The future is now: a call for action for cardiac telerehabilitation in the COVID-19 pandemic from the secondary prevention and rehabilitation section of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology - PubMed (original) (raw)
The future is now: a call for action for cardiac telerehabilitation in the COVID-19 pandemic from the secondary prevention and rehabilitation section of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology
Martijn Scherrenberg et al. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2021.
Abstract
The role of comprehensive cardiac rehabilitation is well established in the secondary prevention of cardiovascular diseases such as coronary artery disease and heart failure. Numerous trials have demonstrated both the effectiveness as well as the cost-effectiveness of comprehensive cardiac rehabilitation in improving exercise capacity and quality of life, and in reducing cardiovascular mortality and morbidity. However, the current COVID-19 pandemic has led to closure of many cardiac rehabilitation centres in Europe resulting in many eligible patients unable to participate in the optimisation of secondary prevention and physical performance. This elicits an even louder call for alternatives such as cardiac telerehabilitation to maintain the delivery of the core components of cardiac rehabilitation to cardiovascular disease patients. The present call for action paper gives an update of recent cardiac telerehabilitation studies and provides a practical guide for the setup of a comprehensive cardiac telerehabilitation intervention during the COVID-19 pandemic. This set up could also be relevant to any cardiovascular disease patient not able to visit cardiac rehabilitation centres regularly after the COVID-19 pandemic ceases.
Keywords: COVID-19; cardiovascular disease; comprehensive cardiac rehabilitation; telerehabilitation.
Published on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology. All rights reserved. © The Author(s) 2020. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
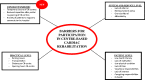
Figure 1.
Overview of barriers for participation in centre-based cardiac rehabilitation.
Figure 2.
Overview of advantages and possible concerns of cardiac telerehabilitation. EMR: electronic medical records.
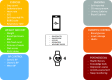
Figure 3.
Overview of remote monitoring parameters and devices.
Comment in
- Telehealth during COVID-19 pandemic: will the future last?
Schmid JP. Schmid JP. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2021 May 14;28(5):522-523. doi: 10.1093/eurjpc/zwaa016. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33623997 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Secondary prevention through comprehensive cardiovascular rehabilitation: From knowledge to implementation. 2020 update. A position paper from the Secondary Prevention and Rehabilitation Section of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology.
Ambrosetti M, Abreu A, Corrà U, Davos CH, Hansen D, Frederix I, Iliou MC, Pedretti RFE, Schmid JP, Vigorito C, Voller H, Wilhelm M, Piepoli MF, Bjarnason-Wehrens B, Berger T, Cohen-Solal A, Cornelissen V, Dendale P, Doehner W, Gaita D, Gevaert AB, Kemps H, Kraenkel N, Laukkanen J, Mendes M, Niebauer J, Simonenko M, Zwisler AO. Ambrosetti M, et al. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2021 May 14;28(5):460-495. doi: 10.1177/2047487320913379. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33611446 - Effects of cardiac telerehabilitation in patients with coronary artery disease using a personalised patient-centred web application: protocol for the SmartCare-CAD randomised controlled trial.
Brouwers RW, Kraal JJ, Traa SC, Spee RF, Oostveen LM, Kemps HM. Brouwers RW, et al. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2017 Jan 31;17(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s12872-017-0477-6. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2017. PMID: 28143388 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Telerehab III: a multi-center randomized, controlled trial investigating the long-term effectiveness of a comprehensive cardiac telerehabilitation program--rationale and study design.
Frederix I, Hansen D, Coninx K, Vandervoort P, Van Craenenbroeck EM, Vrints C, Dendale P. Frederix I, et al. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2015 May 7;15:29. doi: 10.1186/s12872-015-0021-5. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2015. PMID: 25948479 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Exercise-based cardiac rehabilitation programs in the era of COVID-19: a critical review.
Stefanakis M, Batalik L, Papathanasiou J, Dipla L, Antoniou V, Pepera G. Stefanakis M, et al. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Dec 22;22(4):1143-1155. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2204123. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34957758 Review. - The Potential of Cardiac Telerehabilitation as Delivery Rehabilitation Care Model in Heart Failure during COVID-19 and Transmissible Disease Outbreak: A Systematic Scoping Review of the Latest RCTs.
Maulana S, Trisyani Y, Mirwanti R, Amirah S, Kohar K, Priyatmoko Putri AI, Novianti E. Maulana S, et al. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Sep 21;58(10):1321. doi: 10.3390/medicina58101321. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 36295482 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Perceptions of Cardiac Rehabilitation Participants Regarding their Health Behaviors and Information Needs during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Brazil.
Ghisi GLM, Santos RZ, Korbes AS, Souza CA, Karsten M, Oh P, Benetti M. Ghisi GLM, et al. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2022 May;118(5):949-960. doi: 10.36660/abc.20210447. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 35384967 Free PMC article. English, Portuguese. - Cut-off values of 6-min walk test and sit-to-stand test for determining symptom burden in atrial fibrillation.
Zeren M, Karci M, Demir R, Gurses HN, Oktay V, Uzunhasan I, Yigit Z. Zeren M, et al. Ir J Med Sci. 2022 Dec;191(6):2587-2595. doi: 10.1007/s11845-021-02901-y. Epub 2022 Jan 23. Ir J Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35066793 Free PMC article. - Cardiac Telerehabilitation - A Solution for Cardiovascular Care in Japan.
Kaihara T, Scherrenberg M, Falter M, Frederix I, Itoh H, Makita S, Akashi YJ, Dendale P. Kaihara T, et al. Circ Rep. 2021 Oct 29;3(12):733-736. doi: 10.1253/circrep.CR-21-0126. eCollection 2021 Dec 10. Circ Rep. 2021. PMID: 34950799 Free PMC article. - Healthcare professionals' perceptions of using a digital patient educational programme as part of cardiac rehabilitation in patients with coronary artery disease - a qualitative study.
Danielsbacka J, Feldthusen C, Bäck M. Danielsbacka J, et al. BMC Health Serv Res. 2023 Sep 21;23(1):1017. doi: 10.1186/s12913-023-09997-1. BMC Health Serv Res. 2023. PMID: 37735650 Free PMC article. - Impacts of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Cardiac Rehabilitation Delivery around the World.
Ghisi GLM, Xu Z, Liu X, Mola A, Gallagher R, Babu AS, Yeung C, Marzolini S, Buckley J, Oh P, Contractor A, Grace SL. Ghisi GLM, et al. Glob Heart. 2021 Jun 10;16(1):43. doi: 10.5334/gh.939. Glob Heart. 2021. PMID: 34211829 Free PMC article.
References
- Bansilal S, Castellano M, Fuster V.. Global burden of CVD: focus on secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease. Int J Cardiol 2015; 201: S1–S7. - PubMed
- Briffa TG, Hobbs MS, Tonkin A, et al.. Population trends of recurrent coronary heart disease event rates remain high. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 2011; 4: 107–113. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.110.957944 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous