Lifestyle, Oxidative Stress, and Antioxidants: Back and Forth in the Pathophysiology of Chronic Diseases - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00694. eCollection 2020.
Nanjangud V Anil Kumar 2, Paolo Zucca 3, Elena Maria Varoni 4, Luciana Dini 5, Elisa Panzarini 5, Jovana Rajkovic 6, Patrick Valere Tsouh Fokou 7, Elena Azzini 8, Ilaria Peluso 8, Abhay Prakash Mishra 9, Manisha Nigam 10, Youssef El Rayess 11, Marc El Beyrouthy 11, Letizia Polito 12, Marcello Iriti 13, Natália Martins 14 15, Miquel Martorell 16 17, Anca Oana Docea 18, William N Setzer 19, Daniela Calina 18, William C Cho 20, Javad Sharifi-Rad 21
Affiliations
- PMID: 32714204
- PMCID: PMC7347016
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00694
Review
Lifestyle, Oxidative Stress, and Antioxidants: Back and Forth in the Pathophysiology of Chronic Diseases
Mehdi Sharifi-Rad et al. Front Physiol. 2020.
Abstract
Oxidative stress plays an essential role in the pathogenesis of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, neurodegenerative diseases, and cancer. Long term exposure to increased levels of pro-oxidant factors can cause structural defects at a mitochondrial DNA level, as well as functional alteration of several enzymes and cellular structures leading to aberrations in gene expression. The modern lifestyle associated with processed food, exposure to a wide range of chemicals and lack of exercise plays an important role in oxidative stress induction. However, the use of medicinal plants with antioxidant properties has been exploited for their ability to treat or prevent several human pathologies in which oxidative stress seems to be one of the causes. In this review we discuss the diseases in which oxidative stress is one of the triggers and the plant-derived antioxidant compounds with their mechanisms of antioxidant defenses that can help in the prevention of these diseases. Finally, both the beneficial and detrimental effects of antioxidant molecules that are used to reduce oxidative stress in several human conditions are discussed.
Keywords: aging; antioxidant defense; cancer; cardiovascular diseases; natural antioxidants; neurological disorders; oxidative stress; reactive oxygen species.
Copyright © 2020 Sharifi-Rad, Anil Kumar, Zucca, Varoni, Dini, Panzarini, Rajkovic, Tsouh Fokou, Azzini, Peluso, Prakash Mishra, Nigam, El Rayess, Beyrouthy, Polito, Iriti, Martins, Martorell, Docea, Setzer, Calina, Cho and Sharifi-Rad.
Figures
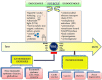
FIGURE 1
Schematic presentation of the sources of free radicals and their effects on the human body.
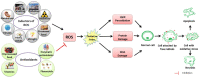
FIGURE 2
Schematic figure of the link between ROS, oxidative stress and their effects on the human body. Oxidative stress is the imbalance that occurs when there is an increased production of free radicals that exceeds the body’s ability to neutralize it. Alteration of chemical reactions at the cellular level leads to the appearance of free radicals and peroxides that affect the intracellular structures – proteins, lipids, DNA, with the disruption of intrinsic mechanisms at this level. Free radicals are normally produced in the body due to the influence of external factors, such as pollution, cigarette smoke, or internal, due to intracellular metabolism when antioxidant mechanisms are exceeded.
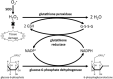
FIGURE 3
Primary enzymes (SOD or peroxidases) act directly in scavenging ROS. Secondary enzymes, such as glutathione reductase and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, support the action of primary enzymes regenerating NAPDH and reduced glutathione.
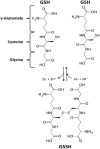
FIGURE 4
Glutathione (GSH), a tripeptide with an active –SH function. GSH undergoes a redox cycle, dimerizing with a disulfide bridge formation.
FIGURE 5
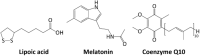
Chemical structures of Lipoic acid, Melatonin, Coenzyme Q10.
FIGURE 6
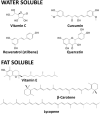
Chemical structures of Vitamin C, Curcumin, Resveratrol, Quercetin, Vitamin E, β-carotene, Lycopene.
Similar articles
- From reactive species to disease development: Effect of oxidants and antioxidants on the cellular biomarkers.
Curieses Andrés CM, Pérez de la Lastra JM, Andrés Juan C, Plou FJ, Pérez-Lebeña E. Curieses Andrés CM, et al. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2023 Nov;37(11):e23455. doi: 10.1002/jbt.23455. Epub 2023 Jul 12. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37437103 Review. - Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Potential of One Hundred Medicinal Plants.
Hassan W, Noreen H, Rehman S, Gul S, Kamal MA, Kamdem JP, Zaman B, da Rocha JBT. Hassan W, et al. Curr Top Med Chem. 2017;17(12):1336-1370. doi: 10.2174/1568026617666170102125648. Curr Top Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28049396 Review. - Mitochondrial biogenesis: pharmacological approaches.
Valero T. Valero T. Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(35):5507-9. doi: 10.2174/138161282035140911142118. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 24606795 - Simultaneous Activation of Nrf2 and Elevation of Dietary and Endogenous Antioxidant Chemicals for Cancer Prevention in Humans.
Prasad KN. Prasad KN. J Am Coll Nutr. 2016;35(2):175-84. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2014.1003419. Epub 2015 Jul 7. J Am Coll Nutr. 2016. PMID: 26151600 Review. - Oxidative stress mitigation by antioxidants - An overview on their chemistry and influences on health status.
Pisoschi AM, Pop A, Iordache F, Stanca L, Predoi G, Serban AI. Pisoschi AM, et al. Eur J Med Chem. 2021 Jan 1;209:112891. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112891. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Eur J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33032084 Review.
Cited by
- Bioactives and Technological Quality of Functional Biscuits Containing Flour and Liquid Extracts from Broccoli By-Products.
Fanesi B, Ismaiel L, Nartea A, Orhotohwo OL, Kuhalskaya A, Pacetti D, Lucci P, Falcone PM. Fanesi B, et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Dec 14;12(12):2115. doi: 10.3390/antiox12122115. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136234 Free PMC article. - The Emerging Roles of the Metabolic Regulator G6PD in Human Cancers.
Ahamed A, Hosea R, Wu S, Kasim V. Ahamed A, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 7;24(24):17238. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417238. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139067 Free PMC article. Review. - Recent advances and limitations of mTOR inhibitors in the treatment of cancer.
Ali ES, Mitra K, Akter S, Ramproshad S, Mondal B, Khan IN, Islam MT, Sharifi-Rad J, Calina D, Cho WC. Ali ES, et al. Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Sep 15;22(1):284. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02706-8. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 36109789 Free PMC article. Review. - Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Opuntia ficus-indica Fruit (OFI-EVs) Speed Up the Normal Wound Healing Processes by Modulating Cellular Responses.
Valentino A, Conte R, Bousta D, Bekkari H, Di Salle A, Calarco A, Peluso G. Valentino A, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 28;25(13):7103. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137103. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000212 Free PMC article. - ROS-generating nanoplatforms as selective and tunable therapeutic weapons against cancer.
Foglietta F, Serpe L, Canaparo R. Foglietta F, et al. Discov Nano. 2023 Dec 11;18(1):151. doi: 10.1186/s11671-023-03939-w. Discov Nano. 2023. PMID: 38078991 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Andreyev A. Y., Kushnareva Y. E., Starkov A. A. (2005). Mitochondrial metabolism of reactive oxygen species. Biochemistry 70 200–214. - PubMed