-Hamid IS, et al. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2019;19(12):1473-1480. doi: 10.2174/1871520619666190618121706. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31244433 - Carnosic Acid and Carnosol, Two Major Antioxidants of Rosemary, Act through Different Mechanisms.
Loussouarn M, Krieger-Liszkay A, Svilar L, Bily A, Birtić S, Havaux M. Loussouarn M, et al. Plant Physiol. 2017 Nov;175(3):1381-1394. doi: 10.1104/pp.17.01183. Epub 2017 Sep 15. Plant Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28916593 Free PMC article. - Critical Assessment of the Prospects of Quorum-Quenching Therapy for Staphylococcus aureus Infection.
Otto M. Otto M. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 16;24(4):4025. doi: 10.3390/ijms24044025. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835436 Free PMC article. Review. - Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L., syn Salvia rosmarinus Spenn.) and Its Topical Applications: A Review.
de Macedo LM, Santos ÉMD, Militão L, Tundisi LL, Ataide JA, Souto EB, Mazzola PG. de Macedo LM, et al. Plants (Basel). 2020 May 21;9(5):651. doi: 10.3390/plants9050651. Plants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32455585 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Anti-Biofilm Activity of Carnosic Acid from Salvia rosmarinus against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
Iobbi V, Parisi V, Bernabè G, De Tommasi N, Bisio A, Brun P. Iobbi V, et al. Plants (Basel). 2023 Oct 25;12(21):3679. doi: 10.3390/plants12213679. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37960038 Free PMC article. - In Situ Application of Anti-Fouling Solutions on a Mosaic of the Archaeological Park of Ostia Antica.
Macchia A, Aureli H, Biribicchi C, Docci A, Alisi C, Prestileo F, Galiano F, Figoli A, Mancuso R, Gabriele B, La Russa MF. Macchia A, et al. Materials (Basel). 2022 Aug 18;15(16):5671. doi: 10.3390/ma15165671. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36013809 Free PMC article. - Therapeutic Potential of Cannabidiol (CBD) for Skin Health and Disorders.
Baswan SM, Klosner AE, Glynn K, Rajgopal A, Malik K, Yim S, Stern N. Baswan SM, et al. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2020 Dec 8;13:927-942. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S286411. eCollection 2020. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 33335413 Free PMC article. Review. - Bacterial Quorum-Sensing Systems and Their Role in Intestinal Bacteria-Host Crosstalk.
Wu L, Luo Y. Wu L, et al. Front Microbiol. 2021 Jan 28;12:611413. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.611413. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33584614 Free PMC article. Review. - In silico design and mechanistic study of niosome-encapsulated curcumin against multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus biofilms.
Khaleghian M, Sahrayi H, Hafezi Y, Mirshafeeyan M, Moghaddam ZS, Farasati Far B, Noorbazargan H, Mirzaie A, Ren Q. Khaleghian M, et al. Front Microbiol. 2023 Nov 30;14:1277533. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1277533. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38098658 Free PMC article.
References
- Aryee A., Edgeworth J.D. Carriage, Clinical Microbiology and Transmission of Staphylococcus aureus. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017;409:1–19. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources