Orthostatic Symptoms and Reductions in Cerebral Blood Flow in Long-Haul COVID-19 Patients: Similarities with Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome - PubMed (original) (raw)
Orthostatic Symptoms and Reductions in Cerebral Blood Flow in Long-Haul COVID-19 Patients: Similarities with Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
C Linda M C van Campen et al. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021.
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Symptoms and hemodynamic findings during orthostatic stress have been reported in both long-haul COVID-19 and myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS), but little work has directly compared patients from these two groups. To investigate the overlap in these clinical phenotypes, we compared orthostatic symptoms in daily life and during head-up tilt, heart rate and blood pressure responses to tilt, and reductions in cerebral blood flow in response to orthostatic stress in long-haul COVID-19 patients, ME/CFS controls, and healthy controls. Materials and Methods: We compared 10 consecutive long-haul COVID-19 cases with 20 age- and gender-matched ME/CFS controls with postural tachycardia syndrome (POTS) during head-up tilt, 20 age- and gender-matched ME/CFS controls with a normal heart rate and blood pressure response to head-up tilt, and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls. Identical symptom questionnaires and tilt test procedures were used for all groups, including measurement of cerebral blood flow and cardiac index during the orthostatic stress. Results: There were no significant differences in ME/CFS symptom prevalence between the long-haul COVID-19 patients and the ME/CFS patients. All long-haul COVID-19 patients developed POTS during tilt. Cerebral blood flow and cardiac index were more significantly reduced in the three patient groups compared with the healthy controls. Cardiac index reduction was not different between the three patient groups. The cerebral blood flow reduction was larger in the long-haul COVID-19 patients compared with the ME/CFS patients with a normal heart rate and blood pressure response. Conclusions: The symptoms of long-haul COVID-19 are similar to those of ME/CFS patients, as is the response to tilt testing. Cerebral blood flow and cardiac index reductions during tilt were more severely impaired than in many patients with ME/CFS. The finding of early-onset orthostatic intolerance symptoms, and the high pre-illness physical activity level of the long-haul COVID-19 patients, makes it unlikely that POTS in this group is due to deconditioning. These data suggest that similar to SARS-CoV-1, SARS-CoV-2 infection acts as a trigger for the development of ME/CFS.
Keywords: cerebral blood flow (CBF); chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS); long-haul COVID-19; myalgic encephalomyelitis (ME); orthostatic intolerance; postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS); tilt testing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
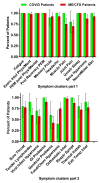
Figure 1
Number of positive symptom clusters derived from ME/CFS/Institute of Medicine criteria in the long-haul COVID-19 patients and all ME/CFS patient. Legend Figure 1 ME/CFS: myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome; Exerc: exercise; Intol: intolerance: Phys: physical; Ment: mental; PEM: post-exertional malaise; Prol: prolonged; Probl: problems; Unrefr: unrefreshing; Sens: sensory; Hypersens: hypersensitivity; Abn: abnormality; Sympt: symptoms: Infect: infection; GI: gastro-intestinal; GenitoUr: genito-urogenital; Respir: respiratory; Instab: instability; Extr: extreme; Temp: temperature.
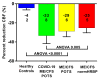
Figure 2
Percent reduction in cerebral blood flow (end-tilt minus supine/supine × 100%) in the long-haul COVID-19 patients, ME/CFS patients with POTS, ME/CFS patients with a normal heart rate and blood pressure response, and healthy controls. Legend Figure 2 CBF: cerebral blood flow; ME/CFS: myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome; BP: blood pressure; HR: heart rate; POTS: postural orthostatic intolerance syndrome.
Figure 3
Mean number of positive response to 15 questions, obtained directly after tilting to the upright position, in long-haul COVID-19 patients, ME/CFS patients with POTS, ME/CFS patients with a normal heart rate and blood pressure response, and healthy controls. Legend Figure 3 ME/CFS: myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome.
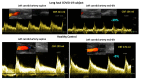
Figure 4
Example of cerebral blood flow images of the left carotid artery supine (left side) and end-tilt standing (right side) of a long-haul COVID-19 subject (upper panel) and a healthy control (lower panel). Legend Figure 4: CBF: cerebral blood flow.
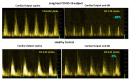
Figure 5
Example of cardiac output images supine (left side) and end-tilt standing (right side) of a long-haul COVID-19 subject (upper panel) and a healthy control (lower panel). Legend Figure 5: CO: cardiac output.
Similar articles
- Cerebral blood flow remains reduced after tilt testing in myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome patients.
van Campen CLMC, Rowe PC, Visser FC. van Campen CLMC, et al. Clin Neurophysiol Pract. 2021 Sep 23;6:245-255. doi: 10.1016/j.cnp.2021.09.001. eCollection 2021. Clin Neurophysiol Pract. 2021. PMID: 34667909 Free PMC article. - Orthostatic Intolerance in Long-Haul COVID after SARS-CoV-2: A Case-Control Comparison with Post-EBV and Insidious-Onset Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Patients.
van Campen CLMC, Visser FC. van Campen CLMC, et al. Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Oct 17;10(10):2058. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10102058. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36292504 Free PMC article. - Deconditioning does not explain orthostatic intolerance in ME/CFS (myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome).
van Campen CLMC, Rowe PC, Visser FC. van Campen CLMC, et al. J Transl Med. 2021 May 4;19(1):193. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-02819-0. J Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33947430 Free PMC article. - The persistence of myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) after SARS-CoV-2 infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Dehlia A, Guthridge MA. Dehlia A, et al. J Infect. 2024 Dec;89(6):106297. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106297. Epub 2024 Sep 29. J Infect. 2024. PMID: 39353473 - Long COVID and Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS)-A Systemic Review and Comparison of Clinical Presentation and Symptomatology.
Wong TL, Weitzer DJ. Wong TL, et al. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021 Apr 26;57(5):418. doi: 10.3390/medicina57050418. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021. PMID: 33925784 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Editorial: Brain, nutrients, and behavior in orthostatic intolerance.
Yamada K. Yamada K. Front Hum Neurosci. 2023 Aug 3;17:1253139. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2023.1253139. eCollection 2023. Front Hum Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37600558 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Cerebral Blood Flow in Orthostatic Intolerance.
Khan MS, Miller AJ, Ejaz A, Molinger J, Goyal P, MacLeod DB, Swavely A, Wilson E, Pergola M, Tandri H, Mills CF, Raj SR, Fudim M. Khan MS, et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2025 Feb 4;14(3):e036752. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.124.036752. Epub 2025 Feb 3. J Am Heart Assoc. 2025. PMID: 39895557 Free PMC article. Review. - Dyspnea in Post-COVID Syndrome following Mild Acute COVID-19 Infections: Potential Causes and Consequences for a Therapeutic Approach.
Wirth KJ, Scheibenbogen C. Wirth KJ, et al. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Mar 12;58(3):419. doi: 10.3390/medicina58030419. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 35334595 Free PMC article. Review. - Post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (Long COVID) in older adults.
Russell SJ, Parker K, Lehoczki A, Lieberman D, Partha IS, Scott SJ, Phillips LR, Fain MJ, Nikolich JŽ. Russell SJ, et al. Geroscience. 2024 Dec;46(6):6563-6581. doi: 10.1007/s11357-024-01227-8. Epub 2024 Jun 14. Geroscience. 2024. PMID: 38874693 Free PMC article. Review. - Cerebral blood flow in patients recovered from mild COVID-19.
Sen S, Newman-Norlund R, Riccardi N, Rorden C, Newman-Norlund S, Sayers S, Fridriksson J, Logue M. Sen S, et al. J Neuroimaging. 2023 Sep-Oct;33(5):764-772. doi: 10.1111/jon.13129. Epub 2023 Jun 2. J Neuroimaging. 2023. PMID: 37265421 Free PMC article.
References
- Institute Of Medicine (IOM) (Ed.) Beyond Mayalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome: Redefining an Illness. The National Academies Press; Washington, DC, USA: 2015. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous