Unique skin manifestations of COVID-19: Is drug eruption specific to COVID-19? - PubMed (original) (raw)
Case Reports
Unique skin manifestations of COVID-19: Is drug eruption specific to COVID-19?
Takashi Sakaida et al. J Dermatol Sci. 2020 Jul.
Abstract
- •
COVID-19 is associated with specific skin manifestations and drug eruption. - •
This case shows COVID-19–related drug eruption and specific clinical features. - •
Drug eruption preceding COVID-19 symptoms may facilitate early diagnosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest No conflict of interest.
Figures
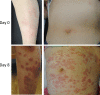
Fig. 1
Clinical features of her trunk and leg Day 0, indurated erythema on her leg, and red papules and erythema on her trunk Day 8, dark red colored papules and indurated erythema were largely observed on her leg and trunk.
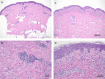
Fig. 2
Pathologic findings (Day 0 and Day 8). (A, B): Pathologic analysis of a skin biopsy sample obtained from an indurated erythematous lesion (Day 0). The size of bar is indicated in the figure. (C, D): Pathologic analysis of a skin biopsy sample from an abdominal lesion. Interface changes with liquefaction and perivascular mixed cell infiltrations in the papillary dermis are observed. There are histiocytic infiltrations around the capillary vessels and neutrophils are scattered in the upper dermis (C–D). The size of bar is indicated in the figure.
Similar articles
- Covid-19-The real role of NSAIDs in Italy.
de Girolamo L, Peretti GM, Maffulli N, Brini AT. de Girolamo L, et al. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020 May 4;15(1):165. doi: 10.1186/s13018-020-01682-x. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020. PMID: 32366317 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Skin manifestations associated with the new coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 disease.
Redondo-Sendino Á, González Sánchez IC, de Victoria Fernández B. Redondo-Sendino Á, et al. Med Clin (Barc). 2020 Nov 13;155(9):414-415. doi: 10.1016/j.medcli.2020.04.057. Epub 2020 Jul 24. Med Clin (Barc). 2020. PMID: 32873395 Free PMC article. English, Spanish. No abstract available. - The Use of Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs in Urological Practice in the COVID-19 Era: Is "Safe Better than Sorry"?
Pradère B, Ploussard G, Catto JWF, Rouprêt M, Misrai V. Pradère B, et al. Eur Urol. 2020 Aug;78(2):134-135. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.03.033. Epub 2020 Apr 10. Eur Urol. 2020. PMID: 32284245 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - [A gastrointestinal overview of COVID-19].
Konturek PC. Konturek PC. MMW Fortschr Med. 2020 Apr;162(8):59-60. doi: 10.1007/s15006-020-0431-x. MMW Fortschr Med. 2020. PMID: 32342369 Free PMC article. Review. German. - Novel coronavirus(Covid19), Its renal manifestations, and complications.
Jadali Z. Jadali Z. Urol J. 2020 Sep 13;17(5):558-559. doi: 10.22037/uj.v16i7.6431. Urol J. 2020. PMID: 32920815 Review.
Cited by
- COVID-19 and Autoimmunity in Dermatology: A Moroccan Case Series and Literature Review.
Benhayoun F, Hali F, El Fatoiki FZ, Chiheb S. Benhayoun F, et al. Cureus. 2024 Apr 4;16(4):e57587. doi: 10.7759/cureus.57587. eCollection 2024 Apr. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38707102 Free PMC article. - Awareness of undergraduate dental students, interns, and freshly graduated dentists about oral manifestation associated with COVID-19.
Alrajhi S, Shalabi M, Alrajhi A, Almarshud T, Almuhaysin M, Alhudaithi A, Alharbi AF, Alamri N, Alhumaid A, Aljuailan A, Algefari S, Salem S, Saad I. Alrajhi S, et al. BMC Oral Health. 2023 Dec 9;23(1):990. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03666-9. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 38071326 Free PMC article. - Oral lesions in patients with severe COVID-19 in the National Institute of Respiratory Diseases in Mexico: Case series.
Rueda CAC, Vinitzky Brener I. Rueda CAC, et al. J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects. 2023 Winter;17(1):54-60. doi: 10.34172/joddd.2023.37072. Epub 2023 Apr 3. J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects. 2023. PMID: 37650015 Free PMC article. - Dermatology Publications on COVID-19 during the First Pandemic Year: Creativity or Opportunism?
Amerio P, Giuliani F, Coppola M, Lobefaro F, Gualdi G. Amerio P, et al. Life (Basel). 2023 Apr 5;13(4):953. doi: 10.3390/life13040953. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37109482 Free PMC article. - Oral Lesions Associated with COVID-19 and the Participation of the Buccal Cavity as a Key Player for Establishment of Immunity against SARS-CoV-2.
Gutierrez-Camacho JR, Avila-Carrasco L, Martinez-Vazquez MC, Garza-Veloz I, Zorrilla-Alfaro SM, Gutierrez-Camacho V, Martinez-Fierro ML. Gutierrez-Camacho JR, et al. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Sep 9;19(18):11383. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191811383. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36141654 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources