Ameliorating Chronic Kidney Disease Using a Whole Food Plant-Based Diet - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Ameliorating Chronic Kidney Disease Using a Whole Food Plant-Based Diet
Kathleen E Adair et al. Nutrients. 2020.
Abstract
Novel approaches to ameliorating chronic kidney disease (CKD) are warranted as most patients are undiagnosed until they begin displaying symptoms of kidney failure. There is increasing evidence that a whole food plant-based (WFPB) diet may offer benefits that slow the progression of CKD, decrease the incidence cardiovascular disease, decrease rates of diabetes and obesity, and reduce inflammation and cholesterol, which in turn can delay kidney failure and the initiation of dialysis. While animal-based protein ingestion promotes an acidic environment, inflammation and renal hyperfiltration, study authors report plant-based protein can be alkaline-producing and anti-inflammatory and can contain renoprotective properties. Although there may be benefits to adopting a WFPB diet, macronutrient and micronutrient content should be carefully considered and adjusted to avoid malnutrition in CKD patients. Further research needs to be done in order to establish the biological plausibility and feasibility of a WFPB in individuals with diagnosed CKD.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; chronic kidney disease; potential renal acid load; whole food plant-based diet.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
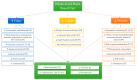
Figure 1
Cited effects of a whole food plant-based diet.
Similar articles
- Plant-based diets to manage the risks and complications of chronic kidney disease.
Carrero JJ, González-Ortiz A, Avesani CM, Bakker SJL, Bellizzi V, Chauveau P, Clase CM, Cupisti A, Espinosa-Cuevas A, Molina P, Moreau K, Piccoli GB, Post A, Sezer S, Fouque D. Carrero JJ, et al. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020 Sep;16(9):525-542. doi: 10.1038/s41581-020-0297-2. Epub 2020 Jun 11. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32528189 Review. - Plant-Dominant Low-Protein Diet for Conservative Management of Chronic Kidney Disease.
Kalantar-Zadeh K, Joshi S, Schlueter R, Cooke J, Brown-Tortorici A, Donnelly M, Schulman S, Lau WL, Rhee CM, Streja E, Tantisattamo E, Ferrey AJ, Hanna R, Chen JLT, Malik S, Nguyen DV, Crowley ST, Kovesdy CP. Kalantar-Zadeh K, et al. Nutrients. 2020 Jun 29;12(7):1931. doi: 10.3390/nu12071931. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32610641 Free PMC article. Review. - Vegetarian Diet in Chronic Kidney Disease-A Friend or Foe.
Gluba-Brzózka A, Franczyk B, Rysz J. Gluba-Brzózka A, et al. Nutrients. 2017 Apr 10;9(4):374. doi: 10.3390/nu9040374. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28394274 Free PMC article. Review. - Nutritional Adequacy of Animal-Based and Plant-Based Asian Diets for Chronic Kidney Disease Patients: A Modeling Study.
Khor BH, Tallman DA, Karupaiah T, Khosla P, Chan M, Kopple JD. Khor BH, et al. Nutrients. 2021 Sep 24;13(10):3341. doi: 10.3390/nu13103341. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34684342 Free PMC article. - Plant-Based Diets for Kidney Disease: A Guide for Clinicians.
Joshi S, McMacken M, Kalantar-Zadeh K. Joshi S, et al. Am J Kidney Dis. 2021 Feb;77(2):287-296. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.10.003. Epub 2020 Oct 16. Am J Kidney Dis. 2021. PMID: 33075387 Review.
Cited by
- Mediterranean Diet Pattern: Potential Impact on the Different Altered Pathways Related to Cardiovascular Risk in Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease.
Rovira J, Ramirez-Bajo MJ, Bañon-Maneus E, Ventura-Aguiar P, Arias-Guillén M, Romano-Andrioni B, Ojeda R, Revuelta I, García-Calderó H, Barberà JA, Dantas AP, Diaz-Ricart M, Crispi F, García-Pagán JC, Campistol JM, Diekmann F. Rovira J, et al. Nutrients. 2024 Oct 31;16(21):3739. doi: 10.3390/nu16213739. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39519573 Free PMC article. - Improvement in symptoms of anxiety and depression in individuals with type 2 diabetes: retrospective analysis of an intensive lifestyle modification program.
Tripathi P, Sharma B, Kadam N, Tiwari D, Kathrikolly T, Vyawahare A, Biswas MD, Vijayakumar V, Kuppusamy M, Ganla M, Saboo B. Tripathi P, et al. BMC Psychiatry. 2024 Oct 22;24(1):714. doi: 10.1186/s12888-024-06130-2. BMC Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39438811 Free PMC article. - Higher oxidative balance score is linearly associated with reduced prevalence of chronic kidney disease in individuals with metabolic syndrome: evidence from NHANES 1999-2018.
Zhu L, Ruan X, Wang J, Yan Y, Tang C, Xu Y. Zhu L, et al. Front Nutr. 2024 Sep 30;11:1442274. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1442274. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39403399 Free PMC article. - Care of Adults with Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease.
Shrestha S, Haq K, Malhotra D, Patel DM. Shrestha S, et al. J Clin Med. 2024 Jul 26;13(15):4378. doi: 10.3390/jcm13154378. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39124645 Free PMC article. Review. - A Therapeutic Approach in the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease: Plant-Based Dietary Models and Associated Parameters.
Sahin K, Yıldıran H. Sahin K, et al. Curr Nutr Rep. 2024 Mar;13(1):39-48. doi: 10.1007/s13668-023-00515-7. Epub 2024 Jan 3. Curr Nutr Rep. 2024. PMID: 38172460 Review.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . National Chronic Kidney Disease Fact. Sheet, 2017. US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; Atlanta, GA, USA: 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical