Analysis of the predictive factors for a critical illness of COVID-19 during treatment - relationship between serum zinc level and critical illness of COVID-19 - PubMed (original) (raw)
Analysis of the predictive factors for a critical illness of COVID-19 during treatment - relationship between serum zinc level and critical illness of COVID-19
Yukako Yasui et al. Int J Infect Dis. 2020 Nov.
Abstract
Objectives: Because most severely ill patients with COVID-19 in our hospital showed zinc deficiency, we aimed to examine the relationship between the patient's serum zinc level and severe cases of COVID-19.
Methods: Serum zinc <70 μg/dL was defined as the criterion for hypozincemia, and patients continuously with serum zinc <70 μg/dL were classified in the hypozincemia cohort. To evaluate whether hypozincemia could be a predictive factor for a critical illness of COVID-19, we performed a multivariate analysis by employing logistic regression analysis.
Results: Prolonged hypozincemia was found to be a risk factor for a severe case of COVID-19. In evaluating the relationship between the serum zinc level and severity of patients with COVID-19 by multivariate logistic regression analysis, critical illness can be predicted through the sensitivity and false specificity of a ROC curve with an error rate of 10.3% and AUC of 94.2% by only two factors: serum zinc value (P = 0.020) and LDH value (P = 0.026).
Conclusions: Proper management of the prediction results in this study can contribute to establishing and maintaining a safe medical system, taking the arrival of the second wave, and the spread of COVID-19 in the future into consideration.
Keywords: COVID-19; Critical illness; Japan; Logistic regression analysis; Predictive factors; Serum zinc.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
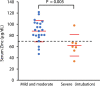
Figure 1
Comparison of serum zinc concentrations in patients with COVID-19 (n = 29) between the mild/moderate and severe (intubation) conditions. Statistical significance: p < 0.01 by Student-t test. The central red lines correspond to the mean values, and the upper and lower red lines correspond to the means + standard deviation (SDs) and means – SDs, respectively. The dotted line denotes the threshold concentration of hypozincemia as 70 μg/dL.
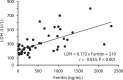
Figure 2
Colinear relationship between the serum ferritin and LDH values in all patients (n = 62) with moderate correlation (r = 0.633, P < 0.001). Collinearity between the data of serum ferritin and LDH was statistically recognized because both parameters would be increased by the infection and inflammation.
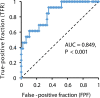
Figure 3
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve for all patients with COVID-19 (n = 62) by LDH and ages.
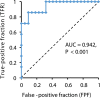
Figure 4
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve for patient subgroups with COVID-19 (n = 29) by LDH and serum Zn.
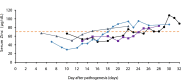
Figure 5
Time-dependent changing profiles of serum zinc concentrations in four critically ill (severe) patients after pathogenesis of COVID-19. These patients were monitored continuously for one month after pathogenesis, treated with enteral nutrition delivered from the tube inserted through the nose. The dotted line denotes the threshold concentration of hypozincemia as 70 μg/dL.
Similar articles
- Risk factors for the critical illness in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a multicenter retrospective cohort study.
Cheng S, Wu D, Li J, Zou Y, Wan Y, Shen L, Zhu L, Shi M, Hou L, Xu T, Jiao N, Li Y, Huang Y, Tang Z, Xu M, Jiang S, Li M, Yan G, Lan P, Zhu R. Cheng S, et al. Respir Res. 2020 Oct 21;21(1):277. doi: 10.1186/s12931-020-01492-z. Respir Res. 2020. PMID: 33087114 Free PMC article. - Predictive model for the development of critical coronavirus disease 2019 and its risk factors among patients in Japan.
Muto Y, Awano N, Inomata M, Kuse N, Tone M, Takada K, Fujimoto K, Ueda A, Hayashi M, Izumo T. Muto Y, et al. Respir Investig. 2021 Nov;59(6):804-809. doi: 10.1016/j.resinv.2021.08.001. Epub 2021 Sep 11. Respir Investig. 2021. PMID: 34538593 Free PMC article. - Sex distinctions regarding serum zinc levels in critically ill COVID-19 patients.
Pereira CGM, Nunes MAP, Lessa AL, Cerqueira LC, Veloso OM, Delpino FM, Ferreira A, de Góis FN, Costa PSR, Santos HO. Pereira CGM, et al. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2023 Sep;79:127262. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2023.127262. Epub 2023 Jul 10. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 37451092 Review. - COVID-19 Racial and Ethnic Inequities in Acute Care and Critical Illness Survivorship.
Tukpah AM, Moll M, Gay E. Tukpah AM, et al. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2021 Jan;18(1):23-25. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202005-549VP. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2021. PMID: 32972205 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
- Association Between Serum Zinc Concentration Levels And Severity Of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (Covid-19) In Japanese Inpatients.
Matsumoto N, Yokokawa H, Mori H, Hiki M, Tabe Y, Takahashi K, Naito T. Matsumoto N, et al. Int J Gen Med. 2024 Oct 16;17:4745-4753. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S476578. eCollection 2024. Int J Gen Med. 2024. PMID: 39429954 Free PMC article. - COVID-19: An Update on Epidemiology, Prevention and Treatment, September-2023.
Şimşek-Yavuz S. Şimşek-Yavuz S. Infect Dis Clin Microbiol. 2023 Sep 30;5(3):165-187. doi: 10.36519/idcm.2023.251. eCollection 2023 Sep. Infect Dis Clin Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38633552 Free PMC article. Review. - Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients with zinc deficiency: analysis of a nationwide Japanese medical claims database.
Yokokawa H, Morita Y, Hamada I, Ohta Y, Fukui N, Makino N, Ohata E, Naito T. Yokokawa H, et al. Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 2;14(1):2791. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-53202-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38307882 Free PMC article. - Zinc Deficiency And sTNF-RII Are Associated With Worse COVID-19 Outcomes.
Mouchati C, Durieux JC, Zisis SN, Tribout H, Scott S, Smith B, Labbato D, McComsey GA. Mouchati C, et al. J Nutr. 2024 May;154(5):1588-1595. doi: 10.1016/j.tjnut.2023.11.026. Epub 2023 Dec 2. J Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38043624
References
- Guy R.K., DiPaola R.S., Romanelli F., Dutch R.E. Rapid repurposing of drugs for COVID-19. Science. 2020;368(6493):829–830. - PubMed
- Higurashi K. Colorimetric reagent for zinc, ACCURAS AUTO Zn. Biomed Res Trace Elem. 2015;26(1):7–9.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical