10. Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2024 - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
10. Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2024
American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Diabetes Care. 2024.
Abstract
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) "Standards of Care in Diabetes" includes the ADA's current clinical practice recommendations and is intended to provide the components of diabetes care, general treatment goals and guidelines, and tools to evaluate quality of care. Members of the ADA Professional Practice Committee, an interprofessional expert committee, are responsible for updating the Standards of Care annually, or more frequently as warranted. For a detailed description of ADA standards, statements, and reports, as well as the evidence-grading system for ADA's clinical practice recommendations and a full list of Professional Practice Committee members, please refer to Introduction and Methodology. Readers who wish to comment on the Standards of Care are invited to do so at professional.diabetes.org/SOC.
© 2024 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures
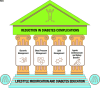
Figure 10.1
Multifactorial approach to reduction in risk of diabetes complications. *Risk reduction interventions to be applied as individually appropriate.
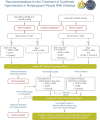
Figure 10.2
Recommendations for the treatment of confirmed hypertension in nonpregnant people with diabetes. *An ACE inhibitor (ACEi) or angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) is suggested to treat hypertension for people with coronary artery disease (CAD) or urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio 30–299 mg/g creatinine and strongly recommended for individuals with urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio ≥300 mg/g creatinine. †Dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker (CCB). ‡Thiazide-like diuretic; long-acting agents shown to reduce cardiovascular events, such as chlorthalidone and indapamide, are preferred. BP, blood pressure. Adapted from de Boer et al. (18).
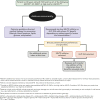
Figure 10.3
Approach to risk reduction with sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor or glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist therapy in conjunction with other traditional, guideline-based preventive medical therapies for blood pressure, lipids, and glycemia and antiplatelet therapy. Reprinted with permission from Das et al. (309).
Similar articles
- 17. Diabetes Advocacy: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2024.
American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Diabetes Care. 2024 Jan 1;47(Suppl 1):S307-S308. doi: 10.2337/dc24-S017. Diabetes Care. 2024. PMID: 38078588 Free PMC article. Review. - 7. Diabetes Technology: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2024.
American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Diabetes Care. 2024 Jan 1;47(Suppl 1):S126-S144. doi: 10.2337/dc24-S007. Diabetes Care. 2024. PMID: 38078575 Free PMC article. Review. - 16. Diabetes Care in the Hospital: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2024.
American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Diabetes Care. 2024 Jan 1;47(Suppl 1):S295-S306. doi: 10.2337/dc24-S016. Diabetes Care. 2024. PMID: 38078585 Free PMC article. Review. - 2. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2024.
American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Diabetes Care. 2024 Jan 1;47(Suppl 1):S20-S42. doi: 10.2337/dc24-S002. Diabetes Care. 2024. PMID: 38078589 Free PMC article. Review. - 6. Glycemic Goals and Hypoglycemia: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2024.
American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Diabetes Care. 2024 Jan 1;47(Suppl 1):S111-S125. doi: 10.2337/dc24-S006. Diabetes Care. 2024. PMID: 38078586 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Evaluating the Impact of Novel Incretin Therapies on Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes: An Early Systematic Review.
Salmen T, Potcovaru CG, Bica IC, Giglio RV, Patti AM, Stoica RA, Ciaccio M, El-Tanani M, Janež A, Rizzo M, Gherghiceanu F, Stoian AP. Salmen T, et al. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Oct 3;17(10):1322. doi: 10.3390/ph17101322. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39458963 Free PMC article. Review. - Oral Semaglutide in Type 2 Diabetes: Clinical-Metabolic Outcomes and Quality of Life in Real-World Practice.
Pantanetti P, Ronconi V, Sguanci M, Palomares SM, Mancin S, Tartaglia FC, Cangelosi G, Petrelli F. Pantanetti P, et al. J Clin Med. 2024 Aug 13;13(16):4752. doi: 10.3390/jcm13164752. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39200893 Free PMC article. - Unseen threat: how subclinical atherosclerosis increases mortality risk in patients with type 1 diabetes.
Sojo-Vega L, Recasens M, Martínez J, Aguilera A, Ayala M, Admetlla N, Pellicer P, Blay C, Fabregat B, Esteve-Serra M, Riera L, Barahona R, Xifra G, Esteve E, Biarnés J, Pérez D, Gifre G, Mauri S, Costa E, Wos M, Buxó M, Fernández-Balsells M. Sojo-Vega L, et al. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Oct 17;23(1):366. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02455-0. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 39420367 Free PMC article. - View on Metformin: Antidiabetic and Pleiotropic Effects, Pharmacokinetics, Side Effects, and Sex-Related Differences.
Froldi G. Froldi G. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Apr 8;17(4):478. doi: 10.3390/ph17040478. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38675438 Free PMC article. Review. - Patients with Type 2 Diabetes, Higher Blood Pressure, and Infrequent Fundus Examinations Have a Higher Risk of Sight-Threatening Retinopathy.
Tomić M, Vrabec R, Ljubić S, Prkačin I, Bulum T. Tomić M, et al. J Clin Med. 2024 Apr 24;13(9):2496. doi: 10.3390/jcm13092496. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38731024 Free PMC article.
References
- Gaede P, Lund-Andersen H, Parving HH, Pedersen O. Effect of a multifactorial intervention on mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2008;358:580–591 - PubMed
- Khunti K, Kosiborod M, Ray KK. Legacy benefits of blood glucose, blood pressure and lipid control in individuals with diabetes and cardiovascular disease: time to overcome multifactorial therapeutic inertia? Diabetes Obes Metab 2018;20:1337–1341 - PubMed
- Ali MK, Bullard KM, Saaddine JB, Cowie CC, Imperatore G, Gregg EW. Achievement of goals in U.S. diabetes care, 1999-2010. N Engl J Med 2013;368:1613–1624 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials