The Effect of Resistance Training on the Rehabilitation of Elderly Patients with Sarcopenia: A Meta-Analysis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Meta-Analysis
The Effect of Resistance Training on the Rehabilitation of Elderly Patients with Sarcopenia: A Meta-Analysis
Haotian Zhao et al. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022.
Abstract
Resistance training is considered to be an efficient treatment for age-related sarcopenia and can improve muscle strength and quality in patients. However, there are currently no recommendations on resistance training parameters to improve muscle strength and quality in elderly patients with sarcopenia. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and included 13 eligible RCTs. Resistance training significantly improved grip strength, gait speed, and skeletal muscle index in patients with age-related sarcopenia, and kettlebell was found to be the most effective modality. However, it is noteworthy that the elastic band is also a recommended form of resistance training considering that the kettlebell intervention was tested in only one study, while the elastic band was confirmed by multiple studies. Elastic band training (Hedges's g = 0.629, 95%CI = 0.090-1.168, p < 0.05) (40-60 min per session, more than three times per week for at least 12 weeks) was the most efficient training method. Thus, resistance training can significantly improve muscle strength and muscle quality in elderly patients with sarcopenia. In addition, moderate-intensity resistance training using elastic bands may be the best training prescription for elderly patients with sarcopenia.
Keywords: elastic bands; optimal training parameters; resistance training; sarcopenia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
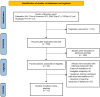
Figure 1
Literature selection process.
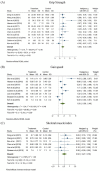
Figure 2
Effects of resistance training on grip strength, gait speed and skeletal muscle index in elderly patients with sarcopenia. (A) Effect of resistance training on grip strength. (B) Effect of resistance training on gait speed. (C) Effect of resistance training on skeletal muscle index [17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29].
Figure 3
Publication bias funnel chart of the effect of resistance training on grip strength.
Similar articles
- Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.
Pasquali S, Hadjinicolaou AV, Chiarion Sileni V, Rossi CR, Mocellin S. Pasquali S, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article. - Interventions for promoting habitual exercise in people living with and beyond cancer.
Turner RR, Steed L, Quirk H, Greasley RU, Saxton JM, Taylor SJ, Rosario DJ, Thaha MA, Bourke L. Turner RR, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Sep 19;9(9):CD010192. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010192.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30229557 Free PMC article. - The effect of Tai Chi in elderly individuals with sarcopenia and frailty: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Huang CY, Mayer PK, Wu MY, Liu DH, Wu PC, Yen HR. Huang CY, et al. Ageing Res Rev. 2022 Dec;82:101747. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2022.101747. Epub 2022 Oct 9. Ageing Res Rev. 2022. PMID: 36223875 - Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
Shepherd J, Jones J, Takeda A, Davidson P, Price A. Shepherd J, et al. Health Technol Assess. 2006 Aug;10(28):iii-iv, xi-xiv, 1-183. doi: 10.3310/hta10280. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16904047 - A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.
Forbes C, Shirran L, Bagnall AM, Duffy S, ter Riet G. Forbes C, et al. Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
Cited by
- Effectiveness of Whey Protein Supplementation during Resistance Exercise Training on Skeletal Muscle Mass and Strength in Older People with Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
Cuyul-Vásquez I, Pezo-Navarrete J, Vargas-Arriagada C, Ortega-Díaz C, Sepúlveda-Loyola W, Hirabara SM, Marzuca-Nassr GN. Cuyul-Vásquez I, et al. Nutrients. 2023 Aug 2;15(15):3424. doi: 10.3390/nu15153424. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37571361 Free PMC article. - Sarcopenia and metabolic dysfunction associated steatotic liver disease: Time to address both.
Wong R, Yuan LY. Wong R, et al. World J Hepatol. 2024 Jun 27;16(6):871-877. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i6.871. World J Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38948439 Free PMC article. - Low Adherence to Mediterranean Diet Is Associated with Probable Sarcopenia in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: Results from the Longevity Check-Up (Lookup) 7+ Project.
Cacciatore S, Calvani R, Marzetti E, Picca A, Coelho-Júnior HJ, Martone AM, Massaro C, Tosato M, Landi F. Cacciatore S, et al. Nutrients. 2023 Feb 18;15(4):1026. doi: 10.3390/nu15041026. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36839385 Free PMC article. - An Overview of Systemic Health Factors Related to Rapid Oral Health Deterioration among Older People.
van der Putten GJ, de Baat C. van der Putten GJ, et al. J Clin Med. 2023 Jun 27;12(13):4306. doi: 10.3390/jcm12134306. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37445340 Free PMC article. - State-of-the-Art and Future Challenges for Nutritional Interventions in Facioscapulohumeral Dystrophy: A Narrative Review.
Quintiero V, Crisafulli O, Diotti D, Tupler R, Negro M, Lavaselli E, D'Antona G. Quintiero V, et al. Nutrients. 2025 Mar 17;17(6):1056. doi: 10.3390/nu17061056. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40292463 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Agergaard J., Bulow J., Jensen J.K., Reitelseder S., Drummond M.J., Schjerling P., Scheike T., Serena A., Holm L. Light-load resistance exercise increases muscle protein synthesis and hypertrophy signaling in elderly men. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2017;312:E326–E338. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00164.2016. - DOI - PubMed
- Oliveira V., Borsari A.L., Cardenas J., Alves J.C., Castro N.F., Marinello P.C., Padilha C.S., Webel A.R., Erlandson K.M., Deminice R. Low Agreement Between Initial and Revised European Consensus on Definition and Diagnosis of Sarcopenia Applied to People Living With HIV. Jaids-J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2021;86:e106–e113. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000002576. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources