Evaluation of Probiotic Properties of Pediococcus acidilactici M76 Producing Functional Exopolysaccharides and Its Lactic Acid Fermentation of Black Raspberry Extract - PubMed (original) (raw)
Evaluation of Probiotic Properties of Pediococcus acidilactici M76 Producing Functional Exopolysaccharides and Its Lactic Acid Fermentation of Black Raspberry Extract
Young-Ran Song et al. Microorganisms. 2021.
Abstract
This study aimed to determine the probiotic potential of Pediococcus acidilactici M76 (PA-M76) for lactic acid fermentation of black raspberry extract (BRE). PA-M76 showed outstanding probiotic properties with high tolerance in acidic GIT environments, broad antimicrobial activity, and high adhesion capability in the intestinal tract of Caenorhabditis elegans. PA-M76 treatment resulted in significant increases of pro-inflammatory cytokine mRNA expression in macrophages, indicating that PA-M76 elicits an effective immune response. When PA-M76 was used for lactic acid fermentation of BRE, an EPS yield of 1.62 g/L was obtained under optimal conditions. Lactic acid fermentation of BRE by PA-M76 did not significantly affect the total anthocyanin and flavonoid content, except for a significant increase in total polyphenol content compared to non-fermented BRE (NfBRE). However, fBRE exhibited increased DPPH radical scavenging activity, linoleic acid peroxidation inhibition rate, and ABTS scavenging activity of fBRE compared to NfBRE. Among the 28 compounds identified in the GC-MS analysis, esters were present as the major groups. The total concentration of volatile compounds was higher in fBRE than that in NfBRE. However, the undesirable flavor of terpenes decreased. PA-M76 might be useful for preparing functionally enhanced fermented beverages with a higher antioxidant activity of EPS and enhanced flavors.
Keywords: Pediococcus acidilactici; antioxidant; black raspberry; exopolysaccharide; flavors; lactic acid fermentation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
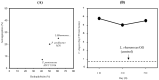
Figure 1
(A) Correlation of the hydrophobicity and coaggregation results of the lactic acid bacteria strains. (B) Adhesion activity of Pediococcus acidilactici M76 in the intestine of Caenorhabditis elegans.
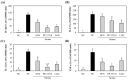
Figure 2
Effect of Pediococcus acidilactici M76 on mRNA expression levels of macrophage-activating factors, such as IL-1β (A), IL-6 (B), IL-12 (C), and TNF-α (D). RAW 264.7 cells were treated with different lactic acid bacteria (LAB) strain fractions for 24 h. Cells treated with media alone were used as the negative control (NC), cells treated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 1 μg/mL) were used as the positive control (PC). PA-M76, Pediococcus acidilactici M76; PP-33316, Pediococcus pentosaceus (ATCC 33316); LGG, Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (ATCC 53103). a–e Means with different letters are significantly different (p < 0.05).
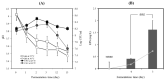
Figure 3
(A) Changes in pH, viable cell count, and (B) exopolysaccharide production of the fermented black raspberry extract by Pediococcus acidilactici M76. Cultivation was done for 15 days. log CFU/mL at 25 °C: (■), log CFU/mL at 30 °C: (●), pH at 25 °C: (□), pH at 30 °C: (○).
Figure 4
Changes in antioxidant activity of the fermented black raspberry extract by Pediococcus acidilactici M76. (A) DPPH radical scavenge activity (%). (B) Lipid peroxidation inhibitory activity (%). (C) Radical cation ABTS+ scavenging activity. NfBRE: (□), fBRE: (■). a,b Means with different letters are significantly different (p < 0.05).
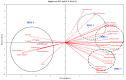
Figure 5
Biplot of the principal component analysis of volatile compounds from fermented black raspberry extract beverage inoculated with Pediococcus acidilactici M76.
Similar articles
- Exopolysaccharide produced by Pediococcus acidilactici M76 isolated from the Korean traditional rice wine, makgeolli.
Song YR, Jeong DY, Cha YS, Baik SH. Song YR, et al. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013 May;23(5):681-8. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1301.01032. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23648859 - Characterization of Lactic Acid Bacterium Exopolysaccharide, Biological, and Nutritional Evaluation of Probiotic Formulated Fermented Coconut Beverage.
Adebayo-Tayo BC, Ogundele BR, Ajani OA, Olaniyi OA. Adebayo-Tayo BC, et al. Int J Food Sci. 2024 Sep 2;2024:8923217. doi: 10.1155/2024/8923217. eCollection 2024. Int J Food Sci. 2024. PMID: 39257841 Free PMC article. Review. - Lipid-lowering effects of Pediococcus acidilactici M76 isolated from Korean traditional makgeolli in high fat diet-induced obese mice.
Moon YJ, Baik SH, Cha YS. Moon YJ, et al. Nutrients. 2014 Mar 7;6(3):1016-28. doi: 10.3390/nu6031016. Nutrients. 2014. PMID: 24609135 Free PMC article. - Effect of Pediococcus acidilactici and mango seed polyphenols on the fermentative profile of the indigestible fraction of yam bean.
Durán-Castañeda AC, Bueno-Durán AY, Girón-Pérez MI, Ragazzo-Sánchez JA, Sánchez-Burgos JA, Sáyago-Ayerdi SG, Zamora-Gasga VM. Durán-Castañeda AC, et al. Food Res Int. 2024 Feb;178:113970. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2024.113970. Epub 2024 Jan 11. Food Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38309916 - Lactic Acid Fermentation of Cactus Cladodes (Opuntia ficus-indica L.) Generates Flavonoid Derivatives with Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties.
Filannino P, Cavoski I, Thlien N, Vincentini O, De Angelis M, Silano M, Gobbetti M, Di Cagno R. Filannino P, et al. PLoS One. 2016 Mar 29;11(3):e0152575. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152575. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27023062 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Genome sequences and functional analysis of Levilactobacillus brevis LSF9-1 and Pediococcus acidilactici LSF1-1 from fermented fish cake (Som-fak) with gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) production.
Phuengjayaem S, Pakdeeto A, Kingkaew E, Tunvongvinis T, Somphong A, Tanasupawat S. Phuengjayaem S, et al. Funct Integr Genomics. 2023 May 12;23(2):158. doi: 10.1007/s10142-023-01085-1. Funct Integr Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37171680 - In-vitro evaluation of the probiotic potential and the fermentation profile of Pediococcus and Enterococcus strains isolated from Moroccan camel milk.
Moussaid S, El Alaoui MA, Ounine K, Benali A, Bouhlal O, Rkhaila A, Hami H, El Maadoudi EH. Moussaid S, et al. Arch Microbiol. 2023 Mar 27;205(4):144. doi: 10.1007/s00203-023-03489-w. Arch Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36967406 - Probiotics Mechanism of Action on Immune Cells and Beneficial Effects on Human Health.
Mazziotta C, Tognon M, Martini F, Torreggiani E, Rotondo JC. Mazziotta C, et al. Cells. 2023 Jan 2;12(1):184. doi: 10.3390/cells12010184. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36611977 Free PMC article. Review. - Assessment of probiotic properties of lactic acid bacteria isolated from an artisanal Colombian cheese.
Roldán-Pérez S, Gómez Rodríguez SL, Sepúlveda-Valencia JU, Ruiz Villadiego OS, Márquez Fernández ME, Montoya Campuzano OI, Durango-Zuleta MM. Roldán-Pérez S, et al. Heliyon. 2023 Nov 3;9(11):e21558. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21558. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38027952 Free PMC article. - Special Issue "Beneficial and Detrimental Microorganisms Occurring in Fermented Foods": Editorial.
Fusco V, Abriouel H, de Souza EL. Fusco V, et al. Microorganisms. 2023 Feb 24;11(3):565. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11030565. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 36985139 Free PMC article.
References
- Ghoson M.D., Marwa O.E., Waill A.E. Contributions of exopolysaccharides from lactic acid bacteria as biotechnological tools in food, pharmaceutical, and medical applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021;173:79–89. - PubMed
- Wisselink H.W., Weusthuis R.A., Eggink G., Hugenholtz J., Grobben G.J. Mannitol production by lactic acid bacteria: A review. Int. Dairy J. 2002;12:151–161. doi: 10.1016/S0958-6946(01)00153-4. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous