Coumarins in Food and Methods of Their Determination - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Coumarins in Food and Methods of Their Determination
Mirjana Lončar et al. Foods. 2020.
Abstract
Coumarin is a natural product with aromatic and fragrant characteristics, widespread in the entire plant kingdom. It is found in different plant sources such as vegetables, spices, fruits, and medicinal plants including all parts of the plants-fruits, roots, stems and leaves. Coumarin is found in high concentrations in certain types of cinnamon, which is one of the most frequent sources for human exposure to this substance. However, human exposure to coumarin has not been strictly determined, since there are no systematic measurements of consumption of cinnamon-containing foods. The addition of pure coumarin to foods is not allowed, since large amounts of coumarin can be hepatotoxic. However, according to the new European aroma law, coumarin may be present in foods only naturally or as a flavoring obtained from natural raw materials (as is the case with cinnamon). In this paper, the overview of the current European regulations on coumarin levels in food is presented, along with the most common coumarin food sources, with a special emphasis on cinnamon-containing food. Human exposure to coumarins in food is also reviewed, as well as the methods for determination and separation of coumarin and its derivatives in food.
Keywords: cinnamon; coumarin; coumarin-containing foods; determination of coumarin in food; human exposure to coumarin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
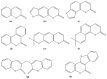
Figure 1
Six basic groups of natural coumarins: (a) simple coumarins; (b) furanocoumarins (linear type); (c) furanocoumarins (angular type); (d) benzocoumarins; (e) pyranocoumarins (linear type); (f) pyranocoumarins (angular type); (g) biscoumarins; (h) coumestans.
Similar articles
- Relative bioavailability of coumarin from cinnamon and cinnamon-containing foods compared to isolated coumarin: a four-way crossover study in human volunteers.
Abraham K, Pfister M, Wöhrlin F, Lampen A. Abraham K, et al. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2011 Apr;55(4):644-53. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201000394. Epub 2010 Dec 20. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2011. PMID: 21462332 Clinical Trial. - Cassia cinnamon as a source of coumarin in cinnamon-flavored food and food supplements in the United States.
Wang YH, Avula B, Nanayakkara NP, Zhao J, Khan IA. Wang YH, et al. J Agric Food Chem. 2013 May 8;61(18):4470-6. doi: 10.1021/jf4005862. Epub 2013 Apr 29. J Agric Food Chem. 2013. PMID: 23627682 - Coumarin and cinnamaldehyde in cinnamon marketed in Italy: a natural chemical hazard?
Lungarini S, Aureli F, Coni E. Lungarini S, et al. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess. 2008 Nov;25(11):1297-305. doi: 10.1080/02652030802105274. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess. 2008. PMID: 19680836 - Toxicology and risk assessment of coumarin: focus on human data.
Abraham K, Wöhrlin F, Lindtner O, Heinemeyer G, Lampen A. Abraham K, et al. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2010 Feb;54(2):228-39. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.200900281. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2010. PMID: 20024932 Review. - A safety assessment of coumarin taking into account species-specificity of toxicokinetics.
Felter SP, Vassallo JD, Carlton BD, Daston GP. Felter SP, et al. Food Chem Toxicol. 2006 Apr;44(4):462-75. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2005.08.019. Epub 2005 Oct 3. Food Chem Toxicol. 2006. PMID: 16203076 Review.
Cited by
- Antioxidant, Anti-Alzheimer's, anticancer, and cytotoxic properties of peanut oil: in vitro, in silico, and GC-MS analysis.
Djeghim H, Benouchenne D, Mokrani EH, Alsaeedi H, Cornu D, Bechelany M, Barhoum A. Djeghim H, et al. Front Chem. 2024 Oct 24;12:1487084. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1487084. eCollection 2024. Front Chem. 2024. PMID: 39512543 Free PMC article. - Harnessing the Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Polyphenols in the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease.
Boaru DL, Fraile-Martinez O, De Leon-Oliva D, Garcia-Montero C, De Castro-Martinez P, Miranda-Gonzalez A, Saez MA, Muñon-Zamarron L, Castillo-Ruiz E, Barrena-Blázquez S, Cañonez-Zafra R, Alvarez-Mon MÁ, Toledo-Lobo MV, Minaya-Bravo AM, Lopez-Gonzalez L, Diaz-Pedrero R, Saz JV, Albillos A, Alvarez-Mon M, Guijarro LG, Ortega MA. Boaru DL, et al. Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Oct 14;20(14):5608-5672. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.98107. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39494333 Free PMC article. Review. - Esculetin Combats Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Infection and Ameliorates Intestinal Dysfunction via the Nrf2 Pathway.
Xu W, Ding W, Jia L, Zhu K, Luo Q. Xu W, et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Sep 26;13(10):1170. doi: 10.3390/antiox13101170. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456424 Free PMC article. - Extraction and Chromatographic Approaches for Coumarin, Furocoumarin, and Polymethoxyflavone Characterization in Foods.
Cafeo G, Irrera E, Russo M, Dugo P. Cafeo G, et al. Foods. 2024 Aug 12;13(16):2517. doi: 10.3390/foods13162517. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39200445 Free PMC article. Review. - Coumarin derivatives ameliorate the intestinal inflammation and pathogenic gut microbiome changes in the model of infectious colitis through antibacterial activity.
Jung HS, Park YJ, Gu BH, Han G, Ji W, Hwang SM, Kim M. Jung HS, et al. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Jul 15;14:1362773. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1362773. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39081865 Free PMC article.
References
- Önder A. Anticancer activity of natural coumarins for biological targets. Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem. 2020:85–109. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-817903-1.00003-6. - DOI
- Yahaya I., Seferoglu N., Seferoğlu Z. Improved one-pot synthetic conditions for synthesis of functionalized fluorescent coumarin-thiophene hybrids: Syntheses, DFT studies, photophysical and thermal properties. Tetrahedron. 2019:2143–2154. doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2019.02.034. - DOI
- Fitoz A., Nazır H., Özgür (nee Yakut) M., Emregül E., Emregül K.C. An experimental and theoretical approach towards understanding the inhibitive behavior of a nitrile substituted coumarin compound as an effective acidic media inhibitor. Corros. Sci. 2018;133:451–464. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2017.10.004. - DOI
- Yang Z., Kinoshita T., Tanida A., Sayama H., Morita A., Watanabe N. Analysis of coumarin and its glycosidically bound precursor in Japanese green tea having sweet-herbaceous odour. Food Chem. 2009;114:289–294. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.09.014. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources