Anatomic localization of alternatively spliced leptin receptors (Ob-R) in mouse brain and other tissues - PubMed (original) (raw)
Anatomic localization of alternatively spliced leptin receptors (Ob-R) in mouse brain and other tissues
H Fei et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997.
Abstract
Leptin's effects are mediated by interactions with a receptor that is alternatively spliced, resulting in at least five different murine forms: Ob-Ra, Ob-Rb, Ob-Rc, Ob-Rd, and Ob-Re. A mutation in one splice form, Ob-Rb, results in obesity in mice. Northern blots, RNase protection assays, and PCR indicate that Ob-Rb is expressed at a relatively high level in hypothalamus and low level in several other tissues. Ob-Ra is expressed ubiquitously, whereas Ob-Rc, -Rd, and -Re RNAs are only detectable using PCR. In hypothalamus, Ob-Rb is present in the arcuate, ventromedial, dorsomedial, and lateral hypothalamic nuclei but is not detectable in other brain regions. These nuclei are known to regulate food intake and body weight. The level of Ob-Rb in hypothalamus is reduced in mice rendered obese by gold thioglucose (GTG), which causes hypothalamic lesions. The obesity in GTG-treated mice is likely to be caused by ablation of Ob-Rb-expressing neurons, which results in leptin resistance.
Figures
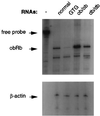
Figure 4
RNase protection assay of mRNA levels of Ob-R in obese mice. The animals used for the preparation of hypothalamic RNAs are indicated across the top. The positions of the free probe and protected bands are indicated on the left. In addition to Ob-Rb probe, β-actin was also probed to the same RNAs in a parallel experiment as a control.
Figure 1
(A) Northern blot analysis of the expression of Ob-R isoforms in mouse tissues. Multiple tissue northern blots (CLONTECH) were hybridized to cDNA probes specific for Ob-Ra, Ob-Rb, Ob-Rc, Ob-Rd, Ob-Re, as well as one that recognizes all Ob-R isoforms. Tissue origins are marked on top (Sk. muscle, skeleton muscle). All blots were also probed with human β-actin cDNA to control for RNA loading. The size of the cDNA probes used for hybridization to each Ob-R isoform is indicated on the right. Exposure times for each probe are as follows: common region, −70°C for 3 days; Ob-Ra, −70°C, overnight; Ob-Rb, −70°C for 2 weeks; actin, room temperature for 30 min. (B) RNase protection assay of mRNA levels of Ob-Rb in fat and pancreas. RNase protection assays were performed for white fat, brown fat, pancreatic islets, and whole pancreas. Each sample was assayed in duplicate, and β-actin was used as an internal control in every sample. The protected RNA bands for Ob-Rb and β-actin are indicated by arrows.
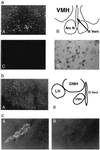
Figure 2
(a) In situ hybridization of Ob-Rb in an adult mouse brain. Dark-field photomicrograph showing Ob-Rb antisense (A) and sense strand (C) riboprobe hybridization to continuous coronal sections through hypothalamus. (B) Camera lucida drawing of the region shown in A, which is showing the location of the ventromedial hypothalamic (VMH) nuclei, the arcuate nuclei (Arc N), and the third ventricle (III Vent). (D) High-magnification bright-field photomicrograph of Ob-Rb mRNA hybridization in VMH. (b) In situ hybridization of Ob-Rb in an adult mouse brain coronal section. (A) Dark-field photomicrograph showing Ob-Rb reactivity in the VMH, dorsomedial hypothalamic (DMH) nuclei, and lateral hypothalamic (LH) nuclei. (B) Camera lucida drawing of A showing the location of the VMH, DMH, LH, and III Vent. (c) Dark-field photomicrograph of Ob-R in situ hybridization in an adult mouse brain adjacent to coronal sections through lateral ventricle. A specific antisense riboprobe corresponding to the extracellular region (common probe) (A) and the cytoplasmic region (Ob-Rb-specific probe) (B) of Ob-R cDNA sequence was used for hybridization. Reactivity observed is in the choroid plexus.
Figure 3
Genomic DNA organization of the 3′ end of the Ob-R gene. The genomic structure of the exons that encode amino acids H796–P890 of Ob-Rb is shown (see ref. 9). All other splicing variants of the receptor, Ob-Ra, Rc, Rd, and Re, end within the 13-kb region shown. Each exon is identified at the top with an arrow. Introns are represented by solid lines, with their approximate sizes labeled above (not drawn to scale).
Similar articles
- The long form of the leptin receptor (OB-Rb) is widely expressed in the human brain.
Burguera B, Couce ME, Long J, Lamsam J, Laakso K, Jensen MD, Parisi JE, Lloyd RV. Burguera B, et al. Neuroendocrinology. 2000 Mar;71(3):187-95. doi: 10.1159/000054536. Neuroendocrinology. 2000. PMID: 10729790 - Leptin receptor long-form splice-variant protein expression in neuron cell bodies of the brain and co-localization with neuropeptide Y mRNA in the arcuate nucleus.
Baskin DG, Schwartz MW, Seeley RJ, Woods SC, Porte D Jr, Breininger JF, Jonak Z, Schaefer J, Krouse M, Burghardt C, Campfield LA, Burn P, Kochan JP. Baskin DG, et al. J Histochem Cytochem. 1999 Mar;47(3):353-62. doi: 10.1177/002215549904700309. J Histochem Cytochem. 1999. PMID: 10026237 - Control of food intake via leptin receptors in the hypothalamus.
Meister B. Meister B. Vitam Horm. 2000;59:265-304. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(00)59010-4. Vitam Horm. 2000. PMID: 10714243 Review. - Localization of leptin receptor mRNA and the long form splice variant (Ob-Rb) in mouse hypothalamus and adjacent brain regions by in situ hybridization.
Mercer JG, Hoggard N, Williams LM, Lawrence CB, Hannah LT, Trayhurn P. Mercer JG, et al. FEBS Lett. 1996 Jun 3;387(2-3):113-6. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(96)00473-5. FEBS Lett. 1996. PMID: 8674530 - A role for dietary fat in leptin receptor, OB-Rb, function.
Heshka JT, Jones PJ. Heshka JT, et al. Life Sci. 2001 Jul 20;69(9):987-1003. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(01)01201-2. Life Sci. 2001. PMID: 11508653 Review.
Cited by
- Upregulation of Xbp1 in NPY/AgRP neurons reverses diet-induced obesity and ameliorates leptin and insulin resistance.
Ajwani J, Hwang E, Portillo B, Lieu L, Wallace B, Kabahizi A, He Z, Dong Y, Grose K, Williams KW. Ajwani J, et al. Neuropeptides. 2024 Dec;108:102461. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2024.102461. Epub 2024 Aug 6. Neuropeptides. 2024. PMID: 39180950 - Appetite- and Weight-Regulating Neuroendocrine Circuitry in Hypothalamic Obesity.
Gan HW, Cerbone M, Dattani MT. Gan HW, et al. Endocr Rev. 2024 May 7;45(3):309-342. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnad033. Endocr Rev. 2024. PMID: 38019584 Free PMC article. Review. - The leptin receptor has no role in delta-cell control of beta-cell function in the mouse.
Zhang J, Katada K, Mosleh E, Yuhas A, Peng G, Golson ML. Zhang J, et al. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Oct 2;14:1257671. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1257671. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37850099 Free PMC article. - Recent progress on action and regulation of anorexigenic adipokine leptin.
Nakagawa T, Hosoi T. Nakagawa T, et al. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jul 20;14:1172060. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1172060. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37547309 Free PMC article. Review. - Deletion of endothelial leptin receptors in mice promotes diet-induced obesity.
Gogiraju R, Witzler C, Shahneh F, Hubert A, Renner L, Bochenek ML, Zifkos K, Becker C, Thati M, Schäfer K. Gogiraju R, et al. Sci Rep. 2023 May 22;13(1):8276. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-35281-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37217565 Free PMC article.
References
- Halaas J L, Gajiwala K S, Maffei M, Cohen S L, Chait B T, Rabinowitz D, Lallone R L, Burley S K, Friedman J M. Science. 1995;269:543–546. - PubMed
- Pelleymounter M A, Cullen M J, Baker M B, Hecht R, Winters D, Boone T, Collins F. Science. 1995;269:540–543. - PubMed
- Campfield L A, Smith F J, Guisez Y, Devos R, Burn P. Science. 1995;269:546–549. - PubMed
- Chehab F F, Lim M E, Lu R. Nat Genet. 1996;12:318–320. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK41096/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA09673-18/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK041096/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034389/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009673/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS34389/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous