Functional and Clinical Significance of Dysregulated microRNAs in Liver Cancer - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Functional and Clinical Significance of Dysregulated microRNAs in Liver Cancer
Po-Shuan Huang et al. Cancers (Basel). 2021.
Abstract
Liver cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related mortality in the world. This mainly reflects the lack of early diagnosis tools and effective treatment methods. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of non-transcribed RNAs, some of which play important regulatory roles in liver cancer. Here, we discuss microRNAs with key impacts on liver cancer, such as miR-122, miR-21, miR-214, and miR-199. These microRNAs participate in various physiological regulatory pathways of liver cancer cells, and their modulation can have non-negligible effects in the treatment of liver cancer. We discuss whether these microRNAs can be used for better clinical diagnosis and/or drug development. With the advent of novel technologies, fast, inexpensive, and non-invasive RNA-based biomarker research has become a new mainstream approach. However, the clinical application of microRNA-based markers has been limited by the high sequence similarity among them and the potential for off-target problems. Therefore, researchers particularly value microRNAs that are specific to or have special functions in liver cancer. These include miR-122, which is specifically expressed in the liver, and miR-34, which is necessary for the replication of the hepatitis C virus in liver cancer. Clinical treatment drugs have been developed based on miR-34 and miR-122 (MRX34 and Miravirsen, respectively), but their side effects have not yet been overcome. Future research is needed to address these weaknesses and establish a feasible microRNA-based treatment strategy for liver cancer.
Keywords: clinical; liver cancer; microRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
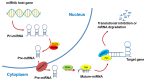
Figure 1
The biosynthesis and action mechanisms of microRNA.
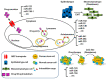
Figure 2
Mechanisms of action of the microRNAs involved in drug resistance of HCC cells.
Figure 3
Typical techniques for detecting miRNAs.
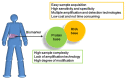
Figure 4
Advantages of RNA as biomarkers in clinical testing.
Similar articles
- Transcriptomic Analysis of Chronic Hepatitis B and C and Liver Cancer Reveals MicroRNA-Mediated Control of Cholesterol Synthesis Programs.
Selitsky SR, Dinh TA, Toth CL, Kurtz CL, Honda M, Struck BR, Kaneko S, Vickers KC, Lemon SM, Sethupathy P. Selitsky SR, et al. mBio. 2015 Dec 8;6(6):e01500-15. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01500-15. mBio. 2015. PMID: 26646011 Free PMC article. - Dysregulated microRNAs in Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Potential as Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets.
Xu J, An P, Winkler CA, Yu Y. Xu J, et al. Front Oncol. 2020 Jul 28;10:1271. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01271. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32850386 Free PMC article. Review. - Long-term safety and efficacy of microRNA-targeted therapy in chronic hepatitis C patients.
van der Ree MH, van der Meer AJ, de Bruijne J, Maan R, van Vliet A, Welzel TM, Zeuzem S, Lawitz EJ, Rodriguez-Torres M, Kupcova V, Wiercinska-Drapalo A, Hodges MR, Janssen HL, Reesink HW. van der Ree MH, et al. Antiviral Res. 2014 Nov;111:53-9. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2014.08.015. Epub 2014 Sep 8. Antiviral Res. 2014. PMID: 25218783 Clinical Trial. - Positive Regulation of Hepatitis E Virus Replication by MicroRNA-122.
Haldipur B, Bhukya PL, Arankalle V, Lole K. Haldipur B, et al. J Virol. 2018 May 14;92(11):e01999-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01999-17. Print 2018 Jun 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29540601 Free PMC article. - Roadmap of miR-122-related clinical application from bench to bedside.
Qiu Z, Dai Y. Qiu Z, et al. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2014 Mar;23(3):347-55. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2014.867327. Epub 2013 Dec 20. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2014. PMID: 24354366 Review.
Cited by
- Evaluation and Application of Drug Resistance by Biomarkers in the Clinical Treatment of Liver Cancer.
Huang PS, Wang LY, Wang YW, Tsai MM, Lin TK, Liao CJ, Yeh CT, Lin KH. Huang PS, et al. Cells. 2023 Mar 10;12(6):869. doi: 10.3390/cells12060869. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36980210 Free PMC article. Review. - Trials and Tribulations of MicroRNA Therapeutics.
Seyhan AA. Seyhan AA. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 25;25(3):1469. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031469. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338746 Free PMC article. Review. - Prospective therapeutics for intestinal and hepatic fibrosis.
Li X, Yu M, Zhao Q, Yu Y. Li X, et al. Bioeng Transl Med. 2023 Aug 2;8(6):e10579. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10579. eCollection 2023 Nov. Bioeng Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 38023697 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources