Berberine Inhibits MDA-MB-231 Cells by Attenuating Their Inflammatory Responses - PubMed (original) (raw)
Berberine Inhibits MDA-MB-231 Cells by Attenuating Their Inflammatory Responses
Lina Zhao et al. Biomed Res Int. 2020.
Abstract
Breast cancer initiation is closely associated with cytokines that can change the inflammatory tumor microenvironment. Compounds extracted from plants have been explored for the possibility of cancer treatment in the recent decades. Berberine is an isoquinoline plant alkaloid with remarkable antioxidant and anti-inflammation roles, which is used in ethnic medicines, including traditional Chinese and North American medicine. In the present study, we investigated the effects of berberine on the malignant tumor cell behaviors in a breast cell line, MDA-MB-231. We found that berberine could not influence the cell viability in normal condition but was able to decrease the cancer cell migration capability in a scratch wound model and accordingly prolong the wound healing time. Furthermore, our results demonstrated that berberine inhibited the increased phosphorylation of c-Jun and c-Fos in these scratched cancer cells. With the cotreatment with LPS, which could boost the expression of cytokines in these cancer cells, berberine significantly reduced the increased expression of TNF-α and IL-6. Meanwhile, we found that berberine inhibited the activation of NF-κ_B by preventing the degradation of I_κ_B_α.
Copyright © 2020 Lina Zhao and Chunhai Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest to disclose in this study.
Figures
Figure 1
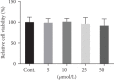
The effects of berberine on the cancer cell viability (24 hours). Data was expressed as mean ± SEM. n = 7.
Figure 2
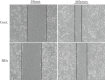
The effects of berberine on the cancer cell migration in a scratch wound model (48 hours). BBA: berberine (25 _μ_mol/L).
Figure 3
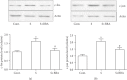
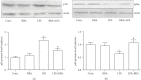
Berberine inhibited the increased expression of c-fos and c-jun in scratched cancer cells. (a) The effect of berberine on the expression of c-fos at 30 min after scratching. (b) The effect of berberine on the expression of c-jun at 30 minutes after scratching. Data was expressed as mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05 compared to control; #p < 0.05 compared to scratch (n = 5). BBA: berberine (25 _μ_mol/L); S: scratch.
Figure 4
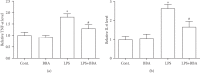
Berberine inhibited the increased expression of TNF-α and IL-6 in cancer cells exposed to LPS. (a) The effect of berberine on the expression of TNF-α at 6 hours after LPS treatment. (b) The effect of berberine on the expression of IL-6 at 6 hours after LPS treatment. Data was expressed as mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05 compared to control; #p < 0.05 compared to LPS (n = 7). BBA: berberine (25 _μ_mol/L).
Figure 5
Berberine inhibited the increased expression of NF-κ_B p65 and prevented the protein loss of I_κ_B_α in cancer cells exposed to LPS. (a) The effect of berberine on the expression of NF-κ_B p65 at 6 hours after LPS treatment. (b) The effect of berberine on the expression of I_κ_B_α at 6 hours after LPS treatment. Data was expressed as mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05 compared to control; #p < 0.05 compared to LPS (n = 6). BBA: berberine (25 _μ_mol/L).
Similar articles
- Regulation of the inflammatory profile of stromal cells in human breast cancer: prominent roles for TNF-α and the NF-κB pathway.
Katanov C, Lerrer S, Liubomirski Y, Leider-Trejo L, Meshel T, Bar J, Feniger-Barish R, Kamer I, Soria-Artzi G, Kahani H, Banerjee D, Ben-Baruch A. Katanov C, et al. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015 May 1;6(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s13287-015-0080-7. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 25928089 Free PMC article. - Huaier extract enhances the treatment efficacy of paclitaxel in breast cancer cells via the NF-κB/IκBα pathway.
Yang L, Song Z, Wang X, Yang W, Wang M, Liu H. Yang L, et al. Oncol Rep. 2017 Dec;38(6):3455-3464. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.6024. Epub 2017 Oct 12. Oncol Rep. 2017. PMID: 29039556 - Downregulation of cellular c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase and NF-κB activation by berberine may result in inhibition of herpes simplex virus replication.
Song S, Qiu M, Chu Y, Chen D, Wang X, Su A, Wu Z. Song S, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014 Sep;58(9):5068-78. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02427-14. Epub 2014 Jun 9. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014. PMID: 24913175 Free PMC article. - Antitumor activity of NAX060: A novel semisynthetic berberine derivative in breast cancer cells.
Pierpaoli E, Fiorillo G, Lombardi P, Salvatore C, Geroni C, Piacenza F, Provinciali M. Pierpaoli E, et al. Biofactors. 2018 Sep;44(5):443-452. doi: 10.1002/biof.1440. Epub 2018 Sep 3. Biofactors. 2018. PMID: 30178609 - Berberine hydrochloride IL-8 dependently inhibits invasion and IL-8-independently promotes cell apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 cells.
Li X, Zhao SJ, Shi HL, Qiu SP, Xie JQ, Wu H, Zhang BB, Wang ZT, Yuan JY, Wu XJ. Li X, et al. Oncol Rep. 2014 Dec;32(6):2777-88. doi: 10.3892/or.2014.3520. Epub 2014 Sep 30. Oncol Rep. 2014. PMID: 25335112
Cited by
- Remodeling tumor microenvironment with natural products to overcome drug resistance.
Zhang W, Li S, Li C, Li T, Huang Y. Zhang W, et al. Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 10;13:1051998. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1051998. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36439106 Free PMC article. Review. - The therapeutic potential of natural metabolites in targeting endocrine-independent HER-2-negative breast cancer.
Püsküllüoğlu M, Michalak I. Püsküllüoğlu M, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2024 Mar 4;15:1349242. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1349242. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38500769 Free PMC article. Review. - Biological Activity of Berberine-A Summary Update.
Och A, Podgórski R, Nowak R. Och A, et al. Toxins (Basel). 2020 Nov 12;12(11):713. doi: 10.3390/toxins12110713. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33198257 Free PMC article. Review. - Apoptosis Induction, a Sharp Edge of Berberine to Exert Anti-Cancer Effects, Focus on Breast, Lung, and Liver Cancer.
Zhu Y, Xie N, Chai Y, Nie Y, Liu K, Liu Y, Yang Y, Su J, Zhang C. Zhu Y, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 27;13:803717. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.803717. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35153781 Free PMC article. Review. - Natural Compounds as Protease Inhibitors in Therapeutic Focus on Cancer Therapy.
Kakali B. Kakali B. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2024;24(16):1167-1181. doi: 10.2174/0118715206303964240708095110. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38988167 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous