A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Comparing FAST and BEFAST in Acute Stroke Patients - PubMed (original) (raw)
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Comparing FAST and BEFAST in Acute Stroke Patients
Xinjie Chen et al. Front Neurol. 2022.
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate and compare the predictive value of Face, Arm, Speech Test (FAST) and Balance, Eyes, Face, Arm, Speech, Time (BEFAST) scale in the acute ischemic stroke (AIS).
Methods: We searched Medline and Ovid databases for relevant literature in the English language. There were no limitations on the date. The sensitivity, specificity, likelihood ratio, and diagnostic odds ratio were pooled for meta-analysis. The symmetric receiver operator characteristic curve and Fagan's Nomogram were drawn, and meta-regression and subgroup analysis were used to explore the source of heterogeneity.
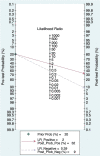
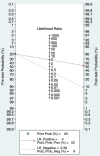
Results: A total of 9 studies, including 6,151 participants, were analyzed. The combined sensitivity of FAST was 0.77 [95% CI (0.64-0.86)], specificity was 0.60 [95% CI (0.38-0.78)], the area under the ROC curve was 0.76, and the diagnostic ratio was 1.57, while the sensitivity of BEFAST was 0.68 [95% CI (0.23-0.93)], specificity was 0.85 [95% CI (0.72-0.92)], the area under the ROC curve was 0.86, and the diagnostic odds ratio was 2.44. No publication bias was detected in Deeks' funnel plot. For FAST, meta-regression analysis showed that the prospective design, satisfactory description of the index test, and a broad spectrum of disease contributed to the heterogeneity in sensitivity, while no sources contributed to the heterogeneity in sensitivity. When the pretest probability was set as 20%, the posterior probability in Fagan's Nomogram was 32%; however, when the pretest probability was set as 20% in BEFAST, the posterior probability in Fagan's Nomogram was 52%.
Conclusions: Our findings indicated that FAST and BEFAST might be useful in the diagnosis of acute ischemic stroke. The diagnostic value of BEFAST in acute ischemic stroke was higher than in FAST; thus, it might have an important role in the fast recognition of acute ischemic stroke.
Keywords: BEFAST; FAST; acute stroke; meta-analysis; stroke; systematic review.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Zhao, Xu, Guo, Yang, Zhong, Weng and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
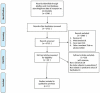
Figure 1
The literature with Face Arm Speech Test (FAST) and Balance, Eyes, Face, Arm, Speech, Time (BEFAST) screening process of the meta-analysis.
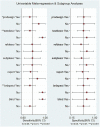
Figure 2
(A) Forest plot of sensitivity (Se) and specificity (Sp) of FAST in the diagnosis of acute ischemic stroke (AIS). (B) Forest plot of diagnosis (positive/negative) likehood ratio (DLR) positive and negative of AIS. (C) Forest map of the diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) of FAST in the diagnosis of AIS.
Figure 3
Deeks' funnel plot asymmetry test for FAST.
Figure 4
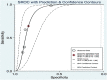
Summary receiver operating characteristic (ROC) of FAST.
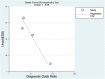
Figure 5
Single-factor meta-regression and subgroup analysis. Prospective design: prodesign, testdescr: satisfactory description of the index test, subjdescr: adequate description of study subjects, refdescr: satisfactory description of ref test, and brdspect: broad spectrum of disease.
Figure 6
Fagan diagram of FAST in the diagnosis of AIS.
Figure 7
(A) Forest plot of Se and Sp of BEFAST in the diagnosis of AIS. (B) Forest plot of diagnosis (positive/negative) likehood ratio (DLR) positive and negative of AIS. (C) Forest map of the DOR of BEFAST in the diagnosis of AIS.
Figure 8
Deeks' funnel plot asymmetry test for BEFAST.
Figure 9
Summary ROC of BEFAST.
Figure 10
Fagan diagram of BEFAST in the diagnosis of AIS.
Similar articles
- Diagnosis Test Meta-Analysis for Apolipoprotein E in Alzheimer's Disease.
Xiong X, Xiao H, Zhang Y, Yu D, Chuan J, Zhong L, Yin Q, Tong R. Xiong X, et al. Dis Markers. 2020 Oct 9;2020:6486031. doi: 10.1155/2020/6486031. eCollection 2020. Dis Markers. 2020. PMID: 33101544 Free PMC article. - A systemic review and meta-analysis comparing the ability of diagnostic of the third heart sound and left ventricular ejection fraction in heart failure.
Dao L, Huang M, Lin X, Li L, Feng X, Wei C, Guo M, Yang Y, Xu F, Weng X. Dao L, et al. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Oct 6;9:918051. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.918051. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36277783 Free PMC article. - Prognostic Value of BEFAST vs. FAST to Identify Stroke in a Prehospital Setting.
Pickham D, Valdez A, Demeestere J, Lemmens R, Diaz L, Hopper S, de la Cuesta K, Rackover F, Miller K, Lansberg MG. Pickham D, et al. Prehosp Emerg Care. 2019 Mar-Apr;23(2):195-200. doi: 10.1080/10903127.2018.1490837. Epub 2018 Aug 23. Prehosp Emerg Care. 2019. PMID: 30118372 - A systematic review and meta-analysis comparing the diagnostic capability of automated breast ultrasound and contrast-enhanced ultrasound in breast cancer.
Zhang H, Hu J, Meng R, Liu F, Xu F, Huang M. Zhang H, et al. Front Oncol. 2024 Jan 9;13:1305545. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1305545. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38264749 Free PMC article. - The diagnostic performance comparison between T2 mapping and Dixon against the activity of thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Zhang F, Wang P, Cao C, Pan X, Zhang T, Fan M, Guan Y. Zhang F, et al. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Dec 12;15:1502296. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1502296. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39726842 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Not so FAST: pre-hospital posterior circulation stroke.
Devlin S. Devlin S. Br Paramed J. 2022 Jun 1;7(1):24-28. doi: 10.29045/14784726.2022.06.7.1.24. Br Paramed J. 2022. PMID: 36452022 Free PMC article. - Clinical Care Pathway and Management of Major Bleeding Associated with Nonvitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulants: A Modified Delphi Consensus from Saudi Arabia and UAE.
Al Raizah A, Alayoubi F, Abdelnaby GH, Alzahrani H, Bakheet MF, Alskaini MA, Buhumaid R, Al Awadhi S, Kazim SN, Jaiganesh T, Naguib MHH, Al Aseri Z. Al Raizah A, et al. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2024 May 1;16(1):e2024038. doi: 10.4084/MJHID.2024.038. eCollection 2024. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38882457 Free PMC article. Review. - Integrative Approaches in Acute Ischemic Stroke: From Symptom Recognition to Future Innovations.
Saceleanu VM, Toader C, Ples H, Covache-Busuioc RA, Costin HP, Bratu BG, Dumitrascu DI, Bordeianu A, Corlatescu AD, Ciurea AV. Saceleanu VM, et al. Biomedicines. 2023 Sep 23;11(10):2617. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11102617. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37892991 Free PMC article. Review. - Knowledge of alarm signs of stroke among caretakers of stroke patients and first contact healthcare providers at two tertiary referral hospitals in Uganda.
Ssemmanda S, Musubire AK. Ssemmanda S, et al. BMC Neurol. 2025 Apr 29;25(1):188. doi: 10.1186/s12883-025-04202-8. BMC Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40301755 Free PMC article. - Characterizing TIA and stroke symptomatology in a population-based study: implications for and diagnostic value of FAST-based public education.
Claus JJ, Berghout BBP, Box CVJ, Licher S, Roozenbeek B, Ikram MK, Wolters FJ. Claus JJ, et al. BMC Public Health. 2024 Dec 18;24(1):3512. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-20960-5. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39696132 Free PMC article.
References
- Duvekot MHC, Venema E, Rozeman AD, Moudrous W, Vermeij FH, Biekart M. Comparison of eight prehospital stroke scales to detect intracranial large-vessel occlusion in suspected stroke (PRESTO): a prospective observational study. Lancet Neurol. (2021) 20:213–21. 10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30439-7 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources