Comparative cardiovascular safety of GLP-1 receptor agonists versus other glucose-lowering agents in real-world patients with type 2 diabetes: a nationwide population-based cohort study - PubMed (original) (raw)
Observational Study
Comparative cardiovascular safety of GLP-1 receptor agonists versus other glucose-lowering agents in real-world patients with type 2 diabetes: a nationwide population-based cohort study
Chun-Ting Yang et al. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020.
Abstract
Background: Current evidence about the cardiovascular safety of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1ra) possesses limited generalizability to real-world patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) in usual practice. This study aimed to investigate the comparative cardiovascular safety of GLP-1ra in comparisons with dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor (DPP-4i), sulfonylurea (SU), and insulin in a real-world population with T2D.
Methods: Adults with newly-diagnosed T2D were identified from Taiwan's National Health Insurance Research Database in 2003-2014. A prevalent new-user cohort design was adopted to include a broad representation of real-world T2D patients being treated with GLP-1ra. The between-group comparability of baseline patient characteristics was achieved by matching on (1) initiation time of study drugs, (2) prior exposure to glucose-lowering agents, and (3) diabetes severity and complications, comorbidities, and concomitant cardiovascular medications using propensity scores. The primary outcome was a composite of cardiovascular disease (CVD) events and assessed up to the end of 2015. Cox modeling was employed to assess the association between study drugs and outcomes.
Results: A total of 3195 GLP-1ra stable users was identified in 2011-2014. 1893, 1829, and 1367 GLP-1ra stable users were 1:1 matched to DPP-4i, SU and insulin users, respectively. Compared to DPP-4i, SU and insulin, the use of GLP-1ra was associated with a lower risk of composite CVD events [hazard ratio (95% confidence interval) 0.73 (0.57-0.96), 0.76 (0.57-1.00), and 0.81 (0.62-1.07), respectively]. Subgroup analyses revealed that GLP-1ra versus DPP-4i yielded a greater cardiovascular benefit in those without established CVD versus those with established CVD.
Conclusions: This comparison study extends the supporting evidence for the cardiovascular safety of GLP-1ra to a broad spectrum of real-world T2D patients using GLP-1ra.
Keywords: Cardiovascular safety; DPP-4 inhibitor; GLP-1 receptor agonist; Insulin; Sulfonylurea.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests to be declared.
Figures
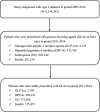
Fig. 1
Flowchart of study population selection and identification
Fig. 2
Primary and subgroup analyses for composite CVD associated with GLP-1ra versus other glucose-lowering agentsa. CVD, cardiovascular disease; DM, diabetes mellitus; DPP-4i, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor; GLP-1ra, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist; HR, hazard ratio; MVD, microvascular disease; SU, sulfonylurea. aComposite CVD was a composite outcome that included acute myocardial infarction, ischemic heart disease, heart failure, stroke, cardiogenic shock, sudden cardiac arrest, arteriosclerotic cardiovascular disease, and arrhythmia. *In the testing of interaction in subgroup analyses, a p value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant
Similar articles
- Better cardiovascular outcomes of type 2 diabetic patients treated with GLP-1 receptor agonists versus DPP-4 inhibitors in clinical practice.
Longato E, Di Camillo B, Sparacino G, Tramontan L, Avogaro A, Fadini GP. Longato E, et al. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020 Jun 10;19(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01049-w. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020. PMID: 32522260 Free PMC article. - Sex Differences in Cardiovascular Effectiveness of Newer Glucose-Lowering Drugs Added to Metformin in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
Raparelli V, Elharram M, Moura CS, Abrahamowicz M, Bernatsky S, Behlouli H, Pilote L. Raparelli V, et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 Jan 7;9(1):e012940. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.012940. Epub 2020 Jan 4. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020. PMID: 31902326 Free PMC article. - Add-on therapy in metformin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes at moderate cardiovascular risk: a nationwide study.
Thein D, Christiansen MN, Mogensen UM, Bundgaard JS, Rørth R, Madelaire C, Fosbøl EL, Schou M, Torp-Pedersen C, Gislason G, Køber L, Kristensen SL. Thein D, et al. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020 Jul 6;19(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01078-5. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020. PMID: 32631337 Free PMC article. - Review of the cardiovascular safety of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and the clinical relevance of the CAROLINA trial.
Santamarina M, Carlson CJ. Santamarina M, et al. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2019 Mar 15;19(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s12872-019-1036-0. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2019. PMID: 30876392 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Cardiovascular and renal outcomes of GLP-1 receptor agonists vs. DPP-4 inhibitors and basal insulin in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Evans M, Kuodi P, Akunna CJ, McCreedy N, Donsmark M, Ren H, Nnaji CA. Evans M, et al. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2023 Nov-Dec;20(6):14791641231221740. doi: 10.1177/14791641231221740. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2023. PMID: 38111352 Free PMC article. Review. - Once-weekly glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists vs dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors: cardiovascular effects in people with diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
Tan X, Liang Y, Rajpura JR, Yedigarova L, Noone J, Xie L, Inzucchi S, de Havenon A. Tan X, et al. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023 Nov 20;22(1):319. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-02051-8. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023. PMID: 37985992 Free PMC article. - Chronic kidney outcomes associated with GLP-1 receptor agonists versus long-acting insulins among type 2 diabetes patients requiring intensive glycemic control: a nationwide cohort study.
Peng ZY, Yang CT, Lin WH, Yao WY, Ou HT, Kuo S. Peng ZY, et al. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023 Oct 4;22(1):272. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-01991-5. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023. PMID: 37794465 Free PMC article. - Treatment effect heterogeneity following type 2 diabetes treatment with GLP1-receptor agonists and SGLT2-inhibitors: a systematic review.
Young KG, McInnes EH, Massey RJ, Kahkoska AR, Pilla SJ, Raghavan S, Stanislawski MA, Tobias DK, McGovern AP, Dawed AY, Jones AG, Pearson ER, Dennis JM; ADA/EASD PDMI. Young KG, et al. Commun Med (Lond). 2023 Oct 5;3(1):131. doi: 10.1038/s43856-023-00359-w. Commun Med (Lond). 2023. PMID: 37794166 Free PMC article. - Cost-effectiveness analysis of once-daily oral semaglutide versus placebo and subcutaneous glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists added to insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes in China.
Feng Z, Tong WK, Zhang X, Tang Z. Feng Z, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 9;14:1226778. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1226778. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37621313 Free PMC article.
References
- American Diabetes Association 9 Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2019. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(1):S90–S102. - PubMed
- Otto T, Myland M, Jung H, Lebrec J, Richter H, Norrbacka K. Utilization patterns of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Germany: a retrospective cohort study. Curr Med Res Opin. 2019;35(5):893–901. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical