Targeted Delivery of Drugs and Genes Using Polymer Nanocarriers for Cancer Therapy - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Targeted Delivery of Drugs and Genes Using Polymer Nanocarriers for Cancer Therapy
Wentao Xia et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2021.
Abstract
Cancer is one of the primary causes of worldwide human deaths. Most cancer patients receive chemotherapy and radiotherapy, but these treatments are usually only partially efficacious and lead to a variety of serious side effects. Therefore, it is necessary to develop new therapeutic strategies. The emergence of nanotechnology has had a profound impact on general clinical treatment. The application of nanotechnology has facilitated the development of nano-drug delivery systems (NDDSs) that are highly tumor selective and allow for the slow release of active anticancer drugs. In recent years, vehicles such as liposomes, dendrimers and polymer nanomaterials have been considered promising carriers for tumor-specific drug delivery, reducing toxicity and improving biocompatibility. Among them, polymer nanoparticles (NPs) are one of the most innovative methods of non-invasive drug delivery. Here, we review the application of polymer NPs in drug delivery, gene therapy, and early diagnostics for cancer therapy.
Keywords: cancer therapy; drug delivery; polymer nanocarriers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
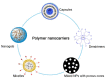
Figure 1
The different types of polymer nanocarriers-based drug delivery for cancer therapeutics [136,137].
Figure 2
The self-assembled polymeric nanocarrier-mediated co-delivery of metformin and doxorubicin for melanoma therapy Reproduced from Song et al. [111].
Similar articles
- Advanced targeted therapies in cancer: Drug nanocarriers, the future of chemotherapy.
Pérez-Herrero E, Fernández-Medarde A. Pérez-Herrero E, et al. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015 Jun;93:52-79. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2015.03.018. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015. PMID: 25813885 Review. - Innovative nano-carriers in anticancer drug delivery-a comprehensive review.
Dong P, Rakesh KP, Manukumar HM, Mohammed YHE, Karthik CS, Sumathi S, Mallu P, Qin HL. Dong P, et al. Bioorg Chem. 2019 Apr;85:325-336. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.01.019. Epub 2019 Jan 10. Bioorg Chem. 2019. PMID: 30658232 Review. - Nanocarriers for cancer-targeted drug delivery.
Kumari P, Ghosh B, Biswas S. Kumari P, et al. J Drug Target. 2016;24(3):179-91. doi: 10.3109/1061186X.2015.1051049. Epub 2015 Jun 10. J Drug Target. 2016. PMID: 26061298 Review. - Glyco-nanoparticles: New drug delivery systems in cancer therapy.
Khan H, Mirzaei HR, Amiri A, Kupeli Akkol E, Ashhad Halimi SM, Mirzaei H. Khan H, et al. Semin Cancer Biol. 2021 Feb;69:24-42. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.12.004. Epub 2019 Dec 20. Semin Cancer Biol. 2021. PMID: 31870939 Review. - Recent progress in nanotechnology for cancer therapy.
Tang MF, Lei L, Guo SR, Huang WL. Tang MF, et al. Chin J Cancer. 2010 Sep;29(9):775-80. doi: 10.5732/cjc.010.10075. Chin J Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20800018 Review.
Cited by
- Nanoliposomes in Cancer Therapy: Marketed Products and Current Clinical Trials.
Taléns-Visconti R, Díez-Sales O, de Julián-Ortiz JV, Nácher A. Taléns-Visconti R, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 12;23(8):4249. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084249. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35457065 Free PMC article. Review. - Microfluidics for nano-drug delivery systems: From fundamentals to industrialization.
Zhang H, Yang J, Sun R, Han S, Yang Z, Teng L. Zhang H, et al. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023 Aug;13(8):3277-3299. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.01.018. Epub 2023 Jan 26. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023. PMID: 37655333 Free PMC article. Review. - Tumor-specific polycistronic miRNA delivered by engineered exosomes for the treatment of glioblastoma.
McDonald MF, Hossain A, Momin EN, Hasan I, Singh S, Adachi S, Gumin J, Ledbetter D, Yang J, Long L, Daou M, Gopakumar S, Phillips LM, Parker Kerrigan B, Lang FF. McDonald MF, et al. Neuro Oncol. 2024 Feb 2;26(2):236-250. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noad199. Neuro Oncol. 2024. PMID: 37847405 Free PMC article. - Dual-Action Therapeutics: DNA Alkylation and Antimicrobial Peptides for Cancer Therapy.
Andrés CMC, Pérez de la Lastra JM, Munguira EB, Andrés Juan C, Pérez-Lebeña E. Andrés CMC, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2024 Sep 10;16(18):3123. doi: 10.3390/cancers16183123. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39335095 Free PMC article. Review. - Nanocarriers in Tuberculosis Treatment: Challenges and Delivery Strategies.
Kumar M, Virmani T, Kumar G, Deshmukh R, Sharma A, Duarte S, Brandão P, Fonte P. Kumar M, et al. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Sep 26;16(10):1360. doi: 10.3390/ph16101360. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895831 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- grant no. 31800992 to S.Y.C., 81800512 to W.X.Z., 92057112 and 31771298 to C.L./National Natural Science Foundation of China
- grant no. BK20180554 to S.Y.C., BK20180577 to W.X.Z./Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources