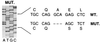Human immune disorder arising from mutation of the alpha chain of the interleukin-2 receptor - PubMed (original) (raw)
Case Reports
Human immune disorder arising from mutation of the alpha chain of the interleukin-2 receptor
N Sharfe et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997.
Abstract
Profound cellular immunodeficiency occurs as the result of mutations in proteins involved in both the differentiation and function of mature lymphoid cells. We describe here a novel human immune aberration arising from a truncation mutation of the interleukin-2 receptor alpha chain (CD25), a subunit of the tripartite high-affinity receptor for interleukin 2. This immunodeficiency is characterized by decreased numbers of peripheral T cells displaying abnormal proliferation but normal B cell development. Extensive lymphocytic infiltration of tissues, including lung, liver, gut, and bone, is observed, accompanied by tissue atrophy and inflammation. Although mature T cells are present, the absence of CD25 does affect the differentiation of thymocytes. While displaying normal development of CD2, CD3, CD4, and CD8 expression, CD25-deficient cortical thymocytes do not express CD1, and furthermore they fail to normally down-regulate levels of the anti-apoptotic protein bcl-2.
Figures
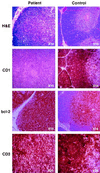
Figure 1
In immunohistological comparison of patient (Left) and normal age-matched (Right) thymus sections, hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining revealed fibrous septa separating lobules of lymphoid tissue as seen in normal thymus. However, although cortex and medulla are present in the patient thymus, there is a loss of the normally distinct demarcation between the two areas. Immunohistochemical analysis clearly showed lack of expression of CD1 (second row) but normal staining for CD3 (bottom row), while control samples stained strongly for all three markers. bcl-2 expression in the normal thymus is restricted to the medulla, with few positive cells present within the cortex, whereas the patient’s sample displays a uniformly high level of bcl-2 expression (third row). (Figure is printed at 74% of original magnification.)
Figure 2
(A) EBV-transformed patient B lymphocytes (trace i) and normal control B lymphocytes (trace ii) were stained with anti-CD25 and analyzed by flow cytometry, demonstrating the absence of CD25 expression on patient cells (1.1% positive) compared with a normal control (44% positive). Isotype-matched antibody control staining of patient cells (1.8% positive) is shown in trace iii. LFL2, count. (B) Western blot analysis demonstrates the absence of IL-2Rα protein and elevated IL-2Rβ expression in patient peripheral blood lymphocytes compared with normal.
Figure 3
A 4-bp deletion in the patient’s CD25 gene results in a frameshift in protein translation. The sequence around the deletion (base pairs 60–64) is shown (MUT.) and compared with the sequence and reading frame of normal CD25 (WT.).
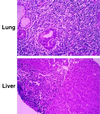
Figure 4
Light microscopy of hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections of patient lung biopsy (Upper; ×18,250) shows dilatation of airways, partially collapsed lung tissue, and dense infiltration of lymphocytes in the bronchial wall as well as in the lung parenchyma. No fungal elements were identified by specific staining and no viral particles were identified by electron microscopy (not shown). In addition, hepatitis B and C virus, EBV, and cytomegalovirus sequences were not detected by PCR. Light microscopy of liver sections (Lower; ×18,250) shows preserved lobular architecture, with marked infiltration of lymphocytes in the portal tracts. Consistent with the analysis of the lung biopsy, no fungal or viral elements were identified. Similar dense lymphocytic infiltrates were found in stomach and duodenal biopsies (not shown).
Similar articles
- Human IL-2 receptor alpha chain deficiency.
Roifman CM. Roifman CM. Pediatr Res. 2000 Jul;48(1):6-11. doi: 10.1203/00006450-200007000-00004. Pediatr Res. 2000. PMID: 10879793 - Interleukin-7 and infection itself by human immunodeficiency virus 1 favor virus persistence in mature CD4(+)CD8(-)CD3(+) thymocytes through sustained induction of Bcl-2.
Guillemard E, Nugeyre MT, Chêne L, Schmitt N, Jacquemot C, Barré-Sinoussi F, Israël N. Guillemard E, et al. Blood. 2001 Oct 1;98(7):2166-74. doi: 10.1182/blood.v98.7.2166. Blood. 2001. PMID: 11568004 - Loss of Bim results in abnormal accumulation of mature CD4-CD8-CD44-CD25- thymocytes.
Hutcheson J, Perlman H. Hutcheson J, et al. Immunobiology. 2007;212(8):629-36. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2007.05.003. Epub 2007 Jun 15. Immunobiology. 2007. PMID: 17869640 Free PMC article. - A novel activation pathway for mature thymocytes. Costimulation of CD2 (T,p50) and CD28 (T,p44) induces autocrine interleukin 2/interleukin 2 receptor-mediated cell proliferation.
Yang SY, Denning SM, Mizuno S, Dupont B, Haynes BF. Yang SY, et al. J Exp Med. 1988 Oct 1;168(4):1457-68. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.4.1457. J Exp Med. 1988. PMID: 3049912 Free PMC article. - Fidelity and infidelity in commitment to B-lymphocyte lineage development.
Rolink AG, Schaniel C, Busslinger M, Nutt SL, Melchers F. Rolink AG, et al. Immunol Rev. 2000 Jun;175:104-11. Immunol Rev. 2000. PMID: 10933595 Review.
Cited by
- Empowering Regulatory T Cells in Autoimmunity.
Kasper IR, Apostolidis SA, Sharabi A, Tsokos GC. Kasper IR, et al. Trends Mol Med. 2016 Sep;22(9):784-797. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2016.07.003. Epub 2016 Jul 25. Trends Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27461103 Free PMC article. Review. - Tregs are regulated by cytokines: implications for autoimmunity.
La Cava A. La Cava A. Autoimmun Rev. 2008 Oct;8(1):83-7. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2008.08.002. Epub 2008 Sep 2. Autoimmun Rev. 2008. PMID: 18771756 Free PMC article. Review. - Contrasting genetic association of IL2RA with SLE and ANCA-associated vasculitis.
Carr EJ, Clatworthy MR, Lowe CE, Todd JA, Wong A, Vyse TJ, Kamesh L, Watts RA, Lyons PA, Smith KG. Carr EJ, et al. BMC Med Genet. 2009 Mar 5;10:22. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-10-22. BMC Med Genet. 2009. PMID: 19265545 Free PMC article. - Multiple vaccinations: friend or foe.
Church SE, Jensen SM, Twitty CG, Bahjat K, Hu HM, Urba WJ, Fox BA. Church SE, et al. Cancer J. 2011 Sep-Oct;17(5):379-96. doi: 10.1097/PPO.0b013e3182346320. Cancer J. 2011. PMID: 21952289 Free PMC article. Review. - Recent advances in the understanding of interleukin-2 signal transduction.
Gesbert F, Delespine-Carmagnat M, Bertoglio J. Gesbert F, et al. J Clin Immunol. 1998 Sep;18(5):307-20. doi: 10.1023/a:1023223614407. J Clin Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9793823 Review.
References
- Minami Y, Kono T, Miyazaki T, Taniguchi T. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:245–267. - PubMed
- Moller, G., ed. (1994) Immunol. Rev. 138. - PubMed
- Noguchi M, Yi H, Rosenblatt H M, Filipovich A H, Adelstein S, Modi W S, McBride O W, Leonard W J. Cell. 1993;73:147–157. - PubMed
- Cao X, Shores E W, Hu-Li J, Anver M R, Kelsall B L, Russell S M, Drago J, Noguchi M, Grinberg A, Bloom E T, Paul W E, Katz S I, Love P E, Leonard W J. Immunity. 1995;2:223–238. - PubMed
- Suzuki H, Kundig T M, Furlonger C, Wakeham A, Timms E, Matsuyama T, Schmidts R, Simard J J L, Ohashi P S, Griesser H, Taniguchi T, Paige C J, Mak T W. Science. 1995;268:1472–1476. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials