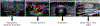Hashimoto thyroiditis: an evidence-based guide to etiology, diagnosis and treatment - PubMed (original) (raw)
Hashimoto thyroiditis: an evidence-based guide to etiology, diagnosis and treatment
Joanna Klubo-Gwiezdzinska et al. Pol Arch Intern Med. 2022.
Abstract
Hashimoto thyroiditis (HT) is a common autoimmune disorder, affecting women 7-10 times more often than men, that develops because of genetic susceptibility, Xchromosome inactivation patterns modulated by environmental factors as well as microbiome composition, and leads to an imbalance in self‑tolerance mechanisms. The consequential thyroid infiltration by lymphocytes, potentiated by antibody‑mediated autoimmune response through the antibodies against thyroid peroxidase (TPOAbs), leads to a destruction of thyrocytes. The presence of TPOAbs is associated with a 2 to 4‑fold increase in the risk of recurrent miscarriages and preterm birth in pregnant women. The clinical presentation of HT includes: (A) thyrotoxicosis, when stored thyroid hormones are released to circulation from destroyed thyroid follicles; (B) euthyroidism, when preserved thyroid tissue compensates for destroyed thyrocytes; and (C) hypothyroidism, when thyroid hormone production by the affected thyroid gland is insufficient. The management of Hashitoxicosis is based on symptoms control usually with β‑blockers, euthyroidism requires periodical thyroid stimulating hormone measurements to assess for progression to hypothyroidism, and hypothyroidism is treated with thyroid hormone replacement therapy. The dose of levothyroxine (LT4) used for treatment is based on the degree of preserved thyroid functionality and lean body mass, and usually ranges from 1.4 to 1.8 mcg/kg/day. There is insufficient evidence to recommend for or against therapy with triiodothyronine (T3), apart from in pregnancy when only levothyroxine is indicated, as T3 does not sufficiently cross fetal blood‑brain barrier. HT is associated with 1.6 times higher risk of papillary thyroid cancer and 60 times higher risk of thyroid lymphoma than in general the population.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST None declared.
Figures
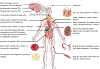
FIGURE 1
Background and natural history of Hashimoto thyroiditis Abbreviations: TPO, thyroid peroxidase; TSH, thyroid-stimulating hormone
FIGURE 2
Signs and symptoms of thyroid hormone deficiency Abbreviations: LDL, low-density lipoprotein; TRH, thyrotropin-releasing hormone; others, see FIGURE 1
FIGURE 3
Sonographic appearance of Hashimoto thyroiditis
Similar articles
- Optimal Thyroid Hormone Replacement Dose in Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Associated Hypothyroidism Is Distinct from Hashimoto's Thyroiditis.
Mosaferi T, Tsai K, Sovich S, Wilhalme H, Kathuria-Prakash N, Praw SS, Drakaki A, Angell TE, Lechner MG. Mosaferi T, et al. Thyroid. 2022 May;32(5):496-504. doi: 10.1089/thy.2021.0685. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Thyroid. 2022. PMID: 35199588 Free PMC article. - [Autoimmune thyroid disease].
Koehler VF, Bojunga J. Koehler VF, et al. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2021 Oct;146(20):1329-1336. doi: 10.1055/a-1258-5674. Epub 2021 Oct 13. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2021. PMID: 34644793 German. - Association between serum thyroid hormone balance and thyroid volume in patients treated with levothyroxine monotherapy for hypothyroidism.
Takahashi S, Ito M, Masaki Y, Hada M, Minakata M, Kohsaka K, Nakamura T, Kasahara T, Kudo T, Nishihara E, Fukata S, Nishikawa M, Akamizu T, Miyauchi A. Takahashi S, et al. Endocr J. 2021 Mar 28;68(3):353-360. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ20-0542. Epub 2020 Nov 25. Endocr J. 2021. PMID: 33239477 - Interventions for clinical and subclinical hypothyroidism pre-pregnancy and during pregnancy.
Reid SM, Middleton P, Cossich MC, Crowther CA, Bain E. Reid SM, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 May 31;2013(5):CD007752. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007752.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23728666 Free PMC article. Review. - Hashimotos' thyroiditis: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinic and therapy.
Ragusa F, Fallahi P, Elia G, Gonnella D, Paparo SR, Giusti C, Churilov LP, Ferrari SM, Antonelli A. Ragusa F, et al. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019 Dec;33(6):101367. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2019.101367. Epub 2019 Nov 26. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019. PMID: 31812326 Review.
Cited by
- Causal effects of post-traumatic stress disorder on autoimmune thyroid disease: insights from mendelian randomization.
Chen Z, Yu Y, Yao J, Guo Z, Cui Y, Li F, Li C. Chen Z, et al. Front Psychiatry. 2024 Sep 20;15:1417302. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1417302. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39371915 Free PMC article. - A COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF HEMOGRAM-DERIVED INFLAMMATORY INDICES IN HASHIMOTO THYROIDITIS AND NON-IMMUNOGENIC HYPOTHYROIDISM.
Erinc O, Yesilyurt S, Senat A. Erinc O, et al. Acta Endocrinol (Buchar). 2023 Oct-Dec;19(4):435-440. doi: 10.4183/aeb.2023.435. Epub 2024 Jun 24. Acta Endocrinol (Buchar). 2023. PMID: 38933249 Free PMC article. - The Role of the Immune System in the Course of Hashimoto's Thyroiditis: The Current State of Knowledge.
Wrońska K, Hałasa M, Szczuko M. Wrońska K, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 23;25(13):6883. doi: 10.3390/ijms25136883. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38999993 Free PMC article. Review. - From Antibodies to Artificial Intelligence: A Comprehensive Review of Diagnostic Challenges in Hashimoto's Thyroiditis.
Kolanu ND, Awan NA, Butt AI, Reza T, Almadhoun MKIK, Janoowala T, Bokhari SFH, Zain Z, Sharif T, Chauhan L, Choudhari J. Kolanu ND, et al. Cureus. 2024 Feb 18;16(2):e54393. doi: 10.7759/cureus.54393. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38505448 Free PMC article. Review. - The prevalence of positive thyroid autoantibodies in patients with subacute thyroiditis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Shekarian A, Fakhrolmobasheri M, Mazaheri-Tehrani S, Yousefian A, Heidarpour M. Shekarian A, et al. Endocrine. 2024 Apr;84(1):29-41. doi: 10.1007/s12020-023-03655-6. Epub 2023 Dec 26. Endocrine. 2024. PMID: 38147263
References
- Hashimoto H The knowledge of the lymphomatous changes in the thyroid gland (struma lymphomatosa) [in German]. Archiv für klinische Chirurgie. 1912; 97: 219.
- Ralli M, Angeletti D, Fiore M, et al. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: an update on pathogenic mechanisms, diagnostic protocols, therapeutic strategies, and potential malignant transformation. Autoimmun Rev. 2020; 19: 102649. - PubMed
- McLeod DS, Caturegli P, Cooper DS, et al. Variation in rates of autoimmune thyroid disease by race/ethnicity in US military personnel. JAMA. 2014; 311: 1563–1565. - PubMed
- Song RH, Yao QM, Wang B, et al. Thyroid disorders in patients with myasthenia gravis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Autoimmun Rev. 2019; 18: 102368. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical