Nanoliposomes in Cancer Therapy: Marketed Products and Current Clinical Trials - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Nanoliposomes in Cancer Therapy: Marketed Products and Current Clinical Trials
Raquel Taléns-Visconti et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022.
Abstract
The drugs used for cancer treatment have many drawbacks, as they damage both tumor and healthy cells and, in addition, they tend to be poorly soluble drugs. Their transport in nanoparticles can solve these problems as these can release the drug into tumor tissues, as well as improve their solubility, bioavailability, and efficacy, reducing their adverse effects. This article focuses on the advantages that nanotechnology can bring to medicine, with special emphasis on nanoliposomes. For this, a review has been made of the nanoliposomal systems marketed for the treatment of cancer, as well as those that are in the research phase, highlighting the clinical trials being carried out. All marketed liposomes studied are intravenously administered, showing a reduced intensity of side-effects compared with the nonliposomal form. Doxorubicin is the active ingredient most frequently employed. Ongoing clinical trials expand the availability of liposomal medicines with new clinical indications. In conclusion, the introduction of drugs in nanoliposomes means an improvement in their efficacy and the quality of life of patients. The future focus of research could be directed to develop multifunctional targeted nanoliposomes using new anticancer drugs, different types of existing drugs, or new standardized methodologies easily translated into industrial scale.
Keywords: cancer; clinical trials; nanoliposomes; translational medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
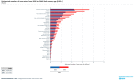
Figure 1
Estimated number of new cancer cases worldwide from 2020 to 2040 [1].
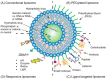
Figure 2
Strategies of functionalized liposome delivery for solid tumor therapy. (A) Conventional liposomes can reach tumor tissues through the EPR effect. (B) Surface-PEGylated liposomes can increase circulation time. (C) Functionalized liposomes modified with appropriate ligands can reach the target site and release the drug. (D) Responsive liposomes activate drug release only under specific environmental conditions. Reproduced from ref. [51].
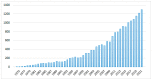
Figure 3
Evolution of the number of publications on (nano)liposomes and cancer.
Similar articles
- Delivery of doxorubicin loaded P18 conjugated-poly(2-ethyl-oxazoline)-DOPE nanoliposomes for targeted therapy of breast cancer.
Bolat ZB, Nezir AE, Devrim B, Zemheri E, Gulyuz S, Ozkose UU, Yilmaz O, Bozkir A, Telci D, Sahin F. Bolat ZB, et al. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2021 Oct 1;428:115671. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2021.115671. Epub 2021 Aug 12. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34391753 - Advanced targeted therapies in cancer: Drug nanocarriers, the future of chemotherapy.
Pérez-Herrero E, Fernández-Medarde A. Pérez-Herrero E, et al. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015 Jun;93:52-79. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2015.03.018. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015. PMID: 25813885 Review. - The Clinical Translation of Organic Nanomaterials for Cancer Therapy: A Focus on Polymeric Nanoparticles, Micelles, Liposomes and Exosomes.
Palazzolo S, Bayda S, Hadla M, Caligiuri I, Corona G, Toffoli G, Rizzolio F. Palazzolo S, et al. Curr Med Chem. 2018;25(34):4224-4268. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170830113755. Curr Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 28875844 Review. - Single-Step Synthesis of Highly Tunable Multifunctional Nanoliposomes for Synergistic Cancer Therapy.
Li M, Liu C, Yin J, Liu G, Chen D. Li M, et al. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022 May 11;14(18):21301-21309. doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c00600. Epub 2022 May 3. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022. PMID: 35502842 - Design and evaluation of peptide-18-targeted nanoliposomes constructed by poly(2-oxazoline)-DOPE for doxorubicin delivery.
Devrim B, Bolat ZB, Telci D, Şahin F, Gulyuz S, Ozkose UU, Yilmaz O, Bozkır A. Devrim B, et al. J Microencapsul. 2021 Aug;38(5):285-297. doi: 10.1080/02652048.2021.1905094. Epub 2021 Apr 14. J Microencapsul. 2021. PMID: 33853478
Cited by
- Nanomedicine marvels: crafting the future of cancer therapy with innovative statin nano-formulation strategies.
Karimi Jirandehi A, Asgari R, Keshavarz Shahbaz S, Rezaei N. Karimi Jirandehi A, et al. Nanoscale Adv. 2024 Oct 18;6(23):5748-72. doi: 10.1039/d4na00808a. Online ahead of print. Nanoscale Adv. 2024. PMID: 39478996 Free PMC article. Review. - Optimizing gefitinib nanoliposomes by Box-Behnken design and coating with chitosan: A sequential approach for enhanced drug delivery.
Rohilla S, Awasthi R, Rohilla A, Singh SK, Chellappan DK, Dua K, Dureja H. Rohilla S, et al. ADMET DMPK. 2024 Jul 31;12(4):657-677. doi: 10.5599/admet.2366. eCollection 2024. ADMET DMPK. 2024. PMID: 39473624 Free PMC article. - Exploring the therapeutic potential of lipid-based nanoparticles in the management of oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Chaudhary AA, Fareed M, Khan SU, Alneghery LM, Aslam M, Alex A, Rizwanullah M. Chaudhary AA, et al. Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2024;5(6):1223-1246. doi: 10.37349/etat.2024.00272. Epub 2024 Sep 29. Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2024. PMID: 39465011 Free PMC article. Review. - Novel _Pseudomonas putida_-derived nanoliposomes enhance the inhibition of MCF-7 breast cancer cells by superb intracellular uptake of doxorubicin.
Asadi Z, Arkan E, Nowroozi G, Aghaz F. Asadi Z, et al. Heliyon. 2024 Sep 26;10(19):e38337. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38337. eCollection 2024 Oct 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39403495 Free PMC article. - Recent Advancements in Biomaterials for Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Immunotherapy.
Yu G, Ye Z, Yuan Y, Wang X, Li T, Wang Y, Wang Y, Yan J. Yu G, et al. Biomater Res. 2024 Jul 15;28:0045. doi: 10.34133/bmr.0045. eCollection 2024. Biomater Res. 2024. PMID: 39011521 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- International Agency for Research on Cancer Elaborated Online on the Website Global Cancer Observatory. [(accessed on 17 February 2022)]. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/tomorrow/en/dataviz/bars?types=0&sexes=0&mode=cancer....
- Abd Elkodous M., El-Sayyad G.S., Abdelrahman I.Y., El-Bastawisy H.S., Mohamed A.E., Mosallam F.M., Nasser H.A., Gobara M., Baraka A., Elsayed M.A., et al. Therapeutic and diagnostic potential of nanomaterials for enhanced biomedical applications. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces. 2019;180:411–428. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.05.008. - DOI - PubMed
- EMA Nanotechnology. [(accessed on 20 February 2022)]; Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/glossary/nanotechnology.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources