Psychophysiological Adaptations to Yoga Practice in Overweight and Obese Individuals: A Topical Review - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Psychophysiological Adaptations to Yoga Practice in Overweight and Obese Individuals: A Topical Review
Alexios Batrakoulis. Diseases. 2022.
Abstract
Physical activity has been documented as a foundational approach for weight management and obesity, improving several cardiometabolic and mental health indices. However, it is not clear whether yoga practice can induce beneficial improvements in anthropometric and body composition parameters, performance, metabolic health, and well-being among overweight/obese people. The aim of this topical review was to catalog training studies examining the psychophysiological responses to yoga interventions in order to detect which outcomes have been investigated, the research methods applied, and the conclusions. The inclusion/exclusion criteria were met by 22 published articles involving 1178 (56% female) overweight/obese participants. This brief review on yoga-induced adaptations demonstrates that this widely used meditative movement activity can meaningfully improve the vast majority of the selected markers. These beneficial alterations are focused mostly on various anthropometric and body composition variables, cardiovascular disease risk factors, physical fitness parameters, quality of life, and stress in previously inactive overweight/obese individuals. Instead, yoga-based physical exercise interventions investigating anxiety, depression, mood state, exercise enjoyment, affect valence, and adherence were limited. Further research should focus on the yoga intervention configuration and potential mechanisms behind favorable changes in various psychophysiological indices through large-scale, rigorously designed randomized controlled trials implementing long-term interventions in overweight/obese individuals.
Keywords: exercise; obesity; overweight; physiological responses; psychological responses; yoga.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
Figure 1
The psychophysiological effects of yoga interventions in overweight and obese individuals. MHR: maximum heart rate; RPE: rating of perceived exertion. [34,43,46,56,57].
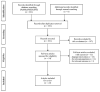
Figure 2
Flowchart of the systematic literature search.
Similar articles
- Psychophysiological Adaptations to Pilates Training in Overweight and Obese Individuals: A Topical Review.
Batrakoulis A. Batrakoulis A. Diseases. 2022 Sep 29;10(4):71. doi: 10.3390/diseases10040071. Diseases. 2022. PMID: 36278570 Free PMC article. Review. - Psychological Adaptations to High-Intensity Interval Training in Overweight and Obese Adults: A Topical Review.
Batrakoulis A, Fatouros IG. Batrakoulis A, et al. Sports (Basel). 2022 Apr 22;10(5):64. doi: 10.3390/sports10050064. Sports (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35622474 Free PMC article. Review. - Role of Mind-Body Fitness in Obesity.
Batrakoulis A. Batrakoulis A. Diseases. 2022 Dec 21;11(1):1. doi: 10.3390/diseases11010001. Diseases. 2022. PMID: 36648866 Free PMC article. - The effectiveness of web-based programs on the reduction of childhood obesity in school-aged children: A systematic review.
Antwi F, Fazylova N, Garcon MC, Lopez L, Rubiano R, Slyer JT. Antwi F, et al. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2012;10(42 Suppl):1-14. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2012-248. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 27820152 - The effect of weight management interventions that include a diet component on weight-related outcomes in pregnant and postpartum women: a systematic review protocol.
Spencer L, Rollo M, Hauck Y, MacDonald-Wicks L, Wood L, Hutchesson M, Giglia R, Smith R, Collins C. Spencer L, et al. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Jan;13(1):88-98. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-1812. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26447010
Cited by
- Effects of combined aerobic exercise and diet on cardiometabolic health in patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Al-Mhanna SB, Rocha-Rodriguesc S, Mohamed M, Batrakoulis A, Aldhahi MI, Afolabi HA, Yagin FH, Alhussain MH, Gülü M, Abubakar BD, Ghazali WSW, Alghannam AF, Badicu G. Al-Mhanna SB, et al. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2023 Dec 4;15(1):165. doi: 10.1186/s13102-023-00766-5. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2023. PMID: 38049873 Free PMC article. - Health and fitness trends in Iran for 2024: A cross-sectional study.
Batrakoulis A, Fatolahi S, Dinizadeh F. Batrakoulis A, et al. AIMS Public Health. 2023 Oct 7;10(4):791-813. doi: 10.3934/publichealth.2023053. eCollection 2023. AIMS Public Health. 2023. PMID: 38187897 Free PMC article. - Physical Activity, Body Image, and Emotional Intelligence Differences in Adults with Overweight and Obesity.
Gilyana M, Batrakoulis A, Zisi V. Gilyana M, et al. Diseases. 2023 May 10;11(2):71. doi: 10.3390/diseases11020071. Diseases. 2023. PMID: 37218884 Free PMC article. - Health and fitness trends in the post-COVID-19 era in the United Arab Emirates: A cross-sectional study.
Batrakoulis A, Banićević Ž, Banićević I, Arumugam A, Marović I, Krstić N, Obradović S. Batrakoulis A, et al. AIMS Public Health. 2024 Jul 5;11(3):861-885. doi: 10.3934/publichealth.2024044. eCollection 2024. AIMS Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39416891 Free PMC article. - High-intensity interval training vs. yoga in improving binge eating and physical fitness in inactive young females.
Li HM, Liu CJ, Shen YH, Zhao L, Yin CQ, Yu JG, Mao SS. Li HM, et al. Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 2;14(1):22912. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74395-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39358484 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
- World Health Organization Overweight and Obesity. WHO Fact Sheet N°311 Website. [(accessed on 9 June 2021)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.
- World Health Organization . Noncommunicable Diseases Country Profiles 2018. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2018.
Publication types
Grants and funding
This research received no external funding.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous