Lutein Supplementation for Eye Diseases - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Lutein Supplementation for Eye Diseases
Long Hin Li et al. Nutrients. 2020.
Abstract
Lutein is one of the few xanthophyll carotenoids that is found in high concentration in the macula of human retina. As de novo synthesis of lutein within the human body is impossible, lutein can only be obtained from diet. It is a natural substance abundant in egg yolk and dark green leafy vegetables. Many basic and clinical studies have reported lutein's anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory properties in the eye, suggesting its beneficial effects on protection and alleviation of ocular diseases such as age-related macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, retinopathy of prematurity, myopia, and cataract. Most importantly, lutein is categorized as Generally Regarded as Safe (GRAS), posing minimal side-effects upon long term consumption. In this review, we will discuss the chemical structure and properties of lutein as well as its application and safety as a nutritional supplement. Finally, the effects of lutein consumption on the aforementioned eye diseases will be reviewed.
Keywords: age-related macular degeneration; antioxidant; carotenoid; cataract; diabetic retinopathy; myopia; nutrition; retina; retinopathy of prematurity; xanthophyll.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
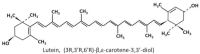
Figure 1
Chemical structure of lutein [29].
Similar articles
- Lutein, zeaxanthin, and meso-zeaxanthin: The basic and clinical science underlying carotenoid-based nutritional interventions against ocular disease.
Bernstein PS, Li B, Vachali PP, Gorusupudi A, Shyam R, Henriksen BS, Nolan JM. Bernstein PS, et al. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2016 Jan;50:34-66. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2015.10.003. Epub 2015 Nov 2. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2016. PMID: 26541886 Free PMC article. Review. - The science behind lutein.
Alves-Rodrigues A, Shao A. Alves-Rodrigues A, et al. Toxicol Lett. 2004 Apr 15;150(1):57-83. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2003.10.031. Toxicol Lett. 2004. PMID: 15068825 Review. - Role of macular xanthophylls in prevention of common neovascular retinopathies: retinopathy of prematurity and diabetic retinopathy.
Gong X, Rubin LP. Gong X, et al. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2015 Apr 15;572:40-48. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2015.02.004. Epub 2015 Feb 18. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2015. PMID: 25701588 Review. - HPLC measurement of ocular carotenoid levels in human donor eyes in the lutein supplementation era.
Bhosale P, Zhao DY, Bernstein PS. Bhosale P, et al. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007 Feb;48(2):543-9. doi: 10.1167/iovs.06-0558. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007. PMID: 17251448 - The Pharmacological Effects of Lutein and Zeaxanthin on Visual Disorders and Cognition Diseases.
Jia YP, Sun L, Yu HS, Liang LP, Li W, Ding H, Song XB, Zhang LJ. Jia YP, et al. Molecules. 2017 Apr 20;22(4):610. doi: 10.3390/molecules22040610. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28425969 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- The Role of Antioxidants in the Interplay between Oxidative Stress and Senescence.
Varesi A, Chirumbolo S, Campagnoli LIM, Pierella E, Piccini GB, Carrara A, Ricevuti G, Scassellati C, Bonvicini C, Pascale A. Varesi A, et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jun 22;11(7):1224. doi: 10.3390/antiox11071224. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35883714 Free PMC article. Review. - The Biochemistry and Effectiveness of Antioxidants in Food, Fruits, and Marine Algae.
Pruteanu LL, Bailey DS, Grădinaru AC, Jäntschi L. Pruteanu LL, et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Apr 2;12(4):860. doi: 10.3390/antiox12040860. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37107235 Free PMC article. Review. - Eye Care Behaviors among Adults in Poland: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Survey.
Kamińska A, Pinkas J, Tyszko P, Wrześniewska-Wal I, Jankowski M. Kamińska A, et al. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Feb 17;20(4):3590. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20043590. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36834285 Free PMC article. - Alpine Diet in Valmalenco (Lombardy, Italy): Nutritional Features of Spontaneous Plants and Traditional Dishes.
Milani F, Bottoni M, Giuliani C, Colombo L, Casiraghi MC, Colombo PS, Bruschi P, Erba D, Fico G. Milani F, et al. Nutrients. 2023 Apr 20;15(8):1988. doi: 10.3390/nu15081988. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37111208 Free PMC article. - The effect of Fernblock® in preventing blue-light-induced oxidative stress and cellular damage in retinal pigment epithelial cells is associated with NRF2 induction.
Gallego-Rentero M, López Sánchez A, Nicolás-Morala J, Alcaraz-Laso P, Zhang N, Juarranz Á, González S, Carrasco E. Gallego-Rentero M, et al. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2024 Aug;23(8):1471-1484. doi: 10.1007/s43630-024-00606-6. Epub 2024 Jun 23. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38909335
References
- Perry A., Rasmussen H., Johnson E. Xanthophyll (lutein, zeaxanthin) content in fruits, vegetables and corn and egg products. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2009;22:9–15. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2008.07.006. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 04150746/Health and Medical Research Fund, the Food and Health Bureau, The Government of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region
- N/A/Boston Children's Hospital OFD/BTREC/CTREC Faculty Career Development Grant
- N/A/Boston Children's Hospital Ophthalmology Foundation
- N/A/Boston Children's Hospital Manton Center for Orphan Disease Research
- N/A/Little Giraffe Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials