Profiling serum cytokines in COVID-19 patients reveals IL-6 and IL-10 are disease severity predictors - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2020 Dec;9(1):1123-1130.
doi: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1770129.
Qingfeng Ma 2, Cong Li 3, Rui Liu 1, Li Zhao 3, Wei Wang 4, Pingan Zhang 1, Xinghui Liu 5, Guosheng Gao 6, Fang Liu 7, Yingan Jiang 8, Xiaoming Cheng 9, Chengliang Zhu 1, Yuchen Xia 3
Affiliations
- PMID: 32475230
- PMCID: PMC7473317
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1770129
Profiling serum cytokines in COVID-19 patients reveals IL-6 and IL-10 are disease severity predictors
Huan Han et al. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020 Dec.
Abstract
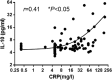
Since the outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China, it has rapidly spread across many other countries. While the majority of patients were considered mild, critically ill patients involving respiratory failure and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome are not uncommon, which could result death. We hypothesized that cytokine storm is associated with severe outcome. We enrolled 102 COVID-19 patients who were admitted to Renmin Hospital (Wuhan, China). All patients were classified into moderate, severe and critical groups according to their symptoms. 45 control samples of healthy volunteers were also included. Inflammatory cytokines and C-Reactive Protein (CRP) profiles of serum samples were analyzed by specific immunoassays. Results showed that COVID-19 patients have higher serum level of cytokines (TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6 and IL-10) and CRP than control individuals. Within COVID-19 patients, serum IL-6 and IL-10 levels are significantly higher in critical group (n = 17) than in moderate (n = 42) and severe (n = 43) group. The levels of IL-10 is positively correlated with CRP amount (r = 0.41, P < 0.01). Using univariate logistic regression analysis, IL-6 and IL-10 are found to be predictive of disease severity and receiver operating curve analysis could further confirm this result (AUC = 0.841, 0.822 respectively). Our result indicated higher levels of cytokine storm is associated with more severe disease development. Among them, IL-6 and IL-10 can be used as predictors for fast diagnosis of patients with higher risk of disease deterioration. Given the high levels of cytokines induced by SARS-CoV-2, treatment to reduce inflammation-related lung damage is critical.
Keywords: COVID-19; Interleukin 10; Interleukin 6; SARS-CoV-2; cytokine storm; inflammatory cytokines.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
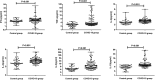
Figure 1.
The levels of cytokines in COVID-19 patients and controls. The serum concentration of TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6 and IL-10 from 102 COVID-19 patients and 42 controls were analyzed immediately after hospital admission. Median with range were presented.
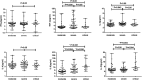
Figure 2.
The levels of cytokines in COVID-19 patients with different severity. 102 COVID-19 patients were divided into three groups: moderate, severe and critical. The serum concentration of TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6 and IL-10 were analyzed. Median with range were presented.
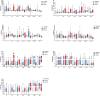
Figure 3.
The kinetics of cytokines and CRP in COVID-19 patients during hospitalization. The serum cytokines levels and CRP of moderate, severe and critical patients during hospitalization were presented. The x-axis represents days after admission. Median with range were presented.
Figure 4.
The relationship between CRP and IL-10. Spearman rank correlation analysis was performed to evaluate the correlation of serum IL-10with CRP in the patients with COVID-19.
Figure 5.
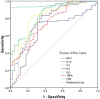
ROC curve of cytokines and CRP. Univariate logistic regression analysis was conducted. Performance of ROC curves of TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10 and CRP for predicting COVID-19.
Figure 6.
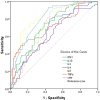
ROC curve for diagnosis of severe and critical patients with COVID-19. Univariate logistic regression analysis was used to identify the severe and critical patients from controls and moderate COVID-19 patients. Performance of ROC curves of TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10 and CRP for predicting severe and critical COVID-19 patients.
Figure 7.
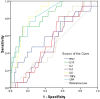
ROC curve for diagnosis of severe and critical patients with COVID-19. Univariate logistic regression analysis was used to identify the critical patients from moderate, severe COVID-19 patients and controls. Performance of ROC curves of TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10 and CRP for predicting critical COVID-19 patients.
Similar articles
- Using IL-2R/lymphocytes for predicting the clinical progression of patients with COVID-19.
Hou H, Zhang B, Huang H, Luo Y, Wu S, Tang G, Liu W, Mao L, Mao L, Wang F, Sun Z. Hou H, et al. Clin Exp Immunol. 2020 Jul;201(1):76-84. doi: 10.1111/cei.13450. Epub 2020 May 15. Clin Exp Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32365221 Free PMC article. - Detectable Serum Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Viral Load (RNAemia) Is Closely Correlated With Drastically Elevated Interleukin 6 Level in Critically Ill Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019.
Chen X, Zhao B, Qu Y, Chen Y, Xiong J, Feng Y, Men D, Huang Q, Liu Y, Yang B, Ding J, Li F. Chen X, et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2020 Nov 5;71(8):1937-1942. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa449. Clin Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32301997 Free PMC article. - Longitudinal COVID-19 profiling associates IL-1RA and IL-10 with disease severity and RANTES with mild disease.
Zhao Y, Qin L, Zhang P, Li K, Liang L, Sun J, Xu B, Dai Y, Li X, Zhang C, Peng Y, Feng Y, Li A, Hu Z, Xiang H, Ogg G, Ho LP, McMichael A, Jin R, Knight JC, Dong T, Zhang Y. Zhao Y, et al. JCI Insight. 2020 Jul 9;5(13):e139834. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.139834. JCI Insight. 2020. PMID: 32501293 Free PMC article. - Cytokine storm and leukocyte changes in mild versus severe SARS-CoV-2 infection: Review of 3939 COVID-19 patients in China and emerging pathogenesis and therapy concepts.
Wang J, Jiang M, Chen X, Montaner LJ. Wang J, et al. J Leukoc Biol. 2020 Jul;108(1):17-41. doi: 10.1002/JLB.3COVR0520-272R. Epub 2020 Jun 13. J Leukoc Biol. 2020. PMID: 32534467 Free PMC article. Review. - COVID-19, Mast Cells, Cytokine Storm, Psychological Stress, and Neuroinflammation.
Kempuraj D, Selvakumar GP, Ahmed ME, Raikwar SP, Thangavel R, Khan A, Zaheer SA, Iyer SS, Burton C, James D, Zaheer A. Kempuraj D, et al. Neuroscientist. 2020 Oct-Dec;26(5-6):402-414. doi: 10.1177/1073858420941476. Epub 2020 Jul 18. Neuroscientist. 2020. PMID: 32684080 Review.
Cited by
- Role of interleukin 6 as a predictive factor for a severe course of Covid-19: retrospective data analysis of patients from a long-term care facility during Covid-19 outbreak.
Sabaka P, Koščálová A, Straka I, Hodosy J, Lipták R, Kmotorková B, Kachlíková M, Kušnírová A. Sabaka P, et al. BMC Infect Dis. 2021 Mar 29;21(1):308. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-05945-8. BMC Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33781216 Free PMC article. - The radiographic assessment of lung edema score of lung edema severity correlates with inflammatory parameters in patients with coronavirus disease 2019-Potential new admission biomarkers to predict coronavirus disease 2019 worsening.
Marques P, Fernandez-Presa L, Carretero A, Gómez-Cabrera MC, Viña J, Signes-Costa J, Sanz MJ. Marques P, et al. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 11;9:871714. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.871714. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36035415 Free PMC article. - Evaluation of the immunomodulatory effects of interleukin-10 on peripheral blood immune cells of COVID-19 patients: Implication for COVID-19 therapy.
Najafi-Fard S, Petruccioli E, Farroni C, Petrone L, Vanini V, Cuzzi G, Salmi A, Altera AMG, Navarra A, Alonzi T, Nicastri E, Palmieri F, Gualano G, Carlini V, Noonan DM, Albini A, Goletti D. Najafi-Fard S, et al. Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 6;13:984098. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.984098. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36148228 Free PMC article. - Combined plasma levels of IL-10 and testosterone, but not soluble HLA-G5, predict the risk of death in COVID-19 patients.
Amodio G, Capogrosso P, Pontillo M, Tassara M, Boeri L, Carenzi C, Cignoli D, Ferrara AM, Ramirez GA, Tresoldi C, Locatelli M, Santoleri L, Castagna A, Zangrillo A, De Cobelli F, Tresoldi M, Landoni G, Rovere-Querini P, Ciceri F, Montorsi F, Salonia A, Gregori S. Amodio G, et al. Andrology. 2023 Jan;11(1):32-44. doi: 10.1111/andr.13334. Epub 2022 Nov 21. Andrology. 2023. PMID: 36323494 Free PMC article. - COVID-19 convalescent plasma therapy decreases inflammatory cytokines: a randomized controlled trial.
Habtehyimer F, Zhu X, Redd AD, Gebo KA, Abraham AG, Patel EU, Laeyendecker O, Gniadek TJ, Fernandez RE, Baker OR, Ram M, Cachay ER, Currier JS, Fukuta Y, Gerber JM, Heath SL, Meisenberg B, Huaman MA, Levine AC, Shenoy A, Anjan S, Blair JE, Cruser D, Forthal DN, Hammitt LL, Kassaye S, Mosnaim GS, Patel B, Paxton JH, Raval JS, Sutcliffe CG, Abinante M, Oei KS, Cluzet V, Cordisco ME, Greenblatt B, Rausch W, Shade D, Gawad AL, Klein SL, Pekosz A, Shoham S, Casadevall A, Bloch EM, Hanley D, Tobian AAR, Sullivan DJ. Habtehyimer F, et al. Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Jan 11;12(1):e0328623. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03286-23. Epub 2023 Nov 27. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38009954 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
This work was supported by the National Mega Project on Major Infectious Disease Prevention [grant number 2017ZX10103005], the National Natural Science Foundation of China (project no. 81971936, 82041004 and 81672079), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, Zhejiang University special scientific research fund for COVID-19 prevention and control (2020XGZX089), COVID-19 Platform Program of Hwa Mei Hospital, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (project no. 2020HMZD21) and the Open Research Program of the State Key Laboratory of Virology of China (project no. 2020KF001).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous