Ionizing Radiation Protein Biomarkers in Normal Tissue and Their Correlation to Radiosensitivity: A Systematic Review - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Ionizing Radiation Protein Biomarkers in Normal Tissue and Their Correlation to Radiosensitivity: A Systematic Review
Prabal Subedi et al. J Pers Med. 2021.
Abstract
Background and objectives: Exposure to ionizing radiation (IR) has increased immensely over the past years, owing to diagnostic and therapeutic reasons. However, certain radiosensitive individuals show toxic enhanced reaction to IR, and it is necessary to specifically protect them from unwanted exposure. Although predicting radiosensitivity is the way forward in the field of personalised medicine, there is limited information on the potential biomarkers. The aim of this systematic review is to identify evidence from a range of literature in order to present the status quo of our knowledge of IR-induced changes in protein expression in normal tissues, which can be correlated to radiosensitivity. Methods: Studies were searched in NCBI Pubmed and in ISI Web of Science databases and field experts were consulted for relevant studies. Primary peer-reviewed studies in English language within the time-frame of 2011 to 2020 were considered. Human non-tumour tissues and human-derived non-tumour model systems that have been exposed to IR were considered if they reported changes in protein levels, which could be correlated to radiosensitivity. At least two reviewers screened the titles, keywords, and abstracts of the studies against the eligibility criteria at the first phase and full texts of potential studies at the second phase. Similarly, at least two reviewers manually extracted the data and accessed the risk of bias (National Toxicology Program/Office for Health Assessment and Translation-NTP/OHAT) for the included studies. Finally, the data were synthesised narratively in accordance to synthesis without meta analyses (SWiM) method. Results: In total, 28 studies were included in this review. Most of the records (16) demonstrated increased residual DNA damage in radiosensitive individuals compared to normo-sensitive individuals based on γH2AX and TP53BP1. Overall, 15 studies included proteins other than DNA repair foci, of which five proteins were selected, Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), Caspase 3, p16INK4A (Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A, CDKN2A), Interleukin-6, and Interleukin-1β, that were connected to radiosensitivity in normal tissue and were reported at least in two independent studies. Conclusions and implication of key findings: A majority of studies used repair foci as a tool to predict radiosensitivity. However, its correlation to outcome parameters such as repair deficient cell lines and patients, as well as an association to moderate and severe clinical radiation reactions, still remain contradictory. When IR-induced proteins reported in at least two studies were considered, a protein network was discovered, which provides a direction for further studies to elucidate the mechanisms of radiosensitivity. Although the identification of only a few of the commonly reported proteins might raise a concern, this could be because (i) our eligibility criteria were strict and (ii) radiosensitivity is influenced by multiple factors. Registration: PROSPERO (CRD42020220064).
Keywords: biomarker; ionizing radiation; normal tissue; proteomics; radiosensitivity; radiotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
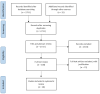
Figure 1
PRISMA flowchart that displays the number of records identified (2733), the number of records screened for a full-text review (100), and the number of records included in the review (28).
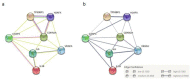
Figure 2
Protein-protein interaction enrichment network generated in STRING 11.0 using proteins identified in at least two studies: p16 (CDKN2A), VEGFA, IL6, IL-1β, CASP3, TP53BP1, and γH2AX: (a) The lines represent protein–protein association where pink lines are known experimentally determined interactions, blue from curated databases, green are from text-mining, and black represents co-expression; (b) The thickness of the edges display the confidence in interaction: medium (0.400), high (0.700), and highest (0.900) in this network.
Similar articles
- Ionizing Radiation Protein Biomarkers in Normal Tissue and Their Correlation to Radiosensitivity: Protocol for a Systematic Review.
Dietz A, Gomolka M, Moertl S, Subedi P. Dietz A, et al. J Pers Med. 2020 Dec 22;11(1):3. doi: 10.3390/jpm11010003. J Pers Med. 2020. PMID: 33375047 Free PMC article. Review. - Human epidemiological evidence about the associations between exposure to organochlorine chemicals and endometriosis: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
Cano-Sancho G, Ploteau S, Matta K, Adoamnei E, Louis GB, Mendiola J, Darai E, Squifflet J, Le Bizec B, Antignac JP. Cano-Sancho G, et al. Environ Int. 2019 Feb;123:209-223. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2018.11.065. Epub 2018 Dec 6. Environ Int. 2019. PMID: 30530163 - Evaluation of different biomarkers to predict individual radiosensitivity in an inter-laboratory comparison--lessons for future studies.
Greve B, Bölling T, Amler S, Rössler U, Gomolka M, Mayer C, Popanda O, Dreffke K, Rickinger A, Fritz E, Eckardt-Schupp F, Sauerland C, Braselmann H, Sauter W, Illig T, Riesenbeck D, Könemann S, Willich N, Mörtl S, Eich HT, Schmezer P. Greve B, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47185. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047185. Epub 2012 Oct 23. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23110060 Free PMC article. - The Effectiveness of Integrated Care Pathways for Adults and Children in Health Care Settings: A Systematic Review.
Allen D, Gillen E, Rixson L. Allen D, et al. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009;7(3):80-129. doi: 10.11124/01938924-200907030-00001. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009. PMID: 27820426 - Clinical Biomarkers of Tumour Radiosensitivity and Predicting Benefit from Radiotherapy: A Systematic Review.
Bleaney CW, Abdelaal H, Reardon M, Anandadas C, Hoskin P, Choudhury A, Forker L. Bleaney CW, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2024 May 20;16(10):1942. doi: 10.3390/cancers16101942. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38792019 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Development of an Ex Vivo Functional Assay for Prediction of Irradiation Related Toxicity in Healthy Oral Mucosa Tissue.
Pachler KS, Lauwers I, Verkaik NS, Rovituso M, van der Wal E, Mast H, Jonker BP, Sewnaik A, Hardillo JA, Keereweer S, Monserez D, Kremer B, Koppes S, van den Bosch TPP, Verduijn GM, Petit S, Sørensen BS, van Gent DC, Capala ME. Pachler KS, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 28;25(13):7157. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137157. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000262 Free PMC article. - Identification of radiation responsive RBC membrane associated proteins (RMAPs) in whole-body γ-irradiated New Zealand white rabbits.
Purkayastha J, Grover P, Mukherjee P, Kumar K, Chandna S. Purkayastha J, et al. Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2023 Jan 18;37:e00783. doi: 10.1016/j.btre.2023.e00783. eCollection 2023 Mar. Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2023. PMID: 36718137 Free PMC article. - ATX-101, a Peptide Targeting PCNA, Has Antitumor Efficacy Alone or in Combination with Radiotherapy in Murine Models of Human Glioblastoma.
Gravina GL, Colapietro A, Mancini A, Rossetti A, Martellucci S, Ventura L, Di Franco M, Marampon F, Mattei V, Biordi LA, Otterlei M, Festuccia C. Gravina GL, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 7;14(2):289. doi: 10.3390/cancers14020289. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35053455 Free PMC article. - Long noncoding RNA BBOX1-AS1 increased radiotherapy sensitivity in colorectal cancer by stabilizing and activating PFK1.
Wang Q, Li XF, Zhou YH, Qin XH, Wang LH, Xiao MQ, Cao K, Ma JK, Huang CH. Wang Q, et al. Transl Oncol. 2023 Oct;36:101751. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2023.101751. Epub 2023 Aug 4. Transl Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37544035 Free PMC article. - Impact of dietary ingredients on radioprotection and radiosensitization: a comprehensive review.
Islam MM, Sultana N, Liu C, Mao A, Katsube T, Wang B. Islam MM, et al. Ann Med. 2024 Dec;56(1):2396558. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2396558. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Ann Med. 2024. PMID: 39320122 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Global Cancer Observatory. [(accessed on 11 December 2020)]; Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/39-All-cancers-fact-sh....
- Fazel R., Gerber T.C., Balter S., Brenner D.J., Carr J.J., Cerqueira M.D., Chen J., Einstein A.J., Krumholz H.M., Mahesh M., et al. Approaches to enhancing radiation safety in cardiovascular imaging: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2014;130:1730–1748. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000048. - DOI - PubMed
- Gomolka M., Blyth B., Bourguignon M., Badie C., Schmitz A., Talbot C., Hoeschen C., Salomaa S. Potential screening assays for individual radiation sensitivity and susceptibility and their current validation state. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2019;96:280–296. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2019.1642544. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous