Risk of aortic aneurysm and aortic dissection with the use of fluoroquinolones in Korea: a nested case-control study - PubMed (original) (raw)
Risk of aortic aneurysm and aortic dissection with the use of fluoroquinolones in Korea: a nested case-control study
Nayeong Son et al. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022.
Abstract
Background: Recent studies have raised concern about the association of fluoroquinolones with an increased risk of aortic aneurysm and aortic dissection. We aimed to evaluate such risk in a Korean population.
Methods: We conducted a nested case-control study using data from the National Health Insurance Service collected from 2013 to 2017 in Korea. The study cohort included patients older than 40 years and excluded patients who had used fluoroquinolones or been diagnosed with aortic aneurysm, aortic dissection, or related diseases 1 year prior to the cohort entry date. We randomly matched four controls in the risk set with each case of aortic aneurysm and aortic dissection (same sex, age, and cohort entry date). We assessed the risk of aortic aneurysm and aortic dissection from fluoroquinolones and adjusted for potential confounders using a conditional logistic regression model.
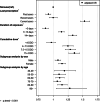
Results: A total of 29,638 aortic aneurysm and aortic dissection patients were identified between 2014 and 2017. The use of fluoroquinolones within a year was associated with a 10% increased risk of aortic aneurysm and aortic dissection (adjusted odds ratio: 1.10, 95% CI 1.07-1.14, p < 0.05) compared with nonusers. The risk was higher in patients who had used fluoroquinolones within 60 days (adjusted odds ratio: 1.53, 95% CI 1.46-1.62, p < 0.05). The risk of aortic aneurysm and aortic dissection positively correlated with the cumulative dose and duration of fluoroquinolone therapy (p < 0.001).
Conclusions: Our study provides real-world evidence of the risk of aortic aneurysm and aortic dissection from fluoroquinolones in Korea. Patients and medical professionals should be aware that fluoroquinolones can increase the risk of aortic aneurysm and aortic dissection, which may be acerbated by high dosage and duration of use.
Keywords: Adverse effect; Aortic aneurysm; Aortic dissection; Drug safety; Fluoroquinolone; Pharmacovigilance.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Fig. 1
Results of conditional logistic regression analysis of the association between AA/AD and FQ use
Similar articles
- Risk of Aortic Dissection and Aortic Aneurysm in Patients Taking Oral Fluoroquinolone.
Lee CC, Lee MT, Chen YS, Lee SH, Chen YS, Chen SC, Chang SC. Lee CC, et al. JAMA Intern Med. 2015 Nov;175(11):1839-47. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.5389. JAMA Intern Med. 2015. PMID: 26436523 - Association Between Fluoroquinolone Use and Hospitalization With Aortic Aneurysm or Aortic Dissection.
Brown JP, Wing K, Leyrat C, Evans SJ, Mansfield KE, Wong AYS, Smeeth L, Galwey NW, Douglas IJ. Brown JP, et al. JAMA Cardiol. 2023 Sep 1;8(9):865-870. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2023.2418. JAMA Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37585175 Free PMC article. - What Fluoroquinolones Have the Highest Risk of Aortic Aneurysm? A Case/Non-case Study in VigiBase®.
Sommet A, Bénévent J, Rousseau V, Chebane L, Douros A, Montastruc JL, Montastruc F. Sommet A, et al. J Gen Intern Med. 2019 Apr;34(4):502-503. doi: 10.1007/s11606-018-4774-2. J Gen Intern Med. 2019. PMID: 30565153 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Current progress of fluoroquinolones-increased risk of aortic aneurysm and dissection.
Jun C, Fang B. Jun C, et al. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021 Sep 28;21(1):470. doi: 10.1186/s12872-021-02258-1. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021. PMID: 34583637 Free PMC article. Review. - Fluoroquinolones and the Risk of Aortopathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
Latif A, Ahsan MJ, Kapoor V, Lateef N, Malik SU, Patel AD, Khan BA, Bittner M, Holmberg M. Latif A, et al. WMJ. 2020 Sep;119(3):185-189. WMJ. 2020. PMID: 33091293 Review.
Cited by
- Ciprofloxacin Accelerates Angiotensin-II-Induced Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Senescence Through Modulating AMPK/ROS pathway in Aortic Aneurysm and Dissection.
Zeng W, Liang Y, Huang S, Zhang J, Mai C, He B, Shi L, Liu B, Li W, Huang X, Li X. Zeng W, et al. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2024 Sep;24(9):889-903. doi: 10.1007/s12012-024-09892-z. Epub 2024 Aug 13. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39138741 Free PMC article. - Do fluoroquinolones increase aortic aneurysm or dissection incidence and mortality? A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Chen C, Patterson B, Simpson R, Li Y, Chen Z, Lv Q, Guo D, Li X, Fu W, Guo B. Chen C, et al. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Aug 9;9:949538. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.949538. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36017083 Free PMC article. - Safety of fluoroquinolones.
Barberán J, de la Cuerda A, Tejeda González MI, López Aparicio A, Monfort Vinuesa C, Ramos Sánchez A, Barberán LC. Barberán J, et al. Rev Esp Quimioter. 2024 Apr;37(2):127-133. doi: 10.37201/req/143.2023. Epub 2023 Dec 22. Rev Esp Quimioter. 2024. PMID: 38140798 Free PMC article. Review. - Weekend Effect and Mortality Outcomes in Aortic Dissection: A Prospective Analysis.
Banceu CM, Harpa M, Brinzaniuc K, Neagu N, Szabo DA, Banceu DM, Al Hussein H, Cristutiu D, Puscas A, Stan A, Oprean M, Popentiu A, Halic MN, Suciu H. Banceu CM, et al. J Crit Care Med (Targu Mures). 2024 Apr 30;10(2):158-167. doi: 10.2478/jccm-2024-0014. eCollection 2024 Apr. J Crit Care Med (Targu Mures). 2024. PMID: 39109277 Free PMC article.
References
- Kim Y, Park Y, Youk T, Lee S, Son Y. A study on the use of antibiotics in Korea and the resistance of major pathogens to antibiotics. NHIS Ilsan hospital Report. 2016:20-001.
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Drug Safety Communication: FDA warns about increased risk of ruptures or tears in the aorta blood vessel with fluoroquinolone antibiotics in certain patients. 2018. https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm628753.htm. Accessed 14 Jan 2022.
- Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS). A notification on the distribution of safety letters on fluoroquinolone antibiotics. https://www.mfds.go.kr/brd/m_545/view.do?seq=286&srchFr=&srchTo=&srchWor.... Accessed 14 Jan 2022.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical