The Role of Animal Cognition in Human-Wildlife Interactions - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
The Role of Animal Cognition in Human-Wildlife Interactions
Madeleine Goumas et al. Front Psychol. 2020.
Abstract
Humans have a profound effect on the planet's ecosystems, and unprecedented rates of human population growth and urbanization have brought wild animals into increasing contact with people. For many species, appropriate responses toward humans are likely to be critical to survival and reproductive success. Although numerous studies have investigated the impacts of human activity on biodiversity and species distributions, relatively few have examined the effects of humans on the behavioral responses of animals during human-wildlife encounters, and the cognitive processes underpinning those responses. Furthermore, while humans often present a significant threat to animals, the presence or behavior of people may be also associated with benefits, such as food rewards. In scenarios where humans vary in their behavior, wild animals would be expected to benefit from the ability to discriminate between dangerous, neutral and rewarding people. Additionally, individual differences in cognitive and behavioral phenotypes and past experiences with humans may affect animals' ability to exploit human-dominated environments and respond appropriately to human cues. In this review, we examine the cues that wild animals use to modulate their behavioral responses toward humans, such as human facial features and gaze direction. We discuss when wild animals are expected to attend to certain cues, how information is used, and the cognitive mechanisms involved. We consider how the cognitive abilities of wild animals are likely to be under selection by humans and therefore influence population and community composition. We conclude by highlighting the need for long-term studies on free-living, wild animals to fully understand the causes and ecological consequences of variation in responses to human cues. The effects of humans on wildlife behavior are likely to be substantial, and a detailed understanding of these effects is key to implementing effective conservation strategies and managing human-wildlife conflict.
Keywords: animal cognition; behavioral flexibility; categorization; class-level recognition; gaze sensitivity; generalization; human-wildlife interactions; individual recognition.
Copyright © 2020 Goumas, Lee, Boogert, Kelley and Thornton.
Figures
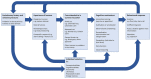
Figure 1
Factors that may affect wild animals’ behavioral responses during interactions with humans.
Similar articles
- Predator or provider? How wild animals respond to mixed messages from humans.
Goumas M, Boogert NJ, Kelley LA, Holding T. Goumas M, et al. R Soc Open Sci. 2022 Mar 16;9(3):211742. doi: 10.1098/rsos.211742. eCollection 2022 Mar. R Soc Open Sci. 2022. PMID: 35308627 Free PMC article. - Implementing social network analysis to understand the socioecology of wildlife co-occurrence and joint interactions with humans in anthropogenic environments.
Balasubramaniam KN, Kaburu SSK, Marty PR, Beisner BA, Bliss-Moreau E, Arlet ME, Ruppert N, Ismail A, Anuar Mohd Sah S, Mohan L, Rattan S, Kodandaramaiah U, McCowan B. Balasubramaniam KN, et al. J Anim Ecol. 2021 Dec;90(12):2819-2833. doi: 10.1111/1365-2656.13584. Epub 2021 Sep 6. J Anim Ecol. 2021. PMID: 34453852 - Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.
Crider K, Williams J, Qi YP, Gutman J, Yeung L, Mai C, Finkelstain J, Mehta S, Pons-Duran C, Menéndez C, Moraleda C, Rogers L, Daniels K, Green P. Crider K, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article. - Animal agency in wildlife conservation and management.
Edelblutte É, Krithivasan R, Hayek MN. Edelblutte É, et al. Conserv Biol. 2023 Feb;37(1):e13853. doi: 10.1111/cobi.13853. Epub 2022 Mar 9. Conserv Biol. 2023. PMID: 35262968 Review. - Impacts of human-induced environmental change in wetlands on aquatic animals.
Sievers M, Hale R, Parris KM, Swearer SE. Sievers M, et al. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2018 Feb;93(1):529-554. doi: 10.1111/brv.12358. Epub 2017 Sep 19. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2018. PMID: 28929570 Review.
Cited by
- Remote islands as natural laboratories: human-food association increases attraction to humans and novelty exploration in a seabird.
Danel S, Rebout N, Belle S, Caro SP, Bonadonna F, Biro D. Danel S, et al. Biol Lett. 2024 Aug;20(8):20240135. doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2024.0135. Epub 2024 Aug 7. Biol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39106948 - The endangered brain: actively preserving ex-situ animal behaviour and cognition will benefit in-situ conservation.
Clark FE, Greggor AL, Montgomery SH, Plotnik JM. Clark FE, et al. R Soc Open Sci. 2023 Aug 30;10(8):230707. doi: 10.1098/rsos.230707. eCollection 2023 Aug. R Soc Open Sci. 2023. PMID: 37650055 Free PMC article. Review. - Sensory integration of danger and safety cues may explain the fear of a quiet coyote.
Smith JE, Carminito C, Hamilton S, Newcomb KL, Randt C, Travenick S. Smith JE, et al. Proc Biol Sci. 2023 Oct 25;290(2009):20231812. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2023.1812. Epub 2023 Oct 25. Proc Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37876200 Free PMC article. - Anti Covid-19 face-masks increases vigilance in Nubian ibex (Capra nubiana).
Yosef R, Hershko M, Zduniak P. Yosef R, et al. Biol Conserv. 2021 Nov;263:109339. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2021.109339. Epub 2021 Sep 21. Biol Conserv. 2021. PMID: 34580549 Free PMC article. - Predator or provider? How wild animals respond to mixed messages from humans.
Goumas M, Boogert NJ, Kelley LA, Holding T. Goumas M, et al. R Soc Open Sci. 2022 Mar 16;9(3):211742. doi: 10.1098/rsos.211742. eCollection 2022 Mar. R Soc Open Sci. 2022. PMID: 35308627 Free PMC article.
References
- Altbäcker V., Csányi V. (1990). The role of eyespots in predator recognition and antipredatory behaviour of the paradise fish, Macropodus opercularis L. Ethology 85, 51–57. 10.1111/j.1439-0310.1990.tb00385.x - DOI
- Ango T. G., Börjeson L., Senbeta F. (2017). Crop raiding by wild mammals in Ethiopia: impacts on the livelihoods of smallholders in an agriculture-forest mosaic landscape. Oryx 51, 527–537. 10.1017/S0030605316000028 - DOI
- Barrett L. P., Stanton L. A., Benson-Amram S. (2019). The cognition of ‘nuisance’ species. Anim. Behav. 147, 167–177. 10.1016/j.anbehav.2018.05.005 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous