Effects of l-Theanine on Cognitive Function in Middle-Aged and Older Subjects: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Study - PubMed (original) (raw)
Randomized Controlled Trial
. 2021 Apr;24(4):333-341.
doi: 10.1089/jmf.2020.4803. Epub 2021 Mar 22.
Affiliations
- PMID: 33751906
- PMCID: PMC8080935
- DOI: 10.1089/jmf.2020.4803
Randomized Controlled Trial
Effects of l-Theanine on Cognitive Function in Middle-Aged and Older Subjects: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Study
Yoshitake Baba et al. J Med Food. 2021 Apr.
Abstract
l-theanine (_γ_-glutamylethylamide), an amino acid in green tea, has been shown to affect brain functions by relieving stress disorders, improving mood, and maintaining normal sleep. However, the cognitive functions for which theanine is effective are unclear. This study aimed to clarify which cognitive functions are positively affected by intake of l-theanine. A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study was conducted. The subjects were Japanese men and women aged 50-69 years. Mini Mental State Examination-Japanese version score was 24 or higher. Cognitrax was used as a test battery for cognitive function. Evaluations were performed before the intervention, after a single dose of l-theanine, and after 12 weeks of regular intake. The single dose of l-theanine reduced the reaction time to attention tasks (Stroop test, Part 1), and it increased the number of correct answers and decreased the number of omission errors in working memory tasks (4-Part continuous performance test, Part 4). In conclusion, our study indicated that l-theanine may contribute to improving attention, thus enhancing working memory and executive functions. Clinical Trial No.: UMIN000033812.
Keywords: Cognitrax; attention; brain function; executive function; green tea amino acid; working memory.
Conflict of interest statement
ITO EN, Ltd. covered the testing costs and provided the test food as the study sponsor. Huma R&D Corp., Contract Research Organization, conducted subject recruitment, selection, allocation, observation, and data collection. Kureha Special Laboratory Co., Ltd. conducted statistical analysis. T.K. was the principal investigator for this study and was contracted by Huma R&D to conduct the study. The study was performed by a third party. The remaining authors report that no competing financial interests exist.
Figures
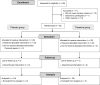
FIG. 1.
Study flow diagram.
Similar articles
- A combination of green tea extract and l-theanine improves memory and attention in subjects with mild cognitive impairment: a double-blind placebo-controlled study.
Park SK, Jung IC, Lee WK, Lee YS, Park HK, Go HJ, Kim K, Lim NK, Hong JT, Ly SY, Rho SS. Park SK, et al. J Med Food. 2011 Apr;14(4):334-43. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2009.1374. Epub 2011 Feb 8. J Med Food. 2011. PMID: 21303262 Clinical Trial. - Effect of Green Tea Phytochemicals on Mood and Cognition.
Dietz C, Dekker M. Dietz C, et al. Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(19):2876-2905. doi: 10.2174/1381612823666170105151800. Curr Pharm Des. 2017. PMID: 28056735 Review. - Effects of chronic l-theanine administration in patients with major depressive disorder: an open-label study.
Hidese S, Ota M, Wakabayashi C, Noda T, Ozawa H, Okubo T, Kunugi H. Hidese S, et al. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2017 Apr;29(2):72-79. doi: 10.1017/neu.2016.33. Epub 2016 Jul 11. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2017. PMID: 27396868 Clinical Trial. - Acute effects of tea constituents L-theanine, caffeine, and epigallocatechin gallate on cognitive function and mood: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Camfield DA, Stough C, Farrimond J, Scholey AB. Camfield DA, et al. Nutr Rev. 2014 Aug;72(8):507-22. doi: 10.1111/nure.12120. Epub 2014 Jun 19. Nutr Rev. 2014. PMID: 24946991 Review.
Cited by
- The role of dietary antioxidants in type 2 diabetes and neurodegenerative disorders: An assessment of the benefit profile.
Fatima MT, Bhat AA, Nisar S, Fakhro KA, Al-Shabeeb Akil AS. Fatima MT, et al. Heliyon. 2022 Dec 30;9(1):e12698. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12698. eCollection 2023 Jan. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36632095 Free PMC article. Review. - Genus Ribes: Ribes aureum, Ribes pauciflorum, Ribes triste, and _Ribes dikuscha_-Comparative Mass Spectrometric Study of Polyphenolic Composition and Other Bioactive Constituents.
Razgonova MP, Nawaz MA, Sabitov AS, Golokhvast KS. Razgonova MP, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 19;25(18):10085. doi: 10.3390/ijms251810085. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337572 Free PMC article. - Effects of green tea and roasted green tea on human responses.
Kurosaka C, Tagata C, Nakagawa S, Kobayashi M, Miyake S. Kurosaka C, et al. Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 13;14(1):8588. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-59383-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38615105 Free PMC article. - Tolerability of glutamine supplementation in older adults: a double-blind placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial.
Nóbrega TCM, Silva MARCPD, Rampani EM, Curi R, Bazotte RB. Nóbrega TCM, et al. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2024 May 20;57:e13468. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2024e13468. eCollection 2024. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2024. PMID: 38808890 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Matcha Does Not Affect Electroencephalography during Sleep but May Enhance Mental Well-Being: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial.
Baba Y, Takihara T, Okamura N. Baba Y, et al. Nutrients. 2024 Aug 31;16(17):2907. doi: 10.3390/nu16172907. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39275223 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
- Sakato Y: Studies on the chemical constituents of tea; III. A new amide theanine. Nippon Nogeikagaku Kaishi (Japanese) 1949;23:262–267
- Casimir J, Jadot J, Renard M: Separation and characterization of N-ethyl-gamma-glutamine from Xerocomus badius. Biochim Biophys Acta 1960;39:462–468 - PubMed
- Goto T, Yoshida Y, Amano I, Horie H: Chemical composition of commercially available Japanese green tea. Foods Food Ingredients J Jpn 1996;170:46–51
- Yoneda Y, Kuramoto N, Kawada K: The role of glutamine in neurogenesis promoted by the green tea amino acid theanine in neural progenitor cells for brain health. Neurochem Int 2019;129:104505. - PubMed
- Tamano H, Fukura K, Suzuki M, Sakamoto K, Yokogoshi H, Takeda A: Preventive effect of theanine intake on stress-induced impairments of hippocamapal long-term potentiation and recognition memory. Brain Res Bull 2013;95:1–6 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources