Impact of Long-Term Supplementation with Fish Oil in Individuals with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Double Blind Randomized Placebo Controlled Clinical Trial - PubMed (original) (raw)
Randomized Controlled Trial
. 2020 Nov 2;12(11):3372.
doi: 10.3390/nu12113372.
Affiliations
- PMID: 33147705
- PMCID: PMC7693661
- DOI: 10.3390/nu12113372
Randomized Controlled Trial
Impact of Long-Term Supplementation with Fish Oil in Individuals with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Double Blind Randomized Placebo Controlled Clinical Trial
Kátia Cansanção et al. Nutrients. 2020.
Abstract
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a chronic disease affecting up to 25% of the population worldwide. n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (n-3 PUFA) have been associated with improved clinical parameters of NAFLD. Our purpose was to conduct a pilot study to evaluate the effects of n-3 PUFA supplementation in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study performed on NAFLD individuals diagnosed by ultrasound. Patients received n-3 PUFA (n = 13) or placebo (n = 11) supplementation for six months. Circulating miR-122 expression (determined by quantitative real time-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR), liver fibrosis (FibroScan®), red blood cells (RBC) fatty acids (gas chromatography), and biochemical tests were performed at baseline and after intervention. After the intervention, in the n-3 PUFA group, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and omega index increased significantly in RBC (p = 0.022 and p = 0.012, respectively), in addition to a significant reduction in alkaline phosphatase (ALP) (p = 0.002) and liver fibrosis (p = 0.039). However, there was no change in the expression of circulating miR-122 in both groups. Our results showed that omega-3 PUFA were incorporated in erythrocytes after six months of fish oil supplementary intake, and that n-3 PUFA were effective in reducing ALP and liver fibrosis without altering the expression of circulating miR-122 in individuals with NAFLD.
Keywords: NAFLD; alkaline phosphatase; fish oil; liver fibrosis; miR-122; miRNA; polyunsaturated fatty acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Figure 1
CONSORT flow chart of participant flow.
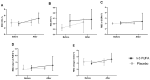
Figure 2
Percentage of DHA (A), EPA (B), n-3 DPA (C), total n-3 PUFAs (D), and omega-3 index (EPA + DHA) (E), in RBC, at baseline and after six months of intervention. Within-group differences were assessed using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test. Values are medians and interquartile ranges (IQRs). * p < 0.05 is considered statistically significant. DHA, docosahexaenoic acid; EPA, eicosapentaenoic acid; n-3 DPA, omega-3 docosapentaenoic acid; n-3 PUFA, omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid; RBC, red blood cell.
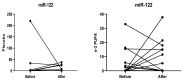
Figure 3
Comparison between the relative expression of miR-122 after six months of intervention. Within-group differences were assessed using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test.
Similar articles
- Effect of fish oil supplementation on the concentration of miRNA-122, FGF-21 and liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD: Study protocol for a randomized, double-blind and placebo-controlled clinical trial.
Barroso LN, Salarini J, Leite NC, Villela-Nogueira CA, Dávalos A, Carmo MDGT, Ferreira Peres WA. Barroso LN, et al. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2023 Oct;57:117-125. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2023.06.027. Epub 2023 Jun 28. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2023. PMID: 37739645 - Evaluation of a High Concentrate Omega-3 for Correcting the Omega-3 Fatty Acid Nutritional Deficiency in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (CONDIN).
Tobin D, Brevik-Andersen M, Qin Y, Innes JK, Calder PC. Tobin D, et al. Nutrients. 2018 Aug 20;10(8):1126. doi: 10.3390/nu10081126. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30127297 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Predictors of change in omega-3 index with fish oil supplementation in peripheral artery disease.
Drudi LM, Schaller MS, Hiramoto J, Gasper W, Harris WS, Hills NK, Grenon SM. Drudi LM, et al. J Surg Res. 2017 Apr;210:124-131. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2016.11.011. Epub 2016 Nov 11. J Surg Res. 2017. PMID: 28457318 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with Long-Chain n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Humans.
Kelley NS. Kelley NS. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2016 Nov;14(9):417-430. doi: 10.1089/met.2016.0051. Epub 2016 Oct 6. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2016. PMID: 27710160 Review. - Systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled intervention studies on the effectiveness of long-chain omega-3 fatty acids in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Musa-Veloso K, Venditti C, Lee HY, Darch M, Floyd S, West S, Simon R. Musa-Veloso K, et al. Nutr Rev. 2018 Aug 1;76(8):581-602. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuy022. Nutr Rev. 2018. PMID: 29917092 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Effectiveness of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
Aziz T, Niraj MK, Kumar S, Kumar R, Parveen H. Aziz T, et al. Cureus. 2024 Aug 28;16(8):e68002. doi: 10.7759/cureus.68002. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39347373 Free PMC article. Review. - Pharmacotherapeutic perspectives on nutraceuticals in the treatment of MASLD and MASH.
Eid AH, Khachab M, Kobeissy F, Sahebkar A. Eid AH, et al. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2025 May 24;16:20406223251339388. doi: 10.1177/20406223251339388. eCollection 2025. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2025. PMID: 40415898 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Can Nutraceuticals Support the Treatment of MASLD/MASH, and thus Affect the Process of Liver Fibrosis?
Sokal-Dembowska A, Jarmakiewicz-Czaja S, Ferenc K, Filip R. Sokal-Dembowska A, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 11;25(10):5238. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105238. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791276 Free PMC article. Review. - Efficacy of fish oil supplementation on metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: a meta-analysis.
Zhou L, Sun D, Bai H. Zhou L, et al. Front Nutr. 2025 Jan 24;12:1524830. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1524830. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39927279 Free PMC article. - Effects of Fish Oil Supplementation on Reducing the Effects of Paternal Obesity and Preventing Fatty Liver in Offspring.
Shrestha A, Dellett SK, Yang J, Sharma U, Ramalingam L. Shrestha A, et al. Nutrients. 2023 Dec 8;15(24):5038. doi: 10.3390/nu15245038. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 38140297 Free PMC article.
References
- Cansanção K., Monteiro L.S., Leite N.C., Dávalos A., Do Carmo M.D.G.T., Ferreira Peres W.A. Advanced liver fibrosis is independently associated with palmitic acid and insulin levels in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutrients. 2018;10:1586. doi: 10.3390/nu10111586. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- ./This research was funded by Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro (FAPERJ),
- E-26/203.250/2017/[Carlos Chagas Filho Foundation for Research Support of the State of Rio de Janeiro (Young Scientist of Our State)
- E-26/010.100978/2018/Apoio às Instituições de Ensino e Pesquisa Sediadas no Rio de Janeiro
- PID2019-109369RB-I00 and RTI2018-093873-A-I00/Agencia Estatal de Investigación and European FEDER Funds
- nº.41/2017/Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel] (Print)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical