ZIP7 (SLC39A7) expression in colorectal cancer and its correlation with clinical prognosis - PubMed (original) (raw)
ZIP7 (SLC39A7) expression in colorectal cancer and its correlation with clinical prognosis
Yang Luo et al. Transl Cancer Res. 2020 Oct.
Abstract
Background: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a common gastrointestinal malignant tumor that occurs in the colon site and accounts for 9% of the total malignant tumors. Among malignant tumors, its morbidity and mortality respectively rank third and fourth, seriously threatening human health and causing a heavy economic burden on society. ZIP7 (SLC39A7), a kind of zinc transporter, plays a crucial role in the self-renewal of intestinal epithelial cells; however, its role in CRC has not been extensively examined. Therefore, our study aimed to analyze the biological function and expression of this zinc transporter in CRC, along with its correlation with disease activity.
Methods: In this study, 118 cases of colorectal carcinoma tissues, 30 normal tissue samples from adjacent cancer tissues, and 30 normal intestinal mucosa tissue samples from non-intestinal cancer patients were collected in our hospital between February 2014 and February 2015. The expressions of ZIP7 were examined immunohistochemically, and the relationship between ZIP7 expression and the clinical pathological features of CRC were analyzed. After appropriate surgical treatment, the patients accepted a 5-year follow-up for evaluation of their recurrence situation and 5-year survival rate.
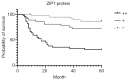
Results: Immunohistochemically, out of 80 CRC tissue samples, 67.8% were found to be positive for ZIP7, 55% (44 cases) were strong positives, and 45% (36 cases) were weak positives. There was a striking coherence between the expression of ZIP7, the depth of lymph node metastasis, CRC invasion, and CRC Dukes stage (P<0.05). Subsequent studies indicated that the mortality rate was positively correlated with the staining intensity of ZIP7 (P<0.05), and the Cox proportional hazards model confirmed that ZIP7 is an independent element of prognostic in patients with CRC (RR =3.896; 95% CI: 1.526-9.951; P=0.004).
Conclusions: The high expression of ZIP 7 in epithelial cells is related to the clinical stage and prognosis of CRC and can be utilized as a biomarker to predict the prognosis of CRC patients.
Keywords: ZIP7; colorectal neoplasms; gene expression; prognosis.
2020 Translational Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (Available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/tcr-20-2640). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
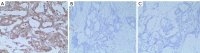
Figure 1
Expression of ZIP7 in CRC tissues/adjacent tissues/and normal intestinal mucosa tissues: (A) CRC tissue, (B) adjacent tissues, (C) normal intestinal mucosa tissues. Scale bars =50 µm. CRC, colorectal cancer.
Figure 2
Relationship between ZIP7 and the prognosis of color cancer.
Similar articles
- Zinc Transporter SLC39A7/ZIP7 Promotes Intestinal Epithelial Self-Renewal by Resolving ER Stress.
Ohashi W, Kimura S, Iwanaga T, Furusawa Y, Irié T, Izumi H, Watanabe T, Hijikata A, Hara T, Ohara O, Koseki H, Sato T, Robine S, Mori H, Hattori Y, Watarai H, Mishima K, Ohno H, Hase K, Fukada T. Ohashi W, et al. PLoS Genet. 2016 Oct 13;12(10):e1006349. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006349. eCollection 2016 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27736879 Free PMC article. - MTSS1 overexpression correlates with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer.
Wang D, Xu MR, Wang T, Li T, Zhu Jw. Wang D, et al. J Gastrointest Surg. 2011 Jul;15(7):1205-12. doi: 10.1007/s11605-011-1546-2. Epub 2011 May 12. J Gastrointest Surg. 2011. PMID: 21562916 - The Prognostic Value of Cancer Stem Cell Markers (Notch1, ALDH1, and CD44) in Primary Colorectal Carcinoma.
Mohamed SY, Kaf RM, Ahmed MM, Elwan A, Ashour HR, Ibrahim A. Mohamed SY, et al. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2019 Dec;50(4):824-837. doi: 10.1007/s12029-018-0156-6. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30136202 - Knockdown of SLC39A7 inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis in human colorectal cancer cells.
Sheng N, Yan L, You W, Tan G, Gong J, Chen H, Yang Y, Hu L, Wang Z. Sheng N, et al. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2017 Oct 1;49(10):926-934. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmx094. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2017. PMID: 28981607
Cited by
- Zinc and its binding proteins: essential roles and therapeutic potential.
Kiouri DP, Chasapis CT, Mavromoustakos T, Spiliopoulou CA, Stefanidou ME. Kiouri DP, et al. Arch Toxicol. 2025 Jan;99(1):23-41. doi: 10.1007/s00204-024-03891-3. Epub 2024 Nov 7. Arch Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39508885 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources