The Intricate Relationship between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM), Insulin Resistance (IR), and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
. 2020 Jul 31:2020:3920196.
doi: 10.1155/2020/3920196. eCollection 2020.
Affiliations
- PMID: 32832560
- PMCID: PMC7424491
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/3920196
Review
The Intricate Relationship between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM), Insulin Resistance (IR), and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Daniela Maria Tanase et al. J Diabetes Res. 2020.
Abstract
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) remain as one of the most global problematic metabolic diseases with rapidly increasing prevalence and incidence. Epidemiological studies noted that T2DM patients have by two-fold increase to develop NAFLD, and vice versa. This complex and intricate association is supported and mediated by insulin resistance (IR). In this review, we discuss the NAFLD immunopathogenesis, connection with IR and T2DM, the role of screening and noninvasive tools, and mostly the impact of the current antidiabetic drugs on steatosis liver and new potential therapeutic targets.
Copyright © 2020 Daniela Maria Tanase et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
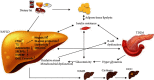
Figure 1
NAFLD, IR, and T2DM complex immunopathogenesis. T2DM: type 2 diabetes mellitus; NAFLD: nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; NASH: nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; IR: insulin resistance; FFAs: free fatty acids; TG: triglyceride; ChREBP: carbohydrate response element-binding protein; SREBP1c: sterol regulating element-binding protein 1c; DAG: diacylglycerols; ROS: high reactive oxygen species;
Similar articles
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes: common pathophysiologic mechanisms.
Saponaro C, Gaggini M, Gastaldelli A. Saponaro C, et al. Curr Diab Rep. 2015 Jun;15(6):607. doi: 10.1007/s11892-015-0607-4. Curr Diab Rep. 2015. PMID: 25894944 Review. - Concurrent nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes: diagnostic and therapeutic considerations.
Arrese M, Barrera F, Triantafilo N, Arab JP. Arrese M, et al. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Sep;13(9):849-866. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2019.1649981. Epub 2019 Aug 8. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 31353974 Review. - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus: the liver disease of our age?
Firneisz G. Firneisz G. World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jul 21;20(27):9072-89. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.9072. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25083080 Free PMC article. Review. - Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Treatment in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus; New Kids on the Block.
Athyros VG, Polyzos SA, Kountouras J, Katsiki N, Anagnostis P, Doumas M, Mantzoros CS. Athyros VG, et al. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2020;18(2):172-181. doi: 10.2174/1570161117666190405164313. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 30961499 Review. - Is HOMA-IR a potential screening test for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in adults with type 2 diabetes?
Gutierrez-Buey G, Núñez-Córdoba JM, Llavero-Valero M, Gargallo J, Salvador J, Escalada J. Gutierrez-Buey G, et al. Eur J Intern Med. 2017 Jun;41:74-78. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2017.03.006. Epub 2017 Mar 7. Eur J Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 28283346
Cited by
- U-shaped relationship between triglyceride glucose-body mass index and suicide attempts in Chinese patients with untreated first-episode major depressive disorder.
Jia F, Ma H, Liu J, Li C, Ye G, Chen T, Huo R, Du X, Zhang X. Jia F, et al. BMC Psychiatry. 2024 Nov 15;24(1):808. doi: 10.1186/s12888-024-06269-y. BMC Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39548411 Free PMC article. - Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells (MDSCs) and Obesity-Induced Inflammation in Type 2 Diabetes.
Ghemiș L, Goriuc A, Minea B, Botnariu GE, Mârțu MA, Ențuc M, Cioloca D, Foia LG. Ghemiș L, et al. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Nov 1;14(21):2453. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14212453. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39518420 Free PMC article. Review. - High-fiber basil seed flour reduces insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis in high-fat diet mice.
Farías C, Cisternas C, Caicedo A, Mercado L, Valenzuela R, Calderón H, Espinosa A, Videla LA, Muñoz LA. Farías C, et al. NPJ Sci Food. 2024 Nov 8;8(1):90. doi: 10.1038/s41538-024-00329-z. NPJ Sci Food. 2024. PMID: 39516211 Free PMC article. - Association of METS-IR index with Type 2 Diabetes: A cross-sectional analysis of national health and nutrition examination survey data from 2009 to 2018.
Hou Y, Li R, Xu Z, Chen W, Li Z, Jiang W, Meng Y, Han J. Hou Y, et al. PLoS One. 2024 Nov 8;19(11):e0308597. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308597. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39514584 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical