Whole genome amplification using a degenerate oligonucleotide primer allows hundreds of genotypes to be performed on less than one nanogram of genomic DNA - PubMed (original) (raw)
Whole genome amplification using a degenerate oligonucleotide primer allows hundreds of genotypes to be performed on less than one nanogram of genomic DNA
V G Cheung et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996.
Abstract
Genetic analysis of limiting quantities of genomic DNA play an important role in DNA forensics, paleoarcheology, genetic disease diagnosis, genetic linkage analysis, and genetic diversity studies. We have tested the ability of degenerate oligonucleotide primed polymerase chain reaction (DOP-PCR) to amplify picogram quantities of human genomic DNA for the purpose of increasing the amount of template for genotyping with microsatellite repeat markers. DNA was uniformly amplified at a large number of typable loci throughout the human genome with starting template DNAs from as little as 15 pg to as much as 400 ng. A much greater-fold enrichment was seen for the smaller genomic DOP-PCRs. All markers tested were amplified from starting genomic DNAs in the range of 0.6-40 ng with amplifications of 200- to 600-fold. The DOP-PCR-amplified genomic DNA was an excellent and reliable template for genotyping with microsatellites, which give distinct bands with no increase in stutter artifact on di-, tri-, and tetranucleotide repeats. There appears to be equal amplification of genomic DNA from 55 of 55 tested discrete microsatellites implying near complete coverage of the human genome. Thus, DOP-PCR appears to allow unbiased, hundreds-fold whole genome amplification of human genomic DNA for genotypic analysis.
Figures
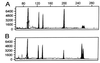
Figure 1
Genotypic analysis of genomic DNA as compared with DOP-PCR-amplified genomic DNA. The individual is homozygous at two loci, D3S2418 (97 bp, 97 bp) and D6S1006 (200 bp, 200 bp) and heterozygous at two loci, D4S2366 (127 bp, 136 bp) and D1S2130 (252 bp, 256 bp). (A) An electropherogram of a multiplex PCR at these four microsatellite loci using 40 ng of genomic DNA as template. (B) An electropherogram of a multiplex PCR at the same four loci using 40 ng of DOP-PCR-amplified genomic DNA as template. Comparison of A and B shows matching genotypes and corresponding peak areas from the two templates. The_y_-axis represents arbitrary fluorescent units, and the_x_-axis represents the size of fragments in base pairs.
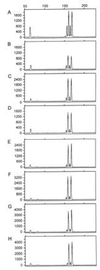
Figure 2
Comparison of yield from the DOP-PCR product generated from serially diluted genomic DNAs. All panels show electropherograms from genotyping of mixtures of DNA with fluorescently labeled D8S1132 primers as discussed. (A) An electropherogram from a mixture of total genomic DNA from two heterozygous individuals: 40 nanograms of genomic DNA from individual 1 (allele sizes 152 bp and 162 bp) were mixed with 80 ng of genomic DNA from individual 2 (allele sizes 158 bp and 168 bp). (B_–_H) Electropherograms at D8S1132 on 40 ng of DOP-PCR product derived from a DOP-PCR of a serial dilution of starting genomic DNA of individual 1 mixed with 80 ng of genomic DNA from individual 2, which allow measurement of relative yield. DOP-PCR product used in_B_–H are derived from starting genomic DNA amounts of 400 ng, 80 ng, 16 ng, 3.2 ng, 640 pg, 128 pg, and 26 pg, respectively. Comparison of the peak areas on the electropherograms reflects how the DOP-PCR products amplify relative to genomic DNA. These data were used to determine the corrected yield in Table 1. The_y_-axis represents arbitrary fluorescent units, and the_x_-axis represents fragment size in base pairs.
Similar articles
- A whole genome amplification method to generate long fragments from low quantities of genomic DNA.
Kittler R, Stoneking M, Kayser M. Kittler R, et al. Anal Biochem. 2002 Jan 15;300(2):237-44. doi: 10.1006/abio.2001.5460. Anal Biochem. 2002. PMID: 11779116 - SNP genotyping on a genome-wide amplified DOP-PCR template.
Grant SF, Steinlicht S, Nentwich U, Kern R, Burwinkel B, Tolle R. Grant SF, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Nov 15;30(22):e125. doi: 10.1093/nar/gnf125. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002. PMID: 12434007 Free PMC article. - dcDegenerate oligonucleotide primed-PCR for multilocus, genome-wide analysis from limited quantities of DNA.
Bonnette MD, Pavlova VR, Rodier DN, Thompson LP, Boone EL, Brown KL, Meyer KM, Trevino MB, Champagne JR, Cruz TD. Bonnette MD, et al. Diagn Mol Pathol. 2009 Sep;18(3):165-75. doi: 10.1097/PDM.0b013e31818d34d1. Diagn Mol Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19704262 - Whole genome amplification from single cells in preimplantation genetic diagnosis and prenatal diagnosis.
Peng W, Takabayashi H, Ikawa K. Peng W, et al. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2007 Mar;131(1):13-20. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2006.07.027. Epub 2006 Dec 8. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2007. PMID: 17157976 Review. - [Quantitative PCR in the diagnosis of Leishmania].
Mortarino M, Franceschi A, Mancianti F, Bazzocchi C, Genchi C, Bandi C. Mortarino M, et al. Parassitologia. 2004 Jun;46(1-2):163-7. Parassitologia. 2004. PMID: 15305709 Review. Italian.
Cited by
- Astroblastoma: clinicopathologic features and chromosomal abnormalities defined by comparative genomic hybridization.
Brat DJ, Hirose Y, Cohen KJ, Feuerstein BG, Burger PC. Brat DJ, et al. Brain Pathol. 2000 Jul;10(3):342-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2000.tb00266.x. Brain Pathol. 2000. PMID: 10885653 Free PMC article. - Assessment of REPLI-g Multiple Displacement Whole Genome Amplification (WGA) Techniques for Metagenomic Applications.
Ahsanuddin S, Afshinnekoo E, Gandara J, Hakyemezoğlu M, Bezdan D, Minot S, Greenfield N, Mason CE. Ahsanuddin S, et al. J Biomol Tech. 2017 Apr;28(1):46-55. doi: 10.7171/jbt.17-2801-008. Epub 2017 Mar 21. J Biomol Tech. 2017. PMID: 28344519 Free PMC article. - Evaluation of genome coverage and fidelity of multiple displacement amplification from single cells by SNP array.
Ling J, Zhuang G, Tazon-Vega B, Zhang C, Cao B, Rosenwaks Z, Xu K. Ling J, et al. Mol Hum Reprod. 2009 Nov;15(11):739-47. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gap066. Epub 2009 Aug 11. Mol Hum Reprod. 2009. PMID: 19671595 Free PMC article. - Genome amplification of single sperm using multiple displacement amplification.
Jiang Z, Zhang X, Deka R, Jin L. Jiang Z, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Jun 7;33(10):e91. doi: 10.1093/nar/gni089. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 15942023 Free PMC article.
References
- Ludecke H J, Senger G, Claussen U, Horsthemke B. Nature (London) 1989;338:348–350. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources