Roles of N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) in Stem Cell Fate Decisions and Early Embryonic Development in Mammals - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Roles of N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) in Stem Cell Fate Decisions and Early Embryonic Development in Mammals
Meng Zhang et al. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020.
Erratum in
- Corrigendum: Roles of N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) in Stem Cell Fate Decisions and Early Embryonic Development in Mammals.
Zhang M, Zhai Y, Zhang S, Dai X, Li Z. Zhang M, et al. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jan 21;9:640806. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.640806. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33553192 Free PMC article.
Abstract
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is one of the most abundant internal mRNA modifications, and it affects multiple biological processes related to eukaryotic mRNA. The majority of m6A sites are located in stop codons and 3'UTR regions of mRNAs. m6A regulates RNA metabolism, including alternative splicing (AS), alternative polyadenylation (APA), mRNA export, decay, stabilization, and translation. The m6A metabolic pathway is regulated by a series of m6A writers, erasers and readers. Recent studies indicate that m6A is essential for the regulation of gene expression, tumor formation, stem cell fate, gametogenesis, and animal development. In this systematic review, we summarized the recent advances in newly identified m6A effectors and the effects of m6A on RNA metabolism. Subsequently, we reviewed the functional roles of RNA m6A modification in diverse cellular bioprocesses, such as stem cell fate decisions, cell reprogramming and early embryonic development, and we discussed the potential of m6A modification to be applied to regenerative medicine, disease treatment, organ transplantation, and animal reproduction.
Keywords: N6-methyladenosine; RNA metabolism; cell reprogramming; embryonic development; stem cell fate.
Copyright © 2020 Zhang, Zhai, Zhang, Dai and Li.
Figures
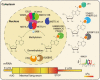
FIGURE 1
The characteristics of RNA m6A modification. The m6A writers, erasers, and readers in eukaryotic cells (Shi et al., 2019). The preferences and density of RNA m6A modification in different regions of mRNAs (Fitzsimmons and Batista, 2019).
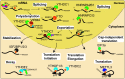
FIGURE 2
RNA m6A modifications regulate RNA metabolism. m6A is deposited onto nascent mRNAs by MTC. Then the m6A-modified mRNAs undergo AS by recruiting splicing factors to m6A sites or their flanking sequences. On the other hand, YTHDC1 and VIRMA can interact with the polyadenylation cleavage factors CPSF5 and CPSF6, thus regulating mRNA APA. Then, mRNAs can be recognized by YTHDC1 or FMRP and exported into the cytoplasm. Cytoplasmic m6A readers regulate mRNA stability (IGF2BPs), decay (YTHDF2), and translation (YTHDF1/3, YTHDC2, EIF3a, and METTL3) under normal and stress conditions.
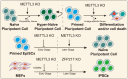
FIGURE 3
m6A regulates the pluripotent stem cell fate. METTL3 or m6A deletion has divergent effects on the fate decision of pluripotent stem cells in different states. METTL3 and ZFP217 play divergent roles in somatic cell reprogramming at different stages.
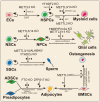
FIGURE 4
The crucial roles of m6A in stem cell and progenitor cell differentiation. m6A plays divergent functions by affecting mRNA splicing (•), stability (■), and translation (★). ECs: endothelial cells; HSPCs: hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells; NSCs: neural stem cells; NPCs: neural progenitor cells; SSCs: spermatogonial stem cells; ADSCs: adipose-derived stem cell; and BMSCs: bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.
FIGURE 5
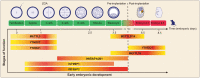
The m6A modification-related proteins exert essential functions in early embryonic development. The highlighted color indicates that the proteins mainly play functions at this stage.
Similar articles
- The emerging roles of N6-methyladenosine RNA methylation in human cancers.
Shen H, Lan Y, Zhao Y, Shi Y, Jin J, Xie W. Shen H, et al. Biomark Res. 2020 Jun 29;8:24. doi: 10.1186/s40364-020-00203-6. eCollection 2020. Biomark Res. 2020. PMID: 32612834 Free PMC article. Review. - The regulatory role of m6A modification in the maintenance and differentiation of embryonic stem cells.
Zhang J, Tong L, Liu Y, Li X, Wang J, Lin R, Zhou Z, Chen Y, Chen Y, Liu Y, Chen D. Zhang J, et al. Genes Dis. 2023 Dec 19;11(5):101199. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2023.101199. eCollection 2024 Sep. Genes Dis. 2023. PMID: 38947741 Free PMC article. Review. - Genetic Regulation of N6-Methyladenosine-RNA in Mammalian Gametogenesis and Embryonic Development.
Chang Y, Yi M, Wang J, Cao Z, Zhou T, Ge W, Muhammad Z, Zhang Z, Feng Y, Yan Z, Felici M, Shen W, Cao H. Chang Y, et al. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Mar 14;10:819044. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.819044. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35359444 Free PMC article. Review. - N6-Methyladenosine Modifications in the Female Reproductive System: Roles in Gonad Development and Diseases.
Mu H, Li H, Liu Y, Wang X, Mei Q, Xiang W. Mu H, et al. Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Jan 1;18(2):771-782. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.66218. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35002524 Free PMC article. Review. - RNA N6-Methyladenine Modification, Cellular Reprogramming, and Cancer Stemness.
Chen H, Wang Y, Su H, Zhang X, Chen H, Yu J. Chen H, et al. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jul 4;10:935224. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.935224. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35859892 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Expression and molecular profiles of the AlkB family in ovarian serous carcinoma.
Cai Y, Wu G, Peng B, Li J, Zeng S, Yan Y, Xu Z. Cai Y, et al. Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Mar 19;13(7):9679-9692. doi: 10.18632/aging.202716. Epub 2021 Mar 19. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 33744868 Free PMC article. - m6A Profile Dynamics Indicates Regulation of Oyster Development by m6A-RNA Epitranscriptomes.
Le Franc L, Petton B, Favrel P, Rivière G. Le Franc L, et al. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2023 Aug;21(4):742-755. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2022.12.002. Epub 2022 Dec 7. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 36496129 Free PMC article. - Cancer stem cells: a major culprit of intra-tumor heterogeneity.
Naz F, Shi M, Sajid S, Yang Z, Yu C. Naz F, et al. Am J Cancer Res. 2021 Dec 15;11(12):5782-5811. eCollection 2021. Am J Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 35018226 Free PMC article. Review. - The role of m6A in angiogenesis and vascular diseases.
Chen K, Li WD, Li XQ. Chen K, et al. iScience. 2024 May 23;27(7):110082. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110082. eCollection 2024 Jul 19. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39055919 Free PMC article. Review. - Modified Messengers: flatworm stem cells and regeneration are guarded by RNA methylation.
Benham-Pyle BW. Benham-Pyle BW. EMBO J. 2022 Nov 2;41(21):e112435. doi: 10.15252/embj.2022112435. Epub 2022 Sep 19. EMBO J. 2022. PMID: 36120982 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials