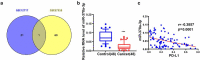microRNA-378a-3p regulates the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating PD-L1 and STAT3 - PubMed (original) (raw)
microRNA-378a-3p regulates the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating PD-L1 and STAT3
Yaqin Li et al. Bioengineered. 2022 Mar.
Abstract
Programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) plays an essential role in the development or progression of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small RNA molecules that regulate gene expression during normal and pathophysiological events. Here, we explored the functions and detailed mechanisms of miR-378a-3p and PD-L1 in HCC progression. First, miR-378a-3p was selected by analyzing miRNA levels in two HCC Gene Expression Omnibus datasets. We found that miR-378a-3p levels exhibited a downward trend in HCC and were negatively correlated with PD-L1 levels. Additionally, a dual luciferase assay predicted that miR-378a-3p directly targets PD-L1. Moreover, the transfection of miR-378a-3p mimics into Li-7 and HuH-7 cells effectively decreased the PD-L1 mRNA and protein expression levels, and inhibited Treg differentiation in co-culture models by modulating the expression levels of certain cytokines. Furthermore, the overexpression of miR-378a-3p hindered cell proliferation and migration but facilitated apoptosis by repressing STAT3 signaling in HCC cells. In conclusion, miR-378a-3p appears to inhibit HCC tumorigenesis by regulating PD-L1 and STAT3 levels. Thus, miR-378a-3p may be a potential target for HCC therapy.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; PD-L1; STAT3; immune escape; miR-378a-3p.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Graphical abstract
Figure 1.
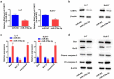
miR-378a-3p is lowly expressed in HCC tissues. (A) HCC GEO datasets (GSE12717 and GSE57555) were analyzed and one lowly expressed gene was identified from the intersection. (B) qRT-PCR analysis of miR-378a-3p expression in 48 pairs of HCC and normal tissues obtained from HCC patients. (C) Negative correlation between miR-378a-3p and PD-L1 expression in HCC samples. ***P < 0.001.
Figure 2.
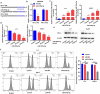
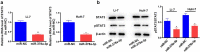
PD-L1 solved as the direct target of miR-378a-3p. (A) Schematic miR-378a-3p putative target sites in 3’UTRs of PD-L1. (B) Dual luciferase reporter assays. (C) The expression level of miR-378a-3p was evaluated using qRT-PCR in HCC cells after transfection. (D) qRT-PCR, (E) Western blot, and (F) flow cytometry were used to evaluate the expression level of PD-L1 after transfection. Data were shown as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.
Figure 3.
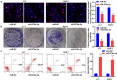
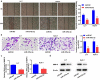
miR-378a-3p overexpression reduced HCC cell viability and promoted cell apoptosis. (A) EdU assay showed that miR-378a-3p reduced HCC cell viability. (B) Colony formation assay showed that miR-378a-3p inhibited HCC cell to form colonies. (C) miR-378a-3p transfection effectively induced apoptosis in HCC cell. Data were shown as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.
Figure 4.
The potential molecular mechanisms of the regulation of miR-378a-3p to the cell viability and apoptosis of HCC cells. (A) C-MYC, as a major gene involving in cell growth, was detected with qRT-PCR. (B) C-MYC was detected with Western blot. (C, D) The levels of major genes related to apoptosis were evaluated using qRT-PCR and Western blot. Data were shown as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. **P < 0.01.
Figure 5.
miR-378a-3p overexpression reduced HCC cell invasion and migration. (A) A wound healing assay was performed to investigate cell migration. (B) Transwell assay was employed to investigate cell invasion status. (C) The mRNA level of MMP-9 was detected in HCC cells using qRT-PCR. (D) The protein level of MMP-9 was detected in HCC cells. Data were shown as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01.
Figure 6.
miR-378a-3p overexpression led to down-regulation of STAT3. (A) qRT-PCR and (B) Western blotting were used to evaluate the expression level of STAT3 in HCC cells after transfection. Data were shown as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01.
Figure 7.
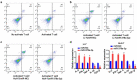
miR-378a-3p modulated the cell differentiation of CD25+ Foxp3+ Treg. (A) The percentage of CD4+CD25+ Foxp3+ Tregs in the CD4+ population was detected using FACS. (B, C) Up-regulation of miR-378a-3p lead to a decrease in Treg induction compared to the negative controls. (D) Detecting cytokine levels with qRT-PCR in co-culture medium. Data were shown as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01.
Similar articles
- MicroRNA-124-3p suppresses PD-L1 expression and inhibits tumorigenesis of colorectal cancer cells via modulating STAT3 signaling.
Roshani Asl E, Rasmi Y, Baradaran B. Roshani Asl E, et al. J Cell Physiol. 2021 Oct;236(10):7071-7087. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30378. Epub 2021 Apr 5. J Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33821473 - lncRNA MIAT targets miR-411-5p/STAT3/PD-L1 axis mediating hepatocellular carcinoma immune response.
Zhang X, Pan B, Qiu J, Ke X, Shen S, Wang X, Tang N. Zhang X, et al. Int J Exp Pathol. 2022 Jun;103(3):102-111. doi: 10.1111/iep.12440. Epub 2022 Apr 15. Int J Exp Pathol. 2022. PMID: 35429078 Free PMC article. - LXR activation potentiates sorafenib sensitivity in HCC by activating microRNA-378a transcription.
Lin Z, Xia S, Liang Y, Ji L, Pan Y, Jiang S, Wan Z, Tao L, Chen J, Lin C, Liang X, Xu J, Cai X. Lin Z, et al. Theranostics. 2020 Jul 11;10(19):8834-8850. doi: 10.7150/thno.45158. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32754282 Free PMC article. - A Systematic Review on the Therapeutic Potentiality of PD-L1-Inhibiting MicroRNAs for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Toward Single-Cell Sequencing-Guided Biomimetic Delivery.
Shadbad MA, Safaei S, Brunetti O, Derakhshani A, Lotfinejad P, Mokhtarzadeh A, Hemmat N, Racanelli V, Solimando AG, Argentiero A, Silvestris N, Baradaran B. Shadbad MA, et al. Genes (Basel). 2021 Aug 4;12(8):1206. doi: 10.3390/genes12081206. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34440380 Free PMC article. - A scoping review on the potentiality of PD-L1-inhibiting microRNAs in treating colorectal cancer: Toward single-cell sequencing-guided biocompatible-based delivery.
Shadbad MA, Asadzadeh Z, Derakhshani A, Hosseinkhani N, Mokhtarzadeh A, Baghbanzadeh A, Hajiasgharzadeh K, Brunetti O, Argentiero A, Racanelli V, Silvestris N, Baradaran B. Shadbad MA, et al. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Nov;143:112213. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112213. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 34560556
Cited by
- MiR-378a-3p acts as a tumor suppressor in gastric cancer via directly targeting RAB31 and inhibiting the Hedgehog pathway proteins GLI1/2.
Xu X, Li Y, Liu G, Li K, Chen P, Gao Y, Liang W, Xi H, Wang X, Wei B, Li H, Chen L. Xu X, et al. Cancer Biol Med. 2022 Oct 18;19(12):1662-82. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2022.0337. Cancer Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 36245214 Free PMC article. - Non-coding RNA in tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells formation and associated immunotherapy.
Ma Y, Xu X, Wang H, Liu Y, Piao H. Ma Y, et al. Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 21;14:1228331. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1228331. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37671150 Free PMC article. Review. - Deciphering STAT3 signaling potential in hepatocellular carcinoma: tumorigenesis, treatment resistance, and pharmacological significance.
Hashemi M, Sabouni E, Rahmanian P, Entezari M, Mojtabavi M, Raei B, Zandieh MA, Behroozaghdam M, Mirzaei S, Hushmandi K, Nabavi N, Salimimoghadam S, Ren J, Rashidi M, Raesi R, Taheriazam A, Alexiou A, Papadakis M, Tan SC. Hashemi M, et al. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023 Apr 21;28(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s11658-023-00438-9. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023. PMID: 37085753 Free PMC article. Review. - Effects of Scutellaria baicalensis Extract-Induced Exosomes on the Periodontal Stem Cells and Immune Cells under Fine Dust.
Yun M, Kim B. Yun M, et al. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Aug 27;14(17):1396. doi: 10.3390/nano14171396. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39269058 Free PMC article. - Evaluation and Application of Drug Resistance by Biomarkers in the Clinical Treatment of Liver Cancer.
Huang PS, Wang LY, Wang YW, Tsai MM, Lin TK, Liao CJ, Yeh CT, Lin KH. Huang PS, et al. Cells. 2023 Mar 10;12(6):869. doi: 10.3390/cells12060869. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36980210 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Tseng CH, Hsu YC, Chen TH, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma incidence with tenofovir versus entecavir in chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5(12):1039–1052. - PubMed
- Romano A, Angeli P, Piovesan S, et al. Newly diagnosed hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with advanced hepatitis C treated with DAAs: a prospective population study. J Hepatol. 2018;69(2):345–352. - PubMed
- Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J.. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2018;391(10127):1301–1314. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous