KDOQI US Commentary on the KDIGO 2020 Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes Management in CKD - PubMed (original) (raw)
KDOQI US Commentary on the KDIGO 2020 Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes Management in CKD
Amy K Mottl et al. Am J Kidney Dis. 2022 Apr.
Abstract
In October 2020, KDIGO (Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes) published its first clinical practice guideline directed specifically to the care of patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease (CKD). This commentary presents the views of the KDOQI (Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative) work group for diabetes in CKD, convened by the National Kidney Foundation to provide an independent expert perspective on the new guideline. The KDOQI work group believes that the KDIGO guideline takes a major step forward in clarifying glycemic targets and use of specific antihyperglycemic agents in diabetes and CKD. The purpose of this commentary is to carry forward the conversation regarding optimization of care for patients with diabetes and CKD. Recent developments for prevention of CKD progression and cardiovascular events in people with diabetes and CKD, particularly related to sodium/glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, have filled a longstanding gap in nephrology's approach to the care of persons with diabetes and CKD. The multifaceted benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors have facilitated interactions between nephrology, cardiology, endocrinology, and primary care, underscoring the need for innovative approaches to multidisciplinary care in these patients. We now have more interventions to slow kidney disease progression and prevent or delay kidney failure in patients with diabetes and kidney disease, but methods to streamline their implementation and overcome barriers in access to care, particularly cost, are essential to ensuring all patients may benefit.
Keywords: Diabetes; SGLT2 inhibitors; blood pressure control; chronic kidney disease (CKD); commentary; evidence-based recommendation; glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists; glycemic targets; guideline implementation; guidelines; metformin; nephrology best practices; physical activity; protein intake; smoking; sodium intake.
Copyright © 2021 National Kidney Foundation, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
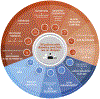
Figure 1.
Schematic for comprehensive care of the patient with type 2 diabetes and CKD. Recommendations from KDIGO (Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes) are represented in orange. Practice points from KDIGO are represented in blue. Asterisk refers to recommendations not specifically addressed by the original schematic in the KDIGO guidelines but deemed important worthy of inclusion by the KDOQI work group. Abbreviations: CKD, chronic kidney disease; HTN, hypertension; GLP-1 RA, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist; RAS, renin-angiotensin system; MRA, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist; SGLT2, sodium/glucose transporter 2; UACR, urinary albumin-creatinine ratio; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; BP, blood pressure.
Similar articles
- KDOQI Commentary on the KDIGO 2022 Update to the Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes Management in CKD.
Mottl AK, Nicholas SB. Mottl AK, et al. Am J Kidney Dis. 2024 Mar;83(3):277-287. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2023.09.003. Epub 2023 Dec 21. Am J Kidney Dis. 2024. PMID: 38142396 - KDOQI US Commentary on the 2017 KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline Update for the Diagnosis, Evaluation, Prevention, and Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD).
Isakova T, Nickolas TL, Denburg M, Yarlagadda S, Weiner DE, Gutiérrez OM, Bansal V, Rosas SE, Nigwekar S, Yee J, Kramer H. Isakova T, et al. Am J Kidney Dis. 2017 Dec;70(6):737-751. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2017.07.019. Epub 2017 Sep 21. Am J Kidney Dis. 2017. PMID: 28941764 - KDOQI US commentary on the 2013 KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Lipid Management in CKD.
Sarnak MJ, Bloom R, Muntner P, Rahman M, Saland JM, Wilson PW, Fried L. Sarnak MJ, et al. Am J Kidney Dis. 2015 Mar;65(3):354-66. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2014.10.005. Epub 2014 Nov 18. Am J Kidney Dis. 2015. PMID: 25465166 Review. - KDOQI US Commentary on the 2021 KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Blood Pressure in CKD.
Drawz PE, Beddhu S, Bignall ONR 2nd, Cohen JB, Flynn JT, Ku E, Rahman M, Thomas G, Weir MR, Whelton PK. Drawz PE, et al. Am J Kidney Dis. 2022 Mar;79(3):311-327. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2021.09.013. Epub 2022 Jan 18. Am J Kidney Dis. 2022. PMID: 35063302 - KDOQI US commentary on the 2012 KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of CKD.
Inker LA, Astor BC, Fox CH, Isakova T, Lash JP, Peralta CA, Kurella Tamura M, Feldman HI. Inker LA, et al. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014 May;63(5):713-35. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2014.01.416. Epub 2014 Mar 16. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014. PMID: 24647050 Review.
Cited by
- Acupuncture improve proteinuria in diabetic kidney disease rats by inhibiting ferroptosis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
Yue JI, Xin-Yuan ZHANG, Yun-Ming XIAO, Zi-Hao ZHUANG, Xiao-Hui YANG, Xin-Ju LI. Yue JI, et al. Heliyon. 2024 Jul 2;10(13):e33675. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33675. eCollection 2024 Jul 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39071725 Free PMC article. - Association between red cell distribution width/serum albumin ratio and diabetic kidney disease.
Chen J, Zhang D, Zhou D, Dai Z, Wang J. Chen J, et al. J Diabetes. 2024 Jul;16(7):e13575. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.13575. J Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 38923843 Free PMC article. - Optimizing Care Delivery in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease in the United States: Proceedings of a Multidisciplinary Roundtable Discussion and Literature Review.
Hirsch JS, Danna SC, Desai N, Gluckman TJ, Jhamb M, Newlin K, Pellechio B, Elbedewe A, Norfolk E. Hirsch JS, et al. J Clin Med. 2024 Feb 20;13(5):1206. doi: 10.3390/jcm13051206. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38592013 Free PMC article. Review. - Show Me CKDintercept Initiative: A Collective Impact Approach to Improve Population Health in Missouri.
Laue K, Schultz M, Talbot-Montgomery E, Garrick A, Java A, Corbett C, Lammert DM, Rogers J, Davis K, Malhotra K, Philipneri M, Kimbel MA, Mustafa RA, Hardesty V. Laue K, et al. Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes. 2024 Jan 12;8(1):82-96. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocpiqo.2023.12.004. eCollection 2024 Feb. Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes. 2024. PMID: 38283097 Free PMC article. - Chronic Kidney Disease in the Older Adult Patient with Diabetes.
Ravender R, Roumelioti ME, Schmidt DW, Unruh ML, Argyropoulos C. Ravender R, et al. J Clin Med. 2024 Jan 8;13(2):348. doi: 10.3390/jcm13020348. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38256482 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- KDOQI Clinical Practice Guidelines and Clinical Practice Recommendations for Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2007;49(suppl 2):S12–S154. - PubMed
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO): KDIGO 2020 Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2020;98(suppl):S1–S115. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous