Fructus lycii: A Natural Dietary Supplement for Amelioration of Retinal Diseases - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Fructus lycii: A Natural Dietary Supplement for Amelioration of Retinal Diseases
Kumari Neelam et al. Nutrients. 2021.
Abstract
Fructus lycii (F. lycii) is an exotic "berry-type" fruit of the plant Lycium barbarum that is characterized by a complex mixture of bioactive compounds distinguished by their high antioxidant potential. F. lycii is used in traditional Chinese home cooking and in the Chinese Pharmacopeia as an aid to vision and longevity as well as a remedy for diabetes to balance "yin" and "yang" in the body for about two centuries. Although a myriad of bioactive compounds have been isolated from F. lycii, polysaccharides, carotenoids, flavonoids, and phenolics represent the key functional components of F. lycii. F. lycii has been shown to exhibit a wide range of biological activities in experimental settings including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antiapoptotic, and neuroprotective effects. Despite its medicinal role dating back to the eighteenth century in the Far East and robust evidence of beneficial effects on ocular health and retinal diseases originating mainly from studies in animal models, the role of F. lycii in the clinical management of retinal diseases is yet to be established. This article comprehensively reviews the literature germane to F. lycii and retinal diseases with particular emphasis on age-related macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, and retinitis pigmentosa, which are commonly seen in clinical practice.
Keywords: Fructus lycii; age-related macular degeneration; antioxidants; carotenoids; diabetic retinopathy; retinitis pigmentosa.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Figure 1
The fresh (left) and dried (right) berry fruits of Lycium barbarum ‘_Fructus lycii_’.
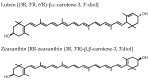
Figure 2
Biochemical structures of the carotenoids lutein and zeaxanthin.
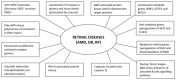
Figure 3
Molecular targets of F. lycii in amelioration of retinal diseases.
Similar articles
- Delay of cone degeneration in retinitis pigmentosa using a 12-month treatment with Lycium barbarum supplement.
Chan HH, Lam HI, Choi KY, Li SZ, Lakshmanan Y, Yu WY, Chang RC, Lai JS, So KF. Chan HH, et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 May 23;236:336-344. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.03.023. Epub 2019 Mar 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30877066 Clinical Trial. - Goji (Lycium barbarum and L. chinense): Phytochemistry, pharmacology and safety in the perspective of traditional uses and recent popularity.
Potterat O. Potterat O. Planta Med. 2010 Jan;76(1):7-19. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1186218. Epub 2009 Oct 20. Planta Med. 2010. PMID: 19844860 Review. - Quantification of zeaxanthin dipalmitate and total carotenoids in Lycium fruits (Fructus Lycii).
Peng Y, Ma C, Li Y, Leung KS, Jiang ZH, Zhao Z. Peng Y, et al. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2005 Dec;60(4):161-4. doi: 10.1007/s11130-005-9550-5. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2005. PMID: 16395626 - [Comparison on effects of Lycii Fructus from different origins on NaIO_3-induced retinal degenerative diseases in mice by multivariate statistical analysis].
Chen X, Guo S, Wang JM, Li J, Ni L, Kang HJ, Qian DW, Duan JA. Chen X, et al. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024 Aug;49(16):4521-4531. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20240414.103. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39307788 Chinese. - Distinct Role of Lycium barbarum L. Polysaccharides in Oxidative Stress-Related Ocular Diseases.
Niu Y, Zhang G, Sun X, He S, Dou G. Niu Y, et al. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Jan 31;16(2):215. doi: 10.3390/ph16020215. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37259363 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- NUTRARET: Effect of 2-Year Nutraceutical Supplementation on Redox Status and Visual Function of Patients With Retinitis Pigmentosa: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial.
Olivares-González L, Salom D, González-García E, Hervás D, Mejía-Chiqui N, Melero M, Velasco S, Muresan BT, Campillo I, Vila-Clérigues N, López-Briz E, Merino-Torres JF, Millán JM, Soriano Del Castillo JM, Rodrigo R. Olivares-González L, et al. Front Nutr. 2022 Mar 21;9:847910. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.847910. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35387197 Free PMC article. - Effects of derivatization and probiotic transformation on the antioxidative activity of fruit polyphenols.
Wang Y, Wang C, Shi J, Zhang Y. Wang Y, et al. Food Chem X. 2024 Aug 26;23:101776. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2024.101776. eCollection 2024 Oct 30. Food Chem X. 2024. PMID: 39280222 Free PMC article. Review. - Network pharmacology-based pharmacological mechanism prediction of Lycii Fructus against postmenopausal osteoporosis.
Wang J, Wang Y, Li L, Cai S, Mao D, Lou H, Zhao J. Wang J, et al. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Dec 1;102(48):e36292. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036292. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 38050297 Free PMC article. - Carotenoid Contents of Lycium barbarum: A Novel QAMS Analyses, Geographical Origins Discriminant Evaluation, and Storage Stability Assessment.
Ren R, Li Y, Chen H, Wang Y, Yang L, Su C, Zhao X, Chen J, Ma X. Ren R, et al. Molecules. 2021 Sep 3;26(17):5374. doi: 10.3390/molecules26175374. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34500806 Free PMC article. - Effect of High-Sucrose Diet on the Occurrence and Progression of Diabetic Retinopathy and Dietary Modification Strategies.
Yang C, Yu Y, An J. Yang C, et al. Nutrients. 2024 May 5;16(9):1393. doi: 10.3390/nu16091393. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38732638 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Stuart G.A., Smith F.P. Chinese Materia Medica. American Presbyterian Mission Press; Shanghai, China: 1991. p. 250.
- Integrated Taxonomic Information System Lycium barbarum L. [(accessed on 29 October 2020)];2019 :22. Taxonomic Serial No: 503599. Available online: https://www.itis.gov.
- Chi Z.S. Chemical constituents of Fructus Lycii and Folium Lycii (I)-Nutrients in Fructus lycii and Folium lycii. Zhong Yao Tong Bao. 1986;11:41. - PubMed
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission . Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China Part I. Chemical Industry Press; Beijing, China: 2015.
- Cao Y.L., Wu P.J. Wolfberry Germplasm Resources in China. China Forestry Publishing House; Beijing, China: 2015.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical