A New Species in Notobitiella Hsiao in China Confirmed by Morphological and Molecular Data (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Coreidae) - PubMed (original) (raw)
A New Species in Notobitiella Hsiao in China Confirmed by Morphological and Molecular Data (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Coreidae)
Kun Jiang et al. Insects. 2022.
Abstract
To date, only one species of genus Notobitiella, N. elegans Hsiao, was found in Yunnan, China. Recently, we confirmed a new species, Notobitiella bispinasp. nov., by morphological and molecular data based on new specimens collected from Yunnan, China. The new species is morphologically similar to N. elegans except for the male genitalia and the sternum of the seventh abdominal segment of the female. The extraordinary difference of the genitalia between these two species inspired us to erect a new genus for this new species. However, considering their sister group relationship to other genera in tribe Cloresmini and the 12.56~12.64% genetic distance (meeting the interspecific genetic distance within genus of tribe Cloresmini) by a complete COI gene, this species was more reasonable as a new species of the genus Notobitiella, and the diagnosis of the genus was revised. The photos of the body and critical morphological characteristics for both male and female were provided for accurate identification.
Keywords: Cloresmini; Notobitiella; bamboo; monotypic genus; species delimitation by COI.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
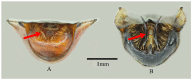
Figure 1
Ventral view of pygophore. (A) male of N. bispina sp. nov., (B) female of N. bispina sp. nov., (C) male of N. elegans, and (D) female of N. elegans.
Figure 2
Posterior view of pygophore. (A) N. bispina sp. nov., and (B) N. elegans.
Figure 3
Neighbor-joining tree for six species of the tribe Cloresmini based on K2P distance in DNA barcodes. Numbers on branches represent bootstrap support based on 1000 replicates; scale equals K2P genetic distance.
Figure 4
N. bispinasp. nov. M1 dorsal side of male M2 ventral side of male F1 dorsal side of female F2 ventral side of female.
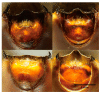
Figure 5
45 degree angle views of the ventral surface for four samples of the new species, N. bispina sp. nov. showing the teeth variation on the posterior margin of male genital capsule.
Figure 6
Field picture of N. bispina sp. nov. at Xiaomengyang, Xishuangbanna, Yunnan, China.
Similar articles
- Revision of the genus Sadoletus Distant, with description of new species from China and Australia (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Heterogastridae).
Gao C, Malipatil MB. Gao C, et al. Zootaxa. 2019 Jun 5;4613(2):zootaxa.4613.2.3. doi: 10.11646/zootaxa.4613.2.3. Zootaxa. 2019. PMID: 31716412 - Contributions to the tribe Leptocorisini, with descriptions of Planusocoris schaeferi gen. & sp. nov. (Hemiptera: Alydidae).
Yi W, Bu W. Yi W, et al. Zootaxa. 2015 Nov 12;4040(4):401-20. doi: 10.11646/zootaxa.4040.4.1. Zootaxa. 2015. PMID: 26624675 - New genus and new species of the tribe Augilini (Hemiptera, Fulgoromorpha: Caliscelidae) from Yunnan Province in China.
Gong N, Yang L, Chen XS. Gong N, et al. Zootaxa. 2020 Dec 16;4895(3):zootaxa.4895.3.6. doi: 10.11646/zootaxa.4895.3.6. Zootaxa. 2020. PMID: 33756895 - A review of the leafhopper tribe Hyalojassini (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae: Iassinae) with description of new taxa.
Dai W, Dietrich CH, Zhang Y. Dai W, et al. Zootaxa. 2015 Jan 16;3911(1):1-42. doi: 10.11646/zootaxa.3911.1.1. Zootaxa. 2015. PMID: 25661594 Review.
Cited by
- Diversity and distribution of bamboo-feeding true bugs in China.
Jiang K, Chen J, Wang S, Li Y, Zhang D, Hu H, Bu W. Jiang K, et al. Ecol Evol. 2024 Jul 18;14(7):e11563. doi: 10.1002/ece3.11563. eCollection 2024 Jul. Ecol Evol. 2024. PMID: 39026951 Free PMC article.
References
- Hsiao T.-Y. Result of the zoologico-botanical expedition to southwest China, 1955–1957 (Hemiptera, Coreidae) Acta Entomol. Sin. 1963;12:310–344.
- Zheng L.-Y. Heteropteran Insects (Hemiptera) Feeding on Bamboos in China. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1994;87:91–96. doi: 10.1093/aesa/87.1.91. - DOI
- Hsiao T.-Y. The Chinese bamboo Coreids of the tribe Cloresmini Stal with the description of a new subspecies (Hemiptera-Heteroptera) Acta Entomol. Sin. 1963;12:506–510.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources