Impact of a Weekly Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist, Albiglutide, on Glycemic Control and on Reducing Prandial Insulin Use in Type 2 Diabetes Inadequately Controlled on Multiple Insulin Therapy: A Randomized Trial - PubMed (original) (raw)
Randomized Controlled Trial
. 2020 Oct;43(10):2509-2518.
doi: 10.2337/dc19-2316. Epub 2020 Jul 21.
Affiliations
- PMID: 32694215
- PMCID: PMC7510023
- DOI: 10.2337/dc19-2316
Randomized Controlled Trial
Impact of a Weekly Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist, Albiglutide, on Glycemic Control and on Reducing Prandial Insulin Use in Type 2 Diabetes Inadequately Controlled on Multiple Insulin Therapy: A Randomized Trial
Julio Rosenstock et al. Diabetes Care. 2020 Oct.
Abstract
Objective: The principle of replacing prandial insulin lispro with a once-weekly glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA) for type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on a multiple daily insulin injections regimen was tested with albiglutide.
Research design and methods: In this treat-to-target study, basal plus prandial insulin was optimized over 4 weeks before participants were randomized (1:1) to albiglutide plus optimized basal insulin glargine and lispro (dose reduced by 50% at randomization; subsequently, lispro injections were fully discontinued 4 weeks later) (n = 402) or to continued optimized lispro plus optimized glargine (n = 412).
Results: Mean ± SD HbA1c at baseline, 7.8 ± 0.6% (61 ± 7 mmol/mol) in the albiglutide + glargine group and 7.7 ± 0.6% (60 ± 7 mmol/mol) in the lispro + glargine group, was reduced at week 26 to 6.7 ± 0.8% (49 ± 8 mmol/mol) and 6.6 ± 0.8% (48 ± 8 mmol/mol), respectively (least squares [LS] difference 0.06% [95% CI -0.05 to 0.17]; noninferiority P < 0.0001). In the albiglutide + glargine group, 218 participants (54%) replaced all prandial insulin without reintroducing lispro up to week 26. Total daily prandial insulin dose was similar at baseline but was lower by 62 units/day (95% CI -65.9 to -57.8; P < 0.0001) at week 26 in the albiglutide + glargine group, and the total number of weekly injections was also reduced from 29 to 13 per week. Less severe/documented symptomatic hypoglycemia (57.2% vs. 75.0%) occurred in the albiglutide + glargine group with meaningful weight differences (LS mean ± SE -2.0 ± 0.2 vs. +2.4 ± 0.2 kg; P < 0.0001) vs. lispro + glargine. Gastrointestinal adverse events were higher with albiglutide + glargine (26% vs. 13%).
Conclusions: A once-weekly GLP-1RA was able to substitute for prandial insulin in 54% of people, substantially reducing the number of prandial insulin injections; glycemic control improved, with the added benefits of weight loss and less hypoglycemia in the GLP-1RA arm. Replacing prandial insulin with a weekly GLP-1RA can simplify basal plus prandial insulin treatments and achieve better outcomes in type 2 diabetes.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02229227.
© 2020 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures
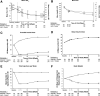
Figure 1
HbA1c, FPG, insulin dose, number of injections, and body weight by study visit (full analysis population). A: Mean HbA1c by study visit from screening to week 26. B: Mean FPG by study visit to week 26. C: Model-adjusted prandial insulin dose by study visit to week 26. D: Model-adjusted basal insulin dose by study visit to week 26. E: Mean number of total injections per week by study visit to week 26. F: Model-adjusted change from baseline in body weight (kg) by study visit to week 26. ●, albiglutide + glargine; □, lispro + glargine.
Comment in
- Switching From Insulin Bolus Treatment to GLP-1 RAs Added to Continued Basal Insulin in People With Type 2 Diabetes on Basal-Bolus Insulin.
Bolli GB, Porcellati F, Meier JJ. Bolli GB, et al. Diabetes Care. 2020 Oct;43(10):2333-2335. doi: 10.2337/dci20-0038. Diabetes Care. 2020. PMID: 32958617 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Advancing basal insulin replacement in type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with insulin glargine plus oral agents: a comparison of adding albiglutide, a weekly GLP-1 receptor agonist, versus thrice-daily prandial insulin lispro.
Rosenstock J, Fonseca VA, Gross JL, Ratner RE, Ahrén B, Chow FC, Yang F, Miller D, Johnson SL, Stewart MW, Leiter LA; Harmony 6 Study Group. Rosenstock J, et al. Diabetes Care. 2014 Aug;37(8):2317-25. doi: 10.2337/dc14-0001. Epub 2014 Jun 4. Diabetes Care. 2014. PMID: 24898300 Clinical Trial. - Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist or bolus insulin with optimized basal insulin in type 2 diabetes.
Diamant M, Nauck MA, Shaginian R, Malone JK, Cleall S, Reaney M, de Vries D, Hoogwerf BJ, MacConell L, Wolffenbuttel BH; 4B Study Group. Diamant M, et al. Diabetes Care. 2014 Oct;37(10):2763-73. doi: 10.2337/dc14-0876. Epub 2014 Jul 10. Diabetes Care. 2014. PMID: 25011946 Clinical Trial. - Tirzepatide vs Insulin Lispro Added to Basal Insulin in Type 2 Diabetes: The SURPASS-6 Randomized Clinical Trial.
Rosenstock J, Frías JP, Rodbard HW, Tofé S, Sears E, Huh R, Fernández Landó L, Patel H. Rosenstock J, et al. JAMA. 2023 Nov 7;330(17):1631-1640. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.20294. JAMA. 2023. PMID: 37786396 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Efficacy and safety of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and mixed-treatment comparison analysis.
Htike ZZ, Zaccardi F, Papamargaritis D, Webb DR, Khunti K, Davies MJ. Htike ZZ, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017 Apr;19(4):524-536. doi: 10.1111/dom.12849. Epub 2017 Feb 17. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017. PMID: 27981757 Review. - Prandial premixed insulin analogue regimens versus basal insulin analogue regimens in the management of type 2 diabetes: an evidence-based comparison.
Ilag LL, Kerr L, Malone JK, Tan MH. Ilag LL, et al. Clin Ther. 2007 Jun;29(6 Pt 1):1254-70. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2007.07.003. Clin Ther. 2007. PMID: 18036388 Review.
Cited by
- 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Management in Korea: Full Version Recommendation of the Korean Diabetes Association.
Moon JS, Kang S, Choi JH, Lee KA, Moon JH, Chon S, Kim DJ, Kim HJ, Seo JA, Kim MK, Lim JH, Song YJ, Yang YS, Kim JH, Lee YB, Noh J, Hur KY, Park JS, Rhee SY, Kim HJ, Kim HM, Ko JH, Kim NH, Kim CH, Ahn J, Oh TJ, Kim SK, Kim J, Han E, Jin SM, Bae J, Jeon E, Kim JM, Kang SM, Park JH, Yun JS, Cha BS, Moon MK, Lee BW. Moon JS, et al. Diabetes Metab J. 2024 Jul;48(4):546-708. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0249. Epub 2024 Jul 26. Diabetes Metab J. 2024. PMID: 39091005 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Tirzepatide Improved Health-Related Quality of Life Compared with Insulin Lispro in Basal Insulin-Treated Adults with Type 2 Diabetes and Inadequate Glycaemic Control: A Randomised Controlled Phase 3b Trial (SURPASS-6).
Boye KS, Poon JL, Landó LF, Sapin H, Huh R, Wang M, Williamson S, Patel H. Boye KS, et al. Diabetes Ther. 2024 Sep;15(9):2039-2059. doi: 10.1007/s13300-024-01620-8. Epub 2024 Jul 15. Diabetes Ther. 2024. PMID: 39008236 Free PMC article. - Efficacy and safety of albiglutide, a once-weekly glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Kamrul-Hasan ABM, Dutta D, Nagendra L, Bhattacharya S, Singla R, Kalra S. Kamrul-Hasan ABM, et al. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Jun 21;103(25):e38568. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038568. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38905435 Free PMC article. - The effect of GLP-1R agonists on the medical triad of obesity, diabetes, and cancer.
Ibrahim SS, Ibrahim RS, Arabi B, Brockmueller A, Shakibaei M, Büsselberg D. Ibrahim SS, et al. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024 Dec;43(4):1297-1314. doi: 10.1007/s10555-024-10192-9. Epub 2024 May 27. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024. PMID: 38801466 Free PMC article. Review. - De-Intensification from Basal-Bolus Insulin Therapy to Liraglutide in Type 2 Diabetes: Predictive Value of Mean Glycaemia during Fasting Test.
Pavlikova B, Breburdova M, Krcma M, Kriz M, Kasparek J, Rusavy Z. Pavlikova B, et al. Life (Basel). 2024 Apr 28;14(5):568. doi: 10.3390/life14050568. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38792590 Free PMC article.
References
- Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, et al. . Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2015: a patient-centered approach: update to a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2015;38:140–149 - PubMed
- Miser WF, Arakaki R, Jiang H, Scism-Bacon J, Anderson PW, Fahrbach JL. Randomized, open-label, parallel-group evaluations of basal-bolus therapy versus insulin lispro premixed therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus failing to achieve control with starter insulin treatment and continuing oral antihyperglycemic drugs: a noninferiority intensification substudy of the DURABLE trial. Clin Ther 2010;32:896–908 - PubMed
- Eng C, Kramer CK, Zinman B, Retnakaran R. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist and basal insulin combination treatment for the management of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2014;384:2228–2234 - PubMed
- Holst JJ, Vilsbøll T. Combining GLP-1 receptor agonists with insulin: therapeutic rationales and clinical findings. Diabetes Obes Metab 2013;15:3–14 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous