MiR-145 in cancer therapy resistance and sensitivity: A comprehensive review - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
. 2020 Sep;111(9):3122-3131.
doi: 10.1111/cas.14517. Epub 2020 Jul 8.
Affiliations
- PMID: 32506767
- PMCID: PMC7469794
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.14517
Review
MiR-145 in cancer therapy resistance and sensitivity: A comprehensive review
Wenxiu Xu et al. Cancer Sci. 2020 Sep.
Abstract
MircoRNA (miRNA) are a group of small, non-coding, regulatory RNA with an average length of approximately 22 nucleotides, which mostly modulate gene expression post-transcriptionally through complementary binding to the 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR) of multiple target genes. Emerging evidence has shown that miRNA are frequently dysregulated in a variety of human malignancies. Among them, microRNA-145 (miR-145) has been increasingly identified as a critical suppressor of carcinogenesis and therapeutic resistance. Resistance to tumor therapy is a challenge in cancer treatment due to the daunting range of resistance mechanisms. We reviewed the status quo of recent advancements in the knowledge of the functional role of miR-145 in therapeutic resistance and the tumor microenvironment. It may serve as an innovative biomarker for therapeutic response and cancer prognosis.
Keywords: MiR-145; Therapeutic sensitivity; biomarker; cancer; therapeutic resistance.
© 2020 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures
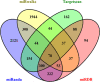
FIGURE 1
Venn diagram of potential targets of miR‐145 by bioinformatics
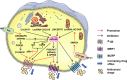
FIGURE 2
Regulatory mechanisms of miR‐145 in cancer therapy resistance by increasing drug efflux. MiR‐145 was sponged by circPVT1, lncRNA CACS15, LINC00707 and lncRNA HOTAIR, which blocked the downstream PI3K/AKT signaling or target genes, thus directly or indirectly inhibiting P‐gp, MRP1 and BCRP
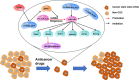
FIGURE 3
Regulatory mechanisms of miR‐145 in cancer therapy resistance by inhibiting cancer stem cells (CSC) properties. MiR‐145 was sponged by lncRNA‐LET, lncRNA MALAT1 and lncRNA ROR, and concomitantly suppressed CD44, SOX2, KLF4, HMGA2, OCT4 and Nanog
Similar articles
- miR-155 in cancer drug resistance and as target for miRNA-based therapeutics.
Bayraktar R, Van Roosbroeck K. Bayraktar R, et al. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018 Mar;37(1):33-44. doi: 10.1007/s10555-017-9724-7. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018. PMID: 29282605 Review. - The microRNA-200 family: small molecules with novel roles in cancer development, progression and therapy.
Humphries B, Yang C. Humphries B, et al. Oncotarget. 2015 Mar 30;6(9):6472-98. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3052. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25762624 Free PMC article. Review. - miR-125a-5p Functions as Tumor Suppressor microRNA And Is a Marker of Locoregional Recurrence And Poor prognosis in Head And Neck Cancer.
Vo DT, Karanam NK, Ding L, Saha D, Yordy JS, Giri U, Heymach JV, Story MD. Vo DT, et al. Neoplasia. 2019 Sep;21(9):849-862. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2019.06.004. Epub 2019 Jul 18. Neoplasia. 2019. PMID: 31325708 Free PMC article. - MicroRNA-21: a novel therapeutic target in human cancer.
Pan X, Wang ZX, Wang R. Pan X, et al. Cancer Biol Ther. 2010 Dec 15;10(12):1224-32. doi: 10.4161/cbt.10.12.14252. Epub 2010 Dec 15. Cancer Biol Ther. 2010. PMID: 21139417 Review. - Dynamically decreased miR-671-5p expression is associated with oncogenic transformation and radiochemoresistance in breast cancer.
Tan X, Li Z, Ren S, Rezaei K, Pan Q, Goldstein AT, Macri CJ, Cao D, Brem RF, Fu SW. Tan X, et al. Breast Cancer Res. 2019 Aug 7;21(1):89. doi: 10.1186/s13058-019-1173-5. Breast Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31391072 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Non-Coding RNAs in Peritoneal Carcinomatosis: From Bench to Bedside.
Bohosova J, Ashraf NS, Slaby O, Calin GA. Bohosova J, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2024 Aug 25;16(17):2961. doi: 10.3390/cancers16172961. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272819 Free PMC article. Review. - Decreased BIRC5-206 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through sponging miR-145-5p.
Xu W, Hu J, Ma Z, Feng W, Gong W, Fu S, Chen X. Xu W, et al. Open Med (Wars). 2024 Sep 17;19(1):20241007. doi: 10.1515/med-2024-1007. eCollection 2024. Open Med (Wars). 2024. PMID: 39308922 Free PMC article. - Alterations in the Ca2+ toolkit in oesophageal adenocarcinoma.
Cutliffe AL, McKenna SL, Chandrashekar DS, Ng A, Devonshire G, Fitzgerald RC, O'Donovan TR, Mackrill JJ. Cutliffe AL, et al. Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2021;2(6):543-575. doi: 10.37349/etat.2021.00063. Epub 2021 Dec 31. Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2021. PMID: 36046118 Free PMC article. - An ultrasensitive electrochemical biosensor with dual-amplification mode and enzyme-deposited silver for detection of miR-205-5p.
Xie X, Chen C, Chen W, Qin Y, Xiang S, Jiang J, Chen X, Li J. Xie X, et al. Mikrochim Acta. 2024 Aug 19;191(9):545. doi: 10.1007/s00604-024-06596-7. Mikrochim Acta. 2024. PMID: 39158763 - Resistance to gemcitabine is mediated by the circ_0036627/miR-145/S100A16 axis in pancreatic cancer.
Yu S, Wang M, Zhang H, Guo X, Qin R. Yu S, et al. J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Jun;28(12):e18444. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18444. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38924205 Free PMC article.
References
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:7‐30. - PubMed
- Dweep H, Gretz N. miRWalk2.0: a comprehensive atlas of microRNA‐target interactions. Nat Methods. 2015;12:697. - PubMed
- Zheng F, Xu R. CircPVT1 contributes to chemotherapy resistance of lung adenocarcinoma through miR‐145‐5p/ABCC1 axis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;124:109828. - PubMed
- Wang Y, Lian YM, Ge CY. MiR‐145 changes sensitivity of non–small cell lung cancer to gefitinib through targeting ADAM19. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23:5831‐5839. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2016YFC0905900/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- BE2019731/Jiangsu Provincial Key Research Development Program
- 81872365/National Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources