Medium-chain triglycerides may improve memory in non-demented older adults: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials - PubMed (original) (raw)
Medium-chain triglycerides may improve memory in non-demented older adults: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials
Panagiotis Giannos et al. BMC Geriatr. 2022.
Abstract
Background: Ketosis has been exploited for its neuroprotective impact and treatment of neurological conditions via ketone production. Exogenous medium-chain triglyceride (MCT) supplementation may induce nutritional ketosis. The aim of this systematic review is to explore the effects of MCTs on memory function in older adults without cognitive impairment.
Methods: A systematic literature search of PubMed, Cochrane Library, Scopus, and Web of Science was employed from inception until April 2022 for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines, investigating the impact of MCT oils on components of memory. Risk of bias (RoB2) tool was utilized for quality assessment.
Results: Six trials were included for qualitative synthesis, in which two studies examined the effect of MCTs through a ketogenic meal. MCT supplementation compared to controls was associated with improved indices of memory function in 4 out of 6 studies, particularly working memory. A meta-analysis was not employed due to the low number of studies, therefore, a true effect measure of MCT supplementation was not explored.
Conclusions: MCT supplementation may enhance working memory in non-demented older adults. These effects may be more prominent in individuals with lower baseline scores, from short and long-term supplementation. Further studies are warranted to confirm these findings in terms of optimal dose and MCTs composition, which may protect from memory decline during aging.
Keywords: Cognitive function; Medium-chain triglycerides; Memory; Non-demented; Nutritional ketosis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
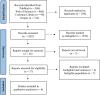
Fig. 1
Flowchart of the employed literature search
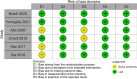
Fig. 2
Risk of bias assessment of the included studies
Similar articles
- Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.
Crider K, Williams J, Qi YP, Gutman J, Yeung L, Mai C, Finkelstain J, Mehta S, Pons-Duran C, Menéndez C, Moraleda C, Rogers L, Daniels K, Green P. Crider K, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article. - High versus low medium chain triglyceride content of formula for promoting short-term growth of preterm infants.
Perretta L, Ouldibbat L, Hagadorn JI, Brumberg HL. Perretta L, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Feb 23;2(2):CD002777. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002777.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33620090 Free PMC article. - To Keto or Not to Keto? A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials Assessing the Effects of Ketogenic Therapy on Alzheimer Disease.
Grammatikopoulou MG, Goulis DG, Gkiouras K, Theodoridis X, Gkouskou KK, Evangeliou A, Dardiotis E, Bogdanos DP. Grammatikopoulou MG, et al. Adv Nutr. 2020 Nov 16;11(6):1583-1602. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmaa073. Adv Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32597927 Free PMC article. - Supplementation of Regular Diet With Medium-Chain Triglycerides for Procognitive Effects: A Narrative Review.
Shcherbakova K, Schwarz A, Apryatin S, Karpenko M, Trofimov A. Shcherbakova K, et al. Front Nutr. 2022 Jul 15;9:934497. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.934497. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35911092 Free PMC article. Review. - Effects of medium-chain triglycerides on weight loss and body composition: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Mumme K, Stonehouse W. Mumme K, et al. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2015 Feb;115(2):249-263. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2014.10.022. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2015. PMID: 25636220 Review.
Cited by
- Beta-Hydroxybutyrate (BHB), Glucose, Insulin, Octanoate (C8), and Decanoate (C10) Responses to a Medium-Chain Triglyceride (MCT) Oil with and without Glucose: A Single-Center Study in Healthy Adults.
Heidt C, Fobker M, Newport M, Feldmann R, Fischer T, Marquardt T. Heidt C, et al. Nutrients. 2023 Feb 24;15(5):1148. doi: 10.3390/nu15051148. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36904147 Free PMC article. - Localized proteomic differences in the choroid plexus of Alzheimer's disease and epilepsy patients.
Leitner DF, Kanshin E, Faustin A, Thierry M, Friedman D, Devore S, Ueberheide B, Devinsky O, Wisniewski T. Leitner DF, et al. Front Neurol. 2023 Jul 14;14:1221775. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1221775. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37521285 Free PMC article.
References
- Cunnane SC, Courchesne-Loyer A, St-Pierre V, Vandenberghe C, Pierotti T, Fortier M, Croteau E, Castellano CA. Can ketones compensate for deteriorating brain glucose uptake during aging? Implications for the risk and treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2016;1367:12–20. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12999. - DOI - PubMed
- Roopashree P, Shetty SS, Kumari NS. Effect of medium chain fatty acid in human health and disease. J Funct Foods. 2021;87:104724. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2021.104724. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous