Exosomes as drug delivery vehicle and contributor of resistance to anticancer drugs - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Exosomes as drug delivery vehicle and contributor of resistance to anticancer drugs
Mahendran Chinnappan et al. Cancer Lett. 2020.
Abstract
Exosomes are small membranous vesicles implicated in intercellular signalling. Through their uncanny ability to carry and deliver donor cellular cargo (biomolecules) to target cells, they exert a profound effect on the regular functioning of healthy cells and play a significant role in pathogenesis and progression of several diseases, including cancer. The composition and number of endogenously circulating exosomes frequently vary, which is often reflective of the pathophysiological status of the cell. Applicability of exosomes derived from normal cells as a drug carrier with or without modifying their intraluminal and surface components are generally tested. Conversely, exosomes also are reported to contribute to resistance towards several anti-cancer therapies. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully evaluate the role of exosomes in cancer progression, resistance and the potential use of exosomes as a delivery vehicle of cancer therapeutics. In this review, we summarize the recent advancements in the exploitation of exosomes as a drug delivery vehicle. We also discuss the role of exosomes in conferring resistance to anti-cancer therapeutics. While this review is focused on cancer, the exosome-based drug delivery and resistance is also applicable to other human diseases.
Keywords: Extracellular vesicles; Nanocarriers; Tangential flow filtration; Tumor-derived exosome; Tumor-microenvironment.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors report no conflict of interest in this work.
Figures
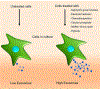
Figure 1.
Strategies to induce exosome induction from cells. Exosome production can be increased by subjecting the cells to electrical signal; knockdown of endo-lysosomal gene (NDRG1); treating cells with calcium phosphate; membrane protein sulfhydryl group blockers; chemotherapy agents; and hypoxia.
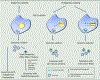
Figure 2.
Method of loading therapeutics in exosome. Exosomes isolated from certain cell types show antitumor effects with its endogenously loaded composition. Exosomes can also be equipped exogenously with therapeutic proteins, nucleic acids, and small molecules. Endogenous loading of exosomes is achieved using a plasmid vector based expression of protein as a fusion protein with the tetraspanin proteins.
Similar articles
- A comprehensive overview of exosomes as drug delivery vehicles - endogenous nanocarriers for targeted cancer therapy.
Johnsen KB, Gudbergsson JM, Skov MN, Pilgaard L, Moos T, Duroux M. Johnsen KB, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Aug;1846(1):75-87. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2014.04.005. Epub 2014 Apr 18. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24747178 Review. - The multifaceted role of exosomes in cancer progression: diagnostic and therapeutic implications [corrected].
Sundararajan V, Sarkar FH, Ramasamy TS. Sundararajan V, et al. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2018 Jun;41(3):223-252. doi: 10.1007/s13402-018-0378-4. Epub 2018 Apr 17. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2018. PMID: 29667069 Review. - Exosomes and their role in tumorigenesis and anticancer drug resistance.
Milman N, Ginini L, Gil Z. Milman N, et al. Drug Resist Updat. 2019 Jul;45:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2019.07.003. Epub 2019 Jul 23. Drug Resist Updat. 2019. PMID: 31369918 Review. - Tumor-targeted exosomes for delivery of anticancer drugs.
Raguraman R, Bhavsar D, Kim D, Ren X, Sikavitsas V, Munshi A, Ramesh R. Raguraman R, et al. Cancer Lett. 2023 Apr 1;558:216093. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216093. Epub 2023 Feb 21. Cancer Lett. 2023. PMID: 36822543 Free PMC article. - Exosomes: Cell-Derived Nanoplatforms for the Delivery of Cancer Therapeutics.
Kim H, Kim EH, Kwak G, Chi SG, Kim SH, Yang Y. Kim H, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 22;22(1):14. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010014. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33374978 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Exosomes as New Generation Vehicles for Drug Delivery: Biomedical Applications and Future Perspectives.
Rajput A, Varshney A, Bajaj R, Pokharkar V. Rajput A, et al. Molecules. 2022 Oct 27;27(21):7289. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217289. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36364116 Free PMC article. Review. - Emerging Significance and Therapeutic Potential of Extracellular vesicles.
Luo R, Liu M, Tan T, Yang Q, Wang Y, Men L, Zhao L, Zhang H, Wang S, Xie T, Tian Q. Luo R, et al. Int J Biol Sci. 2021 Jun 16;17(10):2476-2486. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.59296. eCollection 2021. Int J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34326688 Free PMC article. Review. - Exosomes in diagnostic and therapeutic applications of ovarian cancer.
Bhavsar D, Raguraman R, Kim D, Ren X, Munshi A, Moore K, Sikavitsas V, Ramesh R. Bhavsar D, et al. J Ovarian Res. 2024 May 25;17(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s13048-024-01417-0. J Ovarian Res. 2024. PMID: 38796525 Free PMC article. Review. - Modification of Extracellular Vesicle Surfaces: An Approach for Targeted Drug Delivery.
Mohammadi AH, Ghazvinian Z, Bagheri F, Harada M, Baghaei K. Mohammadi AH, et al. BioDrugs. 2023 May;37(3):353-374. doi: 10.1007/s40259-023-00595-5. Epub 2023 Apr 24. BioDrugs. 2023. PMID: 37093521 Review. - Delivery of functional exogenous proteins by plant-derived vesicles to human cells in vitro.
Garaeva L, Kamyshinsky R, Kil Y, Varfolomeeva E, Verlov N, Komarova E, Garmay Y, Landa S, Burdakov V, Myasnikov A, Vinnikov IA, Margulis B, Guzhova I, Kagansky A, Konevega AL, Shtam T. Garaeva L, et al. Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 22;11(1):6489. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85833-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33753795 Free PMC article.
References
- Livshits Z, Rao RB, Smith SW, An approach to chemotherapy-associated toxicity, Emerg Med Clin North Am, 32 (2014) 167–203. - PubMed
- Adem B, Vieira PF, Melo SA, Decoding the Biology of Exosomes in Metastasis, Trends Cancer, 6 (2020) 20–30. - PubMed
- Dini L, Tacconi S, Carata E, Tata AM, Vergallo C, Panzarini E, Microvesicles and exosomes in metabolic diseases and inflammation, Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA167516/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA225520/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX003420/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- P20 GM103639/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA233201/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources