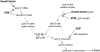Anchorage-dependent cell cycle progression - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Anchorage-dependent cell cycle progression
R K Assoian. J Cell Biol. 1997.
No abstract available
Figures
Figure 1
Coordinated control of G1 phase cell cycle progression by growth factors and the extracellular matrix (ECM). A working model showing the major sites of growth factor and ECM action (solid arrows) during cell cycle progression from G0 to S phase. Cyclin E gene expression is strongly pRb/E2F dependent, but the cyclin E protein is stable and present in G1 phase cells both before and after pRb phosphorylation. Regulatory phosphorylations and the roles of INK4s are not shown.
References
- Barrett JF, Lewis BC, Hoang AT, Alvarez RJ, Dang CV. Cyclin A links c-myc to adhesion-independent cell proliferation. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:15923–15925. - PubMed
- Benecke B-J, Ben-Ze'ev A, Penman S. The control of mRNA production, translation and turnover in suspended and reattached anchorage-dependent fibroblasts. Cell. 1978;14:931–939. - PubMed
- Carstens, C.-P., A. Krämer, and W.E. Fahl. 1996. Adhesion-dependent control of cyclin E/cdk2 activity and cell cycle progression in normal but not in Ha-ras transformed NRK cells. Exp. Cell Res. In press - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources