Prolonged SARS-CoV-2 RNA shedding: Not a rare phenomenon - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2020 Nov;92(11):2286-2287.
doi: 10.1002/jmv.25952. Epub 2020 May 22.
Affiliations
- PMID: 32347980
- PMCID: PMC7267144
- DOI: 10.1002/jmv.25952
Prolonged SARS-CoV-2 RNA shedding: Not a rare phenomenon
Na Li et al. J Med Virol. 2020 Nov.
No abstract available
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures
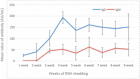
Figure 1
Variation in IgM and IgG levels of SARS‐CoV‐2 with time in the 36 prolonged‐RNA‐shedding patients. SARS‐CoV‐2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
Similar articles
- Prolonged SARS-CoV-2 Viral RNA Shedding and IgG Antibody Response to SARS-CoV-2 in Patients on Hemodialysis.
Shaikh A, Zeldis E, Campbell KN, Chan L. Shaikh A, et al. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021 Feb 8;16(2):290-292. doi: 10.2215/CJN.11120720. Epub 2020 Oct 14. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33055191 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Prolonged SARS-Cov-2 shedding with rapid IgG antibody decay in a COVID-19 patient: A case report.
Huang J, Lan C, Wang X, Huang M. Huang J, et al. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021 Nov;35(11):e24002. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24002. Epub 2021 Sep 15. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021. PMID: 34528306 Free PMC article. - Prolonged shedding of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in patients with COVID-19.
Li Q, Zheng XS, Shen XR, Si HR, Wang X, Wang Q, Li B, Zhang W, Zhu Y, Jiang RD, Zhao K, Wang H, Shi ZL, Zhang HL, Du RH, Zhou P. Li Q, et al. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020 Dec;9(1):2571-2577. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1852058. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020. PMID: 33196399 Free PMC article. - The kinetics of viral load and antibodies to SARS-CoV-2.
Sun J, Tang X, Bai R, Liang C, Zeng L, Lin H, Yuan R, Zhou P, Huang X, Xiong Q, Peng J, Cui F, Ke B, Su J, Liu Z, Lu J, Tian J, Sun R, Ke C. Sun J, et al. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020 Dec;26(12):1690.e1-1690.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.08.043. Epub 2020 Sep 6. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020. PMID: 32898715 Free PMC article. - Serological tests for COVID-19: Potential opportunities.
Tantuoyir MM, Rezaei N. Tantuoyir MM, et al. Cell Biol Int. 2021 Apr;45(4):740-748. doi: 10.1002/cbin.11516. Epub 2021 Jan 13. Cell Biol Int. 2021. PMID: 33289157 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Serum Proteomic Analysis for New Types of Long-Term Persistent COVID-19 Patients in Wuhan.
Li C, Yue L, Ju Y, Wang J, Chen M, Lu H, Liu S, Liu T, Wang J, Hu X, Tuohetaerbaike B, Wen H, Zhang W, Xu S, Jiang C, Chen F. Li C, et al. Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Dec 21;10(6):e0127022. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01270-22. Epub 2022 Oct 31. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36314975 Free PMC article. - Tools and Techniques for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)/COVID-19 Detection.
Safiabadi Tali SH, LeBlanc JJ, Sadiq Z, Oyewunmi OD, Camargo C, Nikpour B, Armanfard N, Sagan SM, Jahanshahi-Anbuhi S. Safiabadi Tali SH, et al. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2021 May 12;34(3):e00228-20. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00228-20. Print 2021 Jun 16. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2021. PMID: 33980687 Free PMC article. Review. - Recurrence of COVID-19 after recovery ? A case series in health care workers, France.
Zayet S, Royer PY, Toko L, Pierron A, Gendrin V, Klopfenstein T. Zayet S, et al. Microbes Infect. 2021 May-Jun;23(4-5):104803. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2021.104803. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Microbes Infect. 2021. PMID: 33667643 Free PMC article. - Follow-up testing of borderline SARS-CoV-2 patients by rRT-PCR allows early diagnosis of COVID-19.
Boeckmans J, Cartuyvels R, Hilkens P, Bruckers L, Magerman K, Waumans L, Raymaekers M. Boeckmans J, et al. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2021 Jun;100(2):115350. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2021.115350. Epub 2021 Feb 18. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33689985 Free PMC article. - Complexities in Case Definition of SARS-CoV-2 Reinfection: Clinical Evidence and Implications in COVID-19 Surveillance and Diagnosis.
Yamasaki L, Moi ML. Yamasaki L, et al. Pathogens. 2021 Sep 29;10(10):1262. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10101262. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 34684211 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- China National Health Commission . Diagnosis and treatment of 2019‐nCoV pneumonia in China (Version 5) (in Chinese). Published 8 February 2020. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/yzygj/s7653p/202002/d4b895337e19445f8d728fcaf1e3e1.... Accessed 20 March 2020.
- World Health Organization (WHO) . Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection when novel coronavirus (nCoV) infection is suspected. Interim Guidance. 2020;Jan 12. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/clinical-management...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous