Highly accurate long-read HiFi sequencing data for five complex genomes - PubMed (original) (raw)
doi: 10.1038/s41597-020-00743-4.
Kristin Mars 1, Greg Young 1, Yu-Chih Tsai 1, Joseph W Karalius 1, Jane M Landolin 2, Nicholas Maurer 3, David Kudrna 4, Michael A Hardigan 5, Cynthia C Steiner 6, Steven J Knapp 5, Doreen Ware 7 8, Beth Shapiro 3 9, Paul Peluso 1, David R Rank 10
Affiliations
- PMID: 33203859
- PMCID: PMC7673114
- DOI: 10.1038/s41597-020-00743-4
Highly accurate long-read HiFi sequencing data for five complex genomes
Ting Hon et al. Sci Data. 2020.
Abstract
The PacBio® HiFi sequencing method yields highly accurate long-read sequencing datasets with read lengths averaging 10-25 kb and accuracies greater than 99.5%. These accurate long reads can be used to improve results for complex applications such as single nucleotide and structural variant detection, genome assembly, assembly of difficult polyploid or highly repetitive genomes, and assembly of metagenomes. Currently, there is a need for sample data sets to both evaluate the benefits of these long accurate reads as well as for development of bioinformatic tools including genome assemblers, variant callers, and haplotyping algorithms. We present deep coverage HiFi datasets for five complex samples including the two inbred model genomes Mus musculus and Zea mays, as well as two complex genomes, octoploid Fragaria × ananassa and the diploid anuran Rana muscosa. Additionally, we release sequence data from a mock metagenome community. The datasets reported here can be used without restriction to develop new algorithms and explore complex genome structure and evolution. Data were generated on the PacBio Sequel II System.
Conflict of interest statement
T.H., K.M., G.Y., Y-C. T., J.W.K., P.S.P. and D.R.R. are employees of Pacific Biosciences of California Inc. a company commercializing DNA sequencing technology. J.M.L. is an employee of Ravel Biotechnology Inc. a company commercializing disease detection from cell-free DNA. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Fig. 1
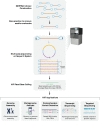
Flowchart of HiFi sequence read generation and downstream applications.
Fig. 2
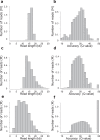
Read length and quality distributions for the three sequenced samples with high quality finished sequence references. M. musculus read length (a) and accuracy (b), Z. mays read length (c) and accuracy (d), and Mock metagenome community ATTC MSA-1003 read length (e) and accuracy (f). All data is mapped to the genomic references (Table 1 and Supplementary Table 1) using minmap2. Accuracies are reported in Phred read quality space (Q value) = −10 × log10(P) where P is the measured error rate.
Fig. 3
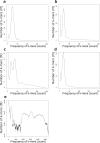
K-mer (length 21) distribution for all HiFi reads for each sequencing dataset. (a) M. musculus (b) Z. mays (c) F. × ananassa (d) R. muscosa (e) Mock metagenome community ATTC MSA-1003.
Similar articles
- Highly accurate long reads are crucial for realizing the potential of biodiversity genomics.
Hotaling S, Wilcox ER, Heckenhauer J, Stewart RJ, Frandsen PB. Hotaling S, et al. BMC Genomics. 2023 Mar 16;24(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09193-9. BMC Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36927511 Free PMC article. - HiFiBGC: an ensemble approach for improved biosynthetic gene cluster detection in PacBio HiFi-read metagenomes.
Yadav A, Subramanian S. Yadav A, et al. BMC Genomics. 2024 Nov 16;25(1):1096. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10950-7. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39550535 Free PMC article. - Comprehensive assessment of 11 de novo HiFi assemblers on complex eukaryotic genomes and metagenomes.
Yu W, Luo H, Yang J, Zhang S, Jiang H, Zhao X, Hui X, Sun D, Li L, Wei XQ, Lonardi S, Pan W. Yu W, et al. Genome Res. 2024 Mar 20;34(2):326-340. doi: 10.1101/gr.278232.123. Genome Res. 2024. PMID: 38428994 Free PMC article. - Tools and Strategies for Long-Read Sequencing and De Novo Assembly of Plant Genomes.
Jung H, Winefield C, Bombarely A, Prentis P, Waterhouse P. Jung H, et al. Trends Plant Sci. 2019 Aug;24(8):700-724. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2019.05.003. Epub 2019 Jun 14. Trends Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 31208890 Review. - Sequencing and Assembly of Polyploid Genomes.
Wang Y, Yu J, Jiang M, Lei W, Zhang X, Tang H. Wang Y, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2545:429-458. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2561-3_23. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36720827 Review.
Cited by
- Experimental and Computational Approaches to Measure Telomere Length: Recent Advances and Future Directions.
Ferrer A, Stephens ZD, Kocher JA. Ferrer A, et al. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2023 Dec;18(6):284-291. doi: 10.1007/s11899-023-00717-4. Epub 2023 Nov 10. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2023. PMID: 37947937 Free PMC article. Review. - Insights into ecological roles of uncultivated bacteria in Katase hot spring sediment from long-read metagenomics.
Kato S, Masuda S, Shibata A, Shirasu K, Ohkuma M. Kato S, et al. Front Microbiol. 2022 Nov 3;13:1045931. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1045931. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36406403 Free PMC article. - BLEND: a fast, memory-efficient and accurate mechanism to find fuzzy seed matches in genome analysis.
Firtina C, Park J, Alser M, Kim JS, Cali DS, Shahroodi T, Ghiasi NM, Singh G, Kanellopoulos K, Alkan C, Mutlu O. Firtina C, et al. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2023 Jan 20;5(1):lqad004. doi: 10.1093/nargab/lqad004. eCollection 2023 Mar. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 36685727 Free PMC article. - Sex differences in the early life stages of the salmon louse Lepeophtheirus salmonis (Copepoda: Caligidae).
Borchel A, Komisarczuk AZ, Nilsen F. Borchel A, et al. PLoS One. 2022 Mar 31;17(3):e0266022. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0266022. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35358250 Free PMC article. - High-throughput telomere length measurement at nucleotide resolution using the PacBio high fidelity sequencing platform.
Tham CY, Poon L, Yan T, Koh JYP, Ramlee MK, Teoh VSI, Zhang S, Cai Y, Hong Z, Lee GS, Liu J, Song HW, Hwang WYK, Teh BT, Tan P, Xu L, Koh AS, Osato M, Li S. Tham CY, et al. Nat Commun. 2023 Jan 17;14(1):281. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-35823-7. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36650155 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2017-51181-26833/United States Department of Agriculture | National Institute of Food and Agriculture (NIFA)/International
- 8062-21000-041/United States Department of Agriculture | Agricultural Research Service (USDA Agricultural Research Service)/International
- IOS-1744001/National Science Foundation (NSF)/International