Genetic diversity and forensic application of Y-filer STRs in four major ethnic groups of Pakistan - PubMed (original) (raw)
Genetic diversity and forensic application of Y-filer STRs in four major ethnic groups of Pakistan
Muhammad Salman Ikram et al. BMC Genomics. 2022.
Abstract
17 Y-chromosomal STRs which are part of the Yfiler Amplification Kit were investigated in 493 unrelated Pakistani individuals belonging to the Punjabi, Sindhi, Baloch, and Pathan ethnic groups. We have assessed the forensic parameters and population genetic structure for each group. Among the 493 unrelated individuals from four ethnic groups (128 Baloch, 122 Pathan, 108 Punjabi, and 135 Sindhi), 82 haplotypes were observed with haplotype diversity (HD) of 0.9906 in Baloch, 102 haplotypes with HD value of 0.9957 in Pathans, 80 haplotypes with HD value of 0.9924 in Punjabi, and 105 haplotypes with HD value of 0.9945 in the Sindhi population. The overall gene diversity for Baloch, Pathan, Punjabi, and Sindhi populations was 0.6367, 0.6479, 0.6657, and 0.6112, respectively. The results had shown us that Pakistani populations do not have a unique set of genes but share the genetic affinity with regional (Central Asia and Northern India) populations. The observed low gene diversity (heterozygosity) values may be because of endogamy trends and this observation is equally supported by the results of forensic parameters which are mostly static across 4 combinations (minimal STRs, extended 11 Y-STRs, Powerplex 12 Y System, and Yfiler 17 Y-STRs) of STRs in these four populations.
Keywords: Baloch; Forensic and population genetic; Pathan; Punjabi; Sindhi; Yfiler amplification kit.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
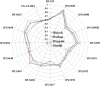
Fig. 1
Heterozygosity scattered plot for four populations
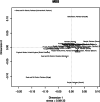
Fig. 2
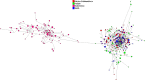
Two-dimensional plot from multi-dimensional scaling analysis of R_st_-values based on Yfiler haplotypes for the currently studied four populations with other reference populations from Pakistan
Fig. 3
Neighbor-joining tree based on the F_st_ values based on Yfiler haplotypes for the currently studied four populations with other reference populations from Pakistan
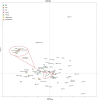
Fig. 4
Two-dimensional plot from multi-dimensional scaling analysis of R_st_-values based on Yfiler haplotypes for the currently studied four populations with other regional populations
Fig. 5
Neighbor-joining tree based on the F_st_ values based on Yfiler haplotypes for the currently studied four populations with other regional populations
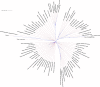
Fig. 6
The median-joining network for four populations based on 14 Y-STRs
Fig. 7
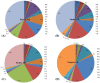
A stacked histogram with haplogroup composition for these four populations
Similar articles
- Forensic features and genetic legacy of the Baloch population of Pakistan and the Hazara population across Durand line revealed by Y-chromosomal STRs.
Adnan A, Rakha A, Nazir S, Alghafri R, Hassan Q, Wang CC, Lu J. Adnan A, et al. Int J Legal Med. 2021 Sep;135(5):1777-1784. doi: 10.1007/s00414-021-02591-2. Epub 2021 Apr 5. Int J Legal Med. 2021. PMID: 33818632 - Evaluation of 13 rapidly mutating Y-STRs in endogamous Punjabi and Sindhi ethnic groups from Pakistan.
Adnan A, Rakha A, Nazir S, Khan MF, Hadi S, Xuan J. Adnan A, et al. Int J Legal Med. 2019 May;133(3):799-802. doi: 10.1007/s00414-018-01997-9. Epub 2019 Jan 4. Int J Legal Med. 2019. PMID: 30610450 - Forensic application and genetic diversity of 21 autosomal STR loci in five major population groups of Pakistan.
Shan MA, Børsting C, Morling N. Shan MA, et al. Int J Legal Med. 2021 May;135(3):775-777. doi: 10.1007/s00414-020-02393-y. Epub 2020 Sep 26. Int J Legal Med. 2021. PMID: 32979087 - Analysis of 22 Y chromosomal STR haplotypes and Y haplogroup distribution in Pathans of Pakistan.
Lee EY, Shin KJ, Rakha A, Sim JE, Park MJ, Kim NY, Yang WI, Lee HY. Lee EY, et al. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2014 Jul;11:111-6. doi: 10.1016/j.fsigen.2014.03.004. Epub 2014 Mar 15. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2014. PMID: 24709582 - Analysis of 27 Y-chromosomal STR haplotypes in a Han population of Henan province, Central China.
Bai R, Liu Y, Zhang J, Shi M, Dong H, Ma S, Bai RF, Shi M. Bai R, et al. Int J Legal Med. 2016 Sep;130(5):1191-4. doi: 10.1007/s00414-016-1326-3. Epub 2016 Mar 1. Int J Legal Med. 2016. PMID: 26932866 Review.
Cited by
- Genetic Diversity Based on Human Y Chromosome Analysis: A Bibliometric Review Between 2014 and 2023.
Hodișan R, Zaha DC, Jurca CM, Petchesi CD, Bembea M. Hodișan R, et al. Cureus. 2024 Apr 18;16(4):e58542. doi: 10.7759/cureus.58542. eCollection 2024 Apr. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38887511 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Long RD, editor. A history of Pakistan. 1. Karachi: Oxford University Press; 2015.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources