Gambling Harm as a Global Public Health Concern: A Mixed Method Investigation of Trends in Wales - PubMed (original) (raw)
Gambling Harm as a Global Public Health Concern: A Mixed Method Investigation of Trends in Wales
Bev John et al. Front Public Health. 2020.
Abstract
Background: Recent research evidence has suggested that gambling is a public health concern. A number of studies report the association between gambling activity and increased instances of various other harms, including substance misuse and psychological disorders. In parallel to alcohol misuse, it is also becoming clear that gambling related harm is more of a continuum of harm, as opposed to traditionally accepted categorisations of gambling behavior: safe and responsible or "problem" and harmful. Previous effective treatment models for alcohol misuse have considered a public health approach to develop interventions. As such, the current research seeks to use a public health approach to both investigate the extent of gambling harm across Wales, and to identify upstream predictors of harm to inform future interventions. Method: A triangulation of data collection methods was utilized across Wales, UK. Two hundred and forty-eight participants completed a quantitative survey relating to gambling behavior and related harm, which included the Problem Severity Gambling Index, the Gambling Commission measure of frequency, The Gambling Motives Questionnaire and the Fast Alcohol Screening tool. Ninety-eight of these participants completed a qualitative subsection. Structured interviews were conducted with 20 individuals from 11 service providers. Semi-structured interviews were conducted for the five case studies of individuals who had previously sought help for gambling. The geographical density and distribution of Licensed Gambling Outlets was also mapped in local areas. Results: The findings provide further evidence of a continuum of gambling related harm. Twenty seven percent of survey participants demonstrate some indicators of risk of gambling harm. Social, cultural and environmental contexts play a role in initiation and maintenance of gambling behavior and the subsequent related harm. Accounts from individuals corroborated the quantitative findings. Conclusions: Findings from this Welsh sample are in line with and add support to the growing international research evidence that gambling harms are a universal issue that cross cultures. It is clear that action is needed by legislators at a policy level and that broadening the focus of intervention to a public health level is necessary to develop effective strategies for harm reduction.
Keywords: gambling density; gambling harm; mixed methods; predictors of harm; prevention; public health.
Copyright © 2020 John, Holloway, Davies, May, Buhociu, Cousins, Thomas and Roderique-Davies.
Figures
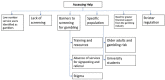
Figure 1
Overarching and sub-themes from qualitative survey data.
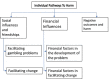
Figure 2
Main themes from Service Provider interview data.
Figure 3
Emergent themes from Case Study interview data.
Similar articles
- Public attitudes towards gambling product harm and harm reduction strategies: an online study of 16-88 year olds in Victoria, Australia.
Thomas SL, Randle M, Bestman A, Pitt H, Bowe SJ, Cowlishaw S, Daube M. Thomas SL, et al. Harm Reduct J. 2017 Jul 25;14(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s12954-017-0173-y. Harm Reduct J. 2017. PMID: 28743300 Free PMC article. - Is gambling an emerging public health issue for Wales, UK?
Atherton F, Beynon C. Atherton F, et al. J Public Health (Oxf). 2019 Dec 20;41(4):858-863. doi: 10.1093/pubmed/fdy164. J Public Health (Oxf). 2019. PMID: 30239763 Review. - Women and gambling-related harm: a narrative literature review and implications for research, policy, and practice.
McCarthy S, Thomas SL, Bellringer ME, Cassidy R. McCarthy S, et al. Harm Reduct J. 2019 Mar 4;16(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s12954-019-0284-8. Harm Reduct J. 2019. PMID: 30832672 Free PMC article. Review. - What is known about population level programs designed to address gambling-related harm: rapid review of the evidence.
Clune S, Ratnaike D, White V, Donaldson A, Randle E, O'Halloran P, Lewis V. Clune S, et al. Harm Reduct J. 2024 Jun 18;21(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s12954-024-01032-8. Harm Reduct J. 2024. PMID: 38890632 Free PMC article. Review. - Understanding gambling related harm: a proposed definition, conceptual framework, and taxonomy of harms.
Langham E, Thorne H, Browne M, Donaldson P, Rose J, Rockloff M. Langham E, et al. BMC Public Health. 2016 Jan 27;16:80. doi: 10.1186/s12889-016-2747-0. BMC Public Health. 2016. PMID: 26818137 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Treatment of harmful gambling: a scoping review of United Kingdom-based intervention research.
Seel CJ, Jones M, Christensen DR, May R, Hoon AE, Dymond S. Seel CJ, et al. BMC Psychiatry. 2024 May 23;24(1):392. doi: 10.1186/s12888-024-05843-8. BMC Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38783231 Free PMC article. Review. - Towards a conceptual framework for the prevention of gambling-related harms: Findings from a scoping review.
Wheaton J, Ford B, Nairn A, Collard S. Wheaton J, et al. PLoS One. 2024 Mar 22;19(3):e0298005. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298005. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38517885 Free PMC article. Review. - Anticipated Motives for Gambling Treatment in Adults from the U.S.
Grant Weinandy JT, Connolly A, Floyd C, Kraus SW, Grubbs JB. Grant Weinandy JT, et al. J Gambl Stud. 2024 Sep;40(3):1585-1605. doi: 10.1007/s10899-024-10287-6. Epub 2024 Feb 24. J Gambl Stud. 2024. PMID: 38400890 Free PMC article. - Involving lived experience in regional efforts to address gambling-related harms: going beyond 'window dressing' and 'tick box exercises'.
Jenkins CL, Mills T, Grimes J, Bland C, Reavey P, Wills J, Sykes S. Jenkins CL, et al. BMC Public Health. 2024 Feb 5;24(1):384. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-17939-7. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38317155 Free PMC article. - Voluntary Self-Exclusion and Contingency Management for the Treatment of Problematic and Harmful Gambling in the UK: An Exploratory Study.
Zolkwer MB, Dymond S, Singer BF. Zolkwer MB, et al. Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Oct 4;11(19):2682. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11192682. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37830719 Free PMC article.
References
- Holdsworth L, Tiyce M. Untangling the complex needs of people experiencing gambling problems and homelessness. Int J Mental Health Addict. (2013) 11:186–98. 10.1007/s11469-012-9409-y - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials