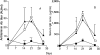Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta)-dependent inhibition of T helper cell 2 (Th2)-induced autoimmunity by self-major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II-specific, regulatory CD4(+) T cell lines - PubMed (original) (raw)
Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta)-dependent inhibition of T helper cell 2 (Th2)-induced autoimmunity by self-major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II-specific, regulatory CD4(+) T cell lines
F Bridoux et al. J Exp Med. 1997.
Abstract
Autoreactive anti-MHC class II T cells are found in Brown Norway (BN) and Lewis (LEW) rats that receive either HgCl2 or gold salts. These T cells have a T helper cell 2 (Th2) phenotype in the former strain and are responsible for Th2-mediated autoimmunity. In contrast, T cells that expand in LEW rats produce IL-2 and prevent experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, a cell-mediated autoimmune disease. The aim of this work was to investigate, using T cell lines derived from HgCl2-injected LEW rats (LEWHg), the effect of these autoreactive T cells on the development of Th2-mediated autoimmunity. The five LEWHg T cell lines obtained protect against Th2-mediated autoimmunity induced by HgCl2 in (LEW x BN)F1 hybrids. The lines produce, in addition to IL-2, IFN-gamma and TGF-beta, and the protective effect is TGF-beta dependent since protection is abrogated by anti-TGF-beta treatment. These results identify regulatory, TGF-beta-producing, autoreactive T cells that are distinct from classical Th1 or Th2 and inhibit both Th1- and Th2-mediated autoimmune diseases.
Figures
Figure 1
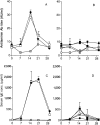
Ability of the LEWHg T cell lines to protect F1 rats against HgCl2-induced immune disorders. Antilaminin antibody titer (A and B) and serum IgE concentration (C and D) in HgCl2-injected rats (□, n = 25); normal rats ( , n = 5); rats injected with HgCl2 and, 2 wk before, with the LEWOVA (♦, n = 5), LEWHgA (▪, n = 21), LEWHgB (○, n = 3), LEWHgC (•, n = 3), LEWHgD (◫̶ , n = 3) or LEWHgE (⋄, n = 6) T cell line. AU, arbitrary units.
Figure 2
Incidence of F1 rats with glomerular IgG deposits (number in brackets) and immunofluorescence score in HgCl2-injected rats, control rats, and rats injected with HgCl2 and, 2 wk before, with one of the T cell lines. The immunofluorescence score concerns only rats that exhibited glomerular IgG deposits.
Figure 3
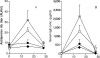
Effect of thymectomy and CD8+ cell depletion on the protective effect of the LEWHgA T cell line on HgCl2-induced disease. Antilaminin antibody titer (A) and serum IgE concentration (B) in HgCl2injected rats (□, n = 5), HgCl2-injected rats that received the LEWHgA T cell line two weeks before (▪, n = 9), thymectomized rats injected with HgCl2 and anti-CD8 mAb (◫̶ , n = 4), and thymectomized rats injected with the LEWHgA T cell line 2 wk before HgCl2 and anti-CD8 mAb administration (♦, n = 4).
Figure 4
Ability of the anti-TGF-β (1D11.16) mAb to reverse LEWHgAmediated protection from mercury disease. Antilaminin antibody titer (A) and serum IgE concentration (B) in HgCl2-injected rats (□, n = 5), and HgCl2-injected rats 2 wk after adoptive transfer of the LEWHgA T cell line treated (▴, n = 4) or not (▪, n = 4) with the 1D11.16 anti-TGF-β mAb (2 mg at day −2, 0, 3, 6, and 9 with respect to the first HgCl2 injection). The result is a pool of two independent experiments.
Similar articles
- Th2 and Th1 autoreactive anti-class II cell lines in the rat suppress or induce autoimmunity.
Druet P, Pelletier L. Druet P, et al. J Autoimmun. 1996 Apr;9(2):221-6. doi: 10.1006/jaut.1996.0027. J Autoimmun. 1996. PMID: 8738966 Review. - Mercury-induced autoreactive anti-class II T cell line protects from experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by the bias of CD8+ antiergotypic cells in Lewis rats.
Castedo M, Pelletier L, Rossert J, Pasquier R, Villarroya H, Druet P. Castedo M, et al. J Exp Med. 1993 Apr 1;177(4):881-9. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.4.881. J Exp Med. 1993. PMID: 8096239 Free PMC article. - Essential role of TGF-beta in the natural resistance to experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in rats.
Cautain B, Damoiseaux J, Bernard I, van Straaten H, van Breda Vriesman P, Boneu B, Druet P, Saoudi A. Cautain B, et al. Eur J Immunol. 2001 Apr;31(4):1132-40. Eur J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11298338 - Self major histocompatibility complex class-II-specific regulatory CD4 T cells prevent both Th1- and Th2-mediated autoimmune diseases in the rat.
Pelletier L, Savignac M, Xystrakis E, Duplan V, Druet P, Abdelhadi S. Pelletier L, et al. Microbes Infect. 2001 Sep;3(11):955-60. doi: 10.1016/s1286-4579(01)01457-5. Microbes Infect. 2001. PMID: 11564444 Review.
Cited by
- Progression of renal disease in interleukin-4 transgenic mice: involvement of transforming growth factor-beta.
Rüger BM, Hasan Q, Erb KJ, Davis PF. Rüger BM, et al. Int J Exp Pathol. 1999 Jun;80(3):113-23. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2613.1999.00105.x. Int J Exp Pathol. 1999. PMID: 10469267 Free PMC article. - Downregulation of TGF-β Receptor-2 Expression and Signaling through Inhibition of Na/K-ATPase.
La J, Reed E, Chan L, Smolyaninova LV, Akomova OA, Mutlu GM, Orlov SN, Dulin NO. La J, et al. PLoS One. 2016 Dec 22;11(12):e0168363. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0168363. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 28006004 Free PMC article. - The correlation between plasma cytokine levels in jaundice-free children with biliary atresia.
Jian ZH, Wang LC, Lin CC, Wang JD. Jian ZH, et al. World J Pediatr. 2015 Nov;11(4):352-7. doi: 10.1007/s12519-015-0023-5. Epub 2015 Apr 6. World J Pediatr. 2015. PMID: 25846069 - Analysis of mercury-induced immune activation in nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice.
Brenden N, Rabbani H, Abedi-Valugerdi M. Brenden N, et al. Clin Exp Immunol. 2001 Aug;125(2):202-10. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2001.01580.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11529910 Free PMC article. - Expression of the integrin alpha Ebeta 7 identifies unique subsets of CD25+ as well as CD25- regulatory T cells.
Lehmann J, Huehn J, de la Rosa M, Maszyna F, Kretschmer U, Krenn V, Brunner M, Scheffold A, Hamann A. Lehmann J, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Oct 1;99(20):13031-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.192162899. Epub 2002 Sep 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12242333 Free PMC article.
References
- Goldman M, Druet P, Gleichmann E. TH2 cells in systemic autoimmunity: insights from allogeneic diseases and chemically-induced autoimmunity. Immunol Today. 1991;12:223–227. - PubMed
- Gillespie KM, Qasim FJ, Tibbats LM, Thiru S, Oliveira DBG, Mathieson PW. Interleukin-4 gene expression in mercury-induced autoimmunity. Scand J Immunol. 1995;41:268–272. - PubMed
- Fillastre, J.P., P. Druet, and J.P. Mery. 1988. Proteinuric nephropathies associated with drugs and substances of abuse. In The Nephrotic Syndrome. J.S. Cameron and R.J. Glassock, editors. Marcel Dekker, New York. 697–744.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials